What Is CRYPTOGRAPHY?
Part 2
Hash Functions and Blockchain Security
A hash function:
Produces a fixed-length output.
Is one-way (cannot easily be reversed).
Changes completely if input data changes.
In the Crypto Market, Hashing Is Used For:
Securing transaction records.
Linking blocks in a blockchain.
Mining processes.
For example, in Bitcoin, SHA-256 secures blocks and validates mining work.
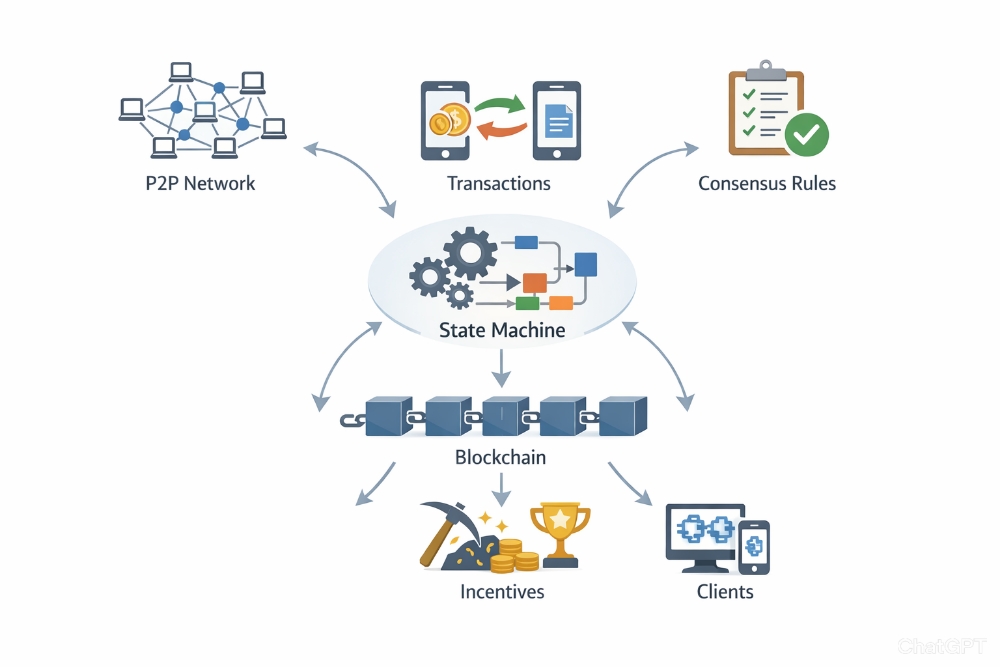
How Cryptography Secures the Blockchain
A blockchain is a distributed ledger recording all transactions. Cryptography secures it through:
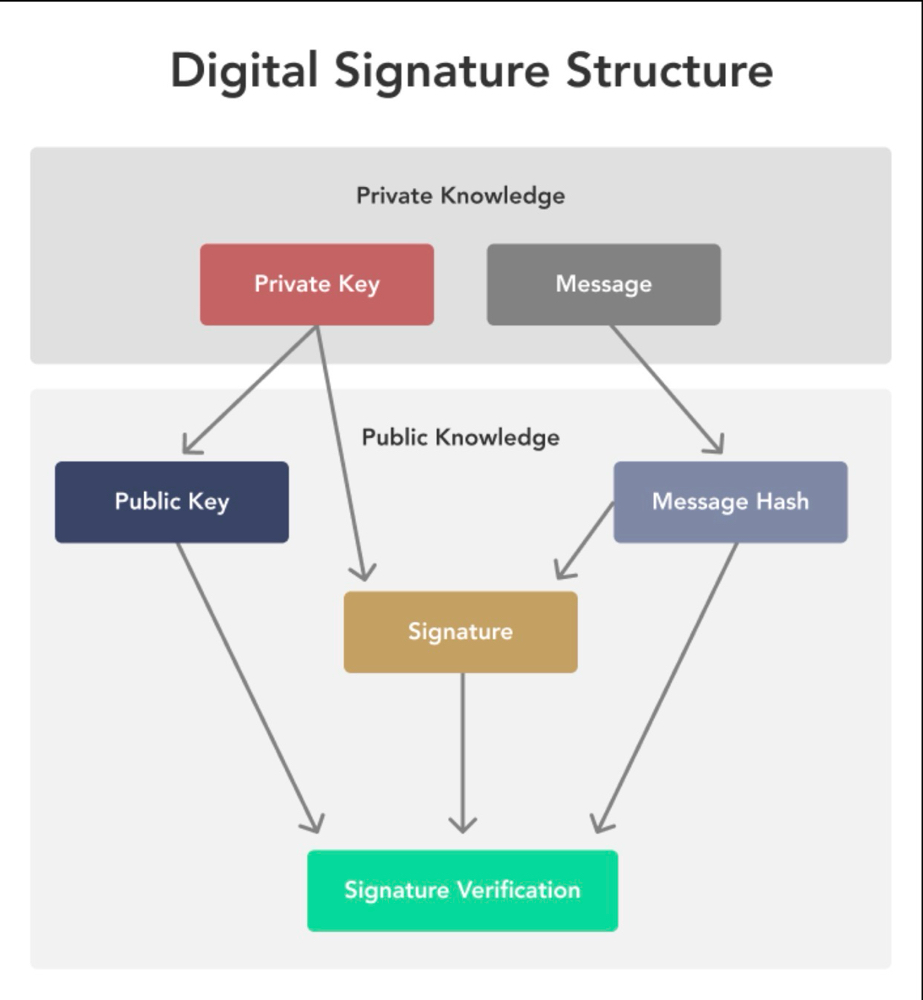
Digital Signatures
Each transaction is digitally signed using a private key. This:
Confirms ownership.
Prevents fraud.
Ensures authenticity.
Hash Linking of Blocks
Each block contains:
Transaction data
A timestamp
The hash of the previous block
Because blocks are linked by hashes, altering one block would require changing all subsequent blocks — making tampering nearly impossible.
Mining and Cryptographic Proof
In Proof-of-Work systems like Bitcoin:
Miners compete to solve mathematical puzzles.
They search for a hash that meets specific network conditions.
The first to solve it adds the block.
The miner receives a reward.
This cryptographic process secures the network and prevents double-spending.
Wallets and Private Key Security
A cryptocurrency wallet does not store coins directly. Instead, it stores private keys that grant access to funds recorded on the blockchain.
If a private key is lost or stolen:
Funds cannot be recovered.
Ownership is permanently transferred.
This shows how cryptography replaces institutional trust with personal responsibility.
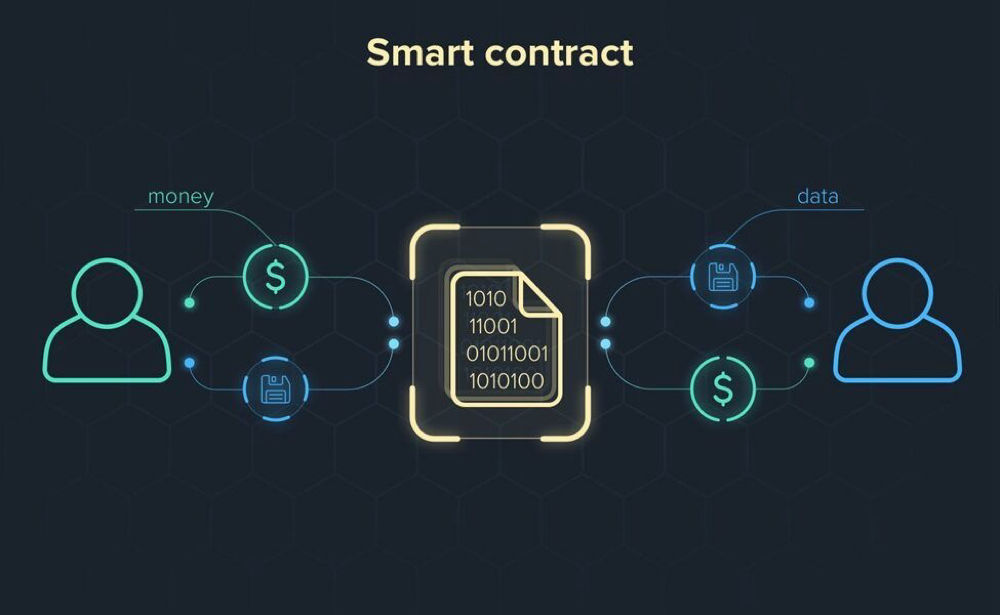
Smart Contracts and Cryptographic Trust
On platforms like Ethereum:
Smart contracts execute automatically.
Cryptographic verification ensures they cannot be altered.
Transactions remain transparent and secure.