Understanding the Mechanics of Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction:
In the realm of digital currencies, Bitcoin has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, revolutionizing the way we perceive and handle money. To comprehend the intricacies of this decentralized currency, it is crucial to delve into the underlying technologies that make it function seamlessly. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the key components that constitute the Bitcoin network, including peer-to-peer networks, blockchain, public key cryptography, Bitcoin addresses, the master public key, mining, proof of work, difficulty adjustment, and the phenomenon known as Bitcoin halving.
Peer-to-Peer Network:
At the core of Bitcoin's functionality is its peer-to-peer (P2P) network. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on centralized authorities, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of nodes. Each node is a computer that participates in maintaining the network by validating transactions and blocks. This decentralized approach ensures that no single entity has control over the entire system, fostering transparency and resilience against potential attacks.
Blockchain:
The backbone of Bitcoin is the blockchain, a distributed ledger that records all transactions made within the network. This ledger is maintained by the nodes in the P2P network, and each block contains a list of transactions. What sets the blockchain apart is its immutability – once a block is added, it cannot be altered retroactively without changing all subsequent blocks, providing a secure and tamper-resistant record of transactions.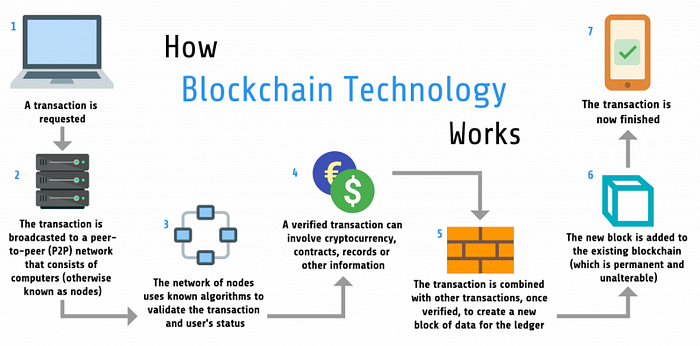
Public Key Cryptography:
To secure transactions and control access to funds, Bitcoin utilizes public key cryptography. Every user in the network possesses a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key, which is shared openly, and a private key, known only to the owner. These keys are mathematically related, allowing for secure digital signatures that authenticate transactions and ensure the integrity of the network.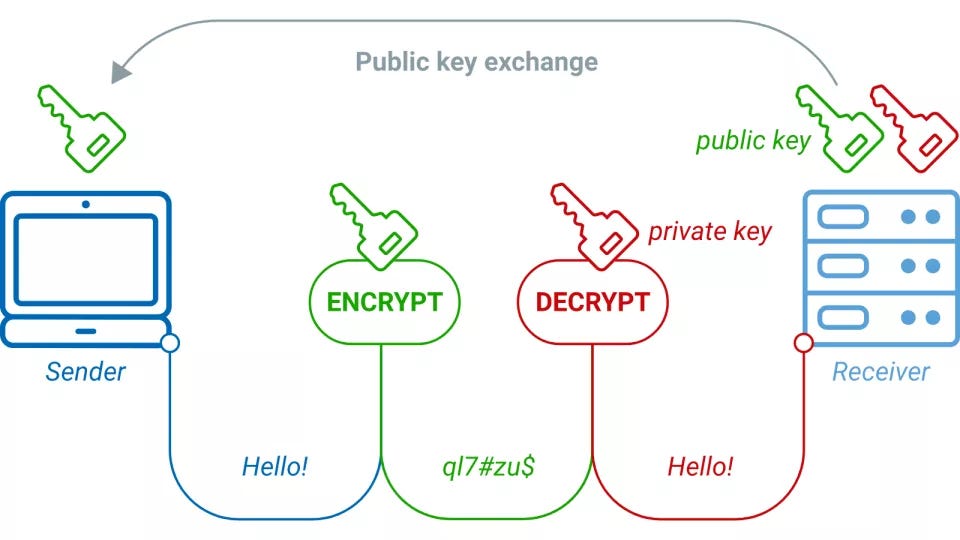
Bitcoin Addresses and Master Public Key:
Bitcoin addresses, generated from public keys, are alphanumeric strings used to receive funds. These addresses provide a layer of privacy, as they do not directly reveal the identity of the user. The master public key is a hierarchical key derived from the private key, enabling the generation of a sequence of public keys. This hierarchy is crucial for creating a deterministic wallet, making it easier to manage multiple addresses and transactions securely.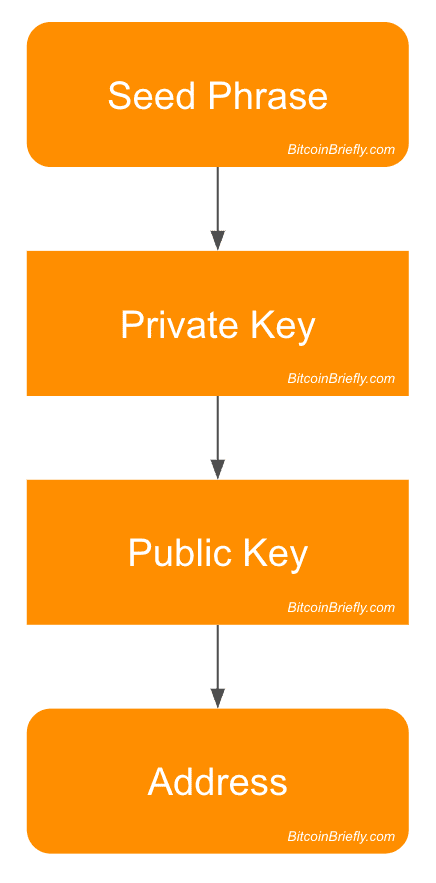
Mining and Proof of Work:
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are added to the blockchain. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles using their computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle broadcasts the solution to the network, and if validated by other nodes, the miner is rewarded with newly created bitcoins and transaction fees. This process is known as proof of work, providing security and decentralization to the network.
Difficulty Adjustment in the Bitcoin Protocol:
To maintain a consistent block creation rate (approximately every 10 minutes), the Bitcoin protocol adjusts the difficulty of the mathematical puzzles based on the total computational power of the network. This ensures that mining remains a competitive and fair process, preventing rapid increases or decreases in the block creation time.
Bitcoin Halving:
Approximately every four years, the reward for miners is halved in an event known as Bitcoin halving. This scarcity mechanism is hardcoded into the Bitcoin protocol, reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created. The halving events have profound implications for the economics of Bitcoin, often leading to increased demand and upward price movements.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bitcoin-halving_sourcefile-v2-5952611ae43d461a8d2414b31bfb8ca0.png)
Conclusion:
Bitcoin's innovative design relies on a combination of peer-to-peer networks, blockchain technology, public key cryptography, mining, proof of work, difficulty adjustment, and the periodic halving of rewards. Together, these elements create a decentralized and secure financial system that has reshaped the landscape of global currencies. As the world continues to adapt to the age of digital finance, understanding the mechanics of Bitcoin becomes increasingly important for both enthusiasts and newcomers alike.