What is CRYPTOGRAPHY?
How can digital money exist without a bank — and still remain secure?
Part 1
Digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum rely entirely on cryptography to secure transactions, verify ownership, and maintain decentralized networks.
What is Cryptography?
Its major goals in cryptocurrency include:
Confidentiality – Protecting user information
Integrity – Preventing data alteration
Authentication – Verifying transaction ownership
Non-repudiation – Ensuring senders cannot deny transactions.
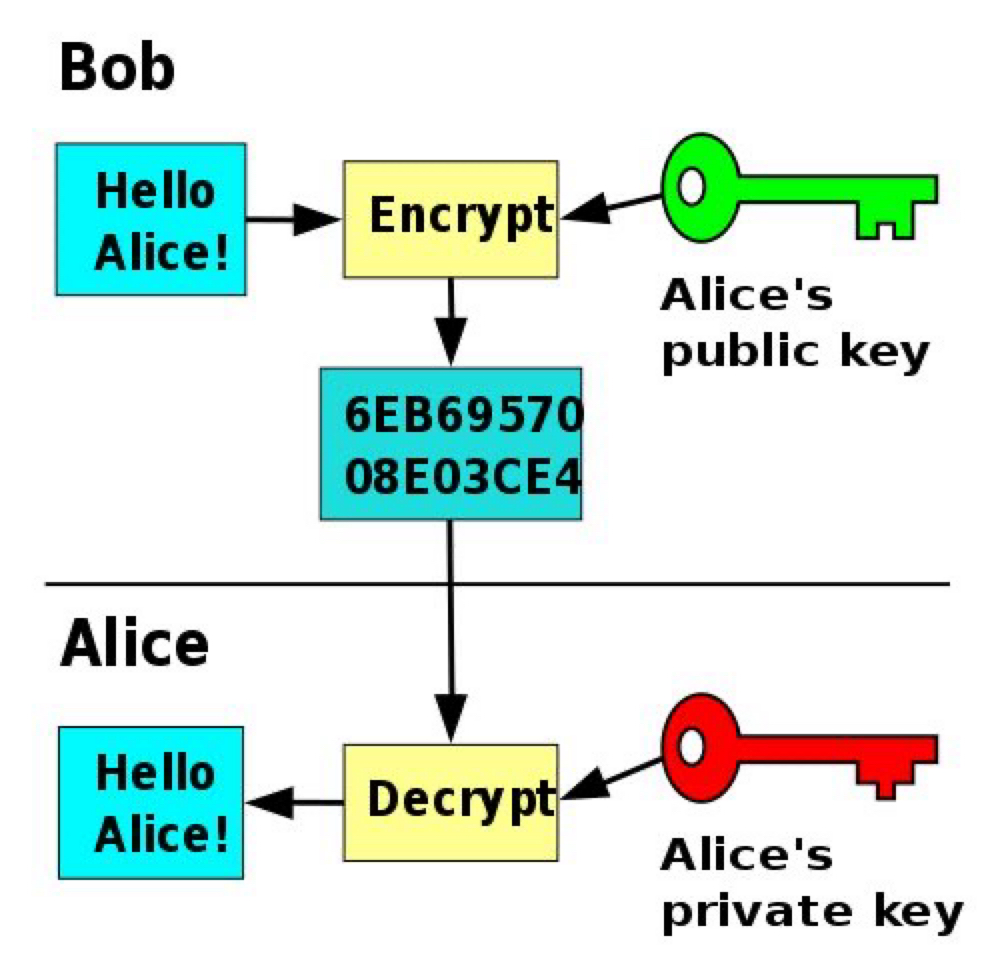
Cryptocurrencies use asymmetric cryptography, which involves two keys:
- Public Key – Shared openly (used as wallet address)
- Private Key – Kept secret (used to sign transactions)
Public Key Cryptography
How It Works:
- A user generates a private key.
- A public key is derived mathematically from it.
- When sending cryptocurrency, the user signs the transaction with the private key.
- The network verifies the signature using the public key.
- If valid, the transaction is approved.
This ensures only the rightful owner can spend the funds.