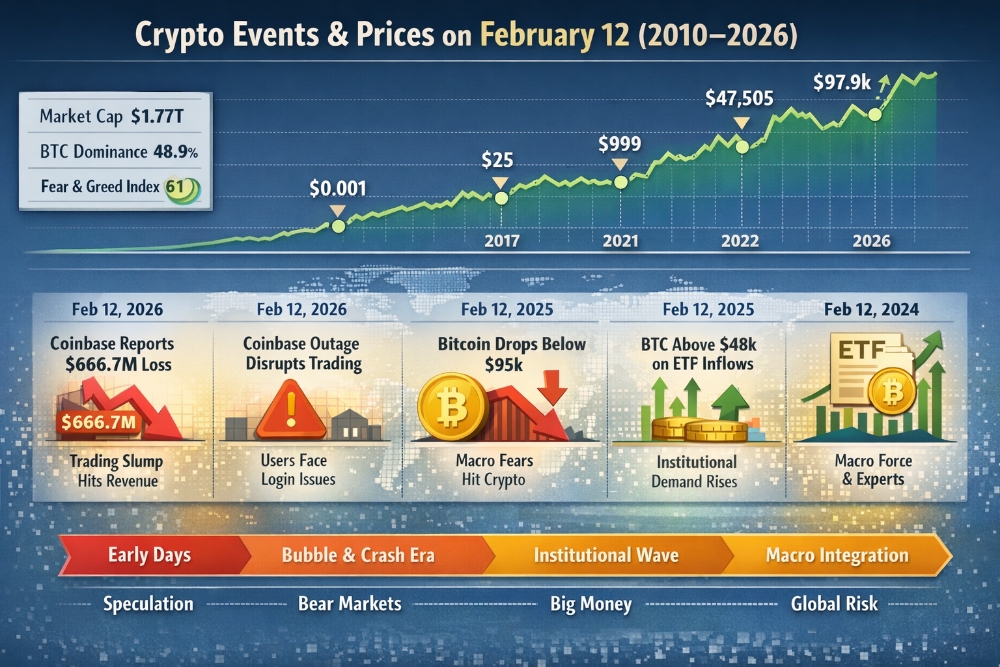
Finance, Blockchain, and Cryptocurrency: How Money Is Being Rewritten in the Digital Age
Finance has always been a reflection of trust. From shells and gold to paper money and digital banking, every financial system humanity has built rests on a shared belief: that value can be stored, transferred, and recognized by others. For centuries, that trust has been enforced by institutions—banks, governments, clearing houses, and regulators.
Today, that foundation is shifting.
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrency are not just introducing new financial tools; they are challenging the very structure of how finance works. Together, they are reshaping money, ownership, and economic participation in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago.
This article explores how finance arrived at this turning point, what blockchain and cryptocurrency actually change, and why their impact goes far beyond speculation or technology trends.
The Traditional Financial System: Strengths and Limits
Modern finance has achieved remarkable things. It has enabled global trade, economic growth, and unprecedented wealth creation. Banks provide security, credit, and infrastructure. Governments stabilize currencies. Financial markets allocate capital across industries.
But these systems also have limitations.
Traditional finance is centralized. Control is concentrated in institutions that act as gatekeepers. Access depends on geography, documentation, credit history, and political stability. Transactions can be slow, expensive, and opaque. Entire populations remain underbanked or excluded from meaningful participation.
For many people, finance is something that happens to them, not something they actively control.
These limitations created the conditions for disruption.
The Digital Transformation of Finance
The internet digitized communication long before it digitized money. Emails replaced letters. Social platforms replaced town squares. Information moved freely across borders.
Money did not.
Online payments still relied on banks. International transfers remained costly. Financial innovation happened, but always within institutional boundaries.
This mismatch between digital communication and analog finance exposed inefficiencies. If information could move instantly, why couldn’t value?
Blockchain technology emerged as an answer to that question.
Understanding Blockchain Beyond the Hype
At its core, blockchain is a shared record system. It allows multiple parties to agree on the state of transactions without relying on a central authority. Instead of trusting a single institution, participants trust a network governed by rules, cryptography, and consensus.
This matters because trust shifts from institutions to systems.
Blockchain introduces three foundational changes to finance:
1. Decentralization – No single entity controls the ledger.
2. Transparency – Transactions are verifiable and auditable.
3. Immutability – Records cannot be easily altered or erased.
These features fundamentally change how financial systems can be designed.
Cryptocurrency as a New Form of Money
Cryptocurrency is the most visible application of blockchain. It represents digital value secured by cryptography and governed by network consensus rather than centralized authority.
Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies are:
- Borderless by default
- Programmable
- Accessible to anyone with internet access
- Independent of banking infrastructure
This does not mean cryptocurrencies replace fiat money overnight. Instead, they introduce an alternative financial layer that exists alongside traditional systems.
For the first time, individuals can hold, transfer, and manage value without permission from intermediaries.
Redefining Ownership in Finance
One of the most profound shifts blockchain introduces is the concept of self-custody. In traditional finance, banks hold assets on behalf of users. Access depends on institutional approval.
In blockchain-based finance, individuals can directly control assets using cryptographic keys. Ownership becomes personal rather than delegated.
This changes the power dynamic.
Control moves closer to the individual. Responsibility increases, but so does autonomy. Finance becomes participatory rather than custodial.
Programmable Money and Smart Contracts
Blockchain enables more than simple transactions. It allows money to be programmable.
Smart contracts are automated agreements that execute when predefined conditions are met. They remove the need for intermediaries in many financial processes.
This has major implications for:
- Lending and borrowing
- Insurance
- Payments
- Asset management
- Escrow services
Financial logic becomes code. Enforcement becomes automatic. Trust becomes algorithmic.
This shift reduces friction and opens space for innovation.
Decentralized Finance and Financial Inclusion
Decentralized finance, often referred to as DeFi, builds financial services on blockchain networks. These services aim to replicate traditional financial products without centralized control.
The promise is powerful.
Anyone can:
- Access financial tools globally
- Participate without traditional credit checks
- Interact directly with protocols
- Earn yields or provide liquidity
For people in regions with limited banking infrastructure, this represents a significant opportunity.
However, it also introduces new risks and learning curves.
Risk, Volatility, and Responsibility
Cryptocurrency markets are volatile. Prices fluctuate rapidly. This volatility attracts speculation but also creates instability.
Financial freedom comes with responsibility.
Without intermediaries:
- Mistakes can be irreversible
- Security becomes personal
- Education is essential
Blockchain-based finance requires a shift in mindset. Users must understand the tools they use. Regulation, education, and infrastructure will play key roles in making these systems sustainable.
Regulation and the Future of Finance
Governments and regulators are still adapting to blockchain and cryptocurrency. These technologies challenge existing legal frameworks designed for centralized systems.
The balance is delicate.
Overregulation can stifle innovation. Underregulation can expose users to harm. The future of finance will likely involve hybrid models where traditional institutions integrate blockchain technology while adapting regulatory approaches.
This evolution will take time.
Blockchain Beyond Currency
While cryptocurrency often dominates headlines, blockchain applications extend far beyond money.
They include:
- Supply chain tracking
- Digital identity
- Asset tokenization
- Voting systems
- Data verification
In finance, tokenization allows real-world assets to be represented digitally. This can increase liquidity, accessibility, and efficiency across markets.
Ownership becomes divisible. Markets become more inclusive.
The Psychological Shift in Finance
Perhaps the most overlooked impact of blockchain and cryptocurrency is psychological.
People begin to think differently about money.
They question:
- Who controls value?
- Why intermediaries exist
- How trust is established
- What ownership truly means
Finance stops feeling distant and institutional. It becomes interactive and personal.
This cultural shift may be as important as the technology itself.
Bridging Traditional Finance and Crypto
The future is not purely decentralized nor purely centralized. It is likely a convergence.
Traditional financial institutions are exploring blockchain for efficiency. Crypto platforms are adopting compliance measures. The lines between systems are blurring.
This convergence could create a more resilient, inclusive, and efficient financial ecosystem.
Long-Term Implications for Global Finance
Blockchain and cryptocurrency challenge assumptions that have defined finance for centuries.
They suggest that:
- Trust can be decentralized
- Ownership can be direct
- Access can be global
- Financial systems can be programmable
If these ideas continue to mature, they could reshape how wealth is created, distributed, and preserved.
Conclusion: A Financial System in Transition
Finance is not being replaced; it is evolving.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency represent an experiment in redesigning financial systems for a digital, global world. They expose inefficiencies, challenge power structures, and open new possibilities.
This transformation will not be instant. It will involve mistakes, corrections, and debate. But the direction is clear.
Money is becoming digital by design. Finance is becoming more transparent. And individuals are gaining tools that were once reserved for institutions.
The question is no longer whether blockchain and cryptocurrency will influence finance.
The question is how deeply and how responsibly we choose to integrate them into the systems that shape our economic lives.
Thank you for reading.