Overview of the History of Science and Main Branches
Science or knowledge [ 1] is a set of intellectual and applied disciplines that cultivate causality , curiosity and purpose, and systematically examine facts and claims through experiment , observation and thought . [2] It should be underlined that in some uses this definition does not apply to "science". Because while science focuses on concrete, universal events, science may also be interested in paranormal events, but it does not provide concrete evidence. Philosophers of science classify science into three groups: formal sciences , social sciences and natural sciences . [3] The most distinguishing feature of science from all other branches is that it presents its defenses with concrete evidence. And this, as the most reliable branch, has divided science into many sub-branches until today, paving the way for people to have better living conditions, finding unknown facts and understanding the universe. All branches of science choose a part of the universe as their subject and try to derive laws based on experimental methods and reality. [4] Einstein defines science as the effort to establish harmony between sense data devoid of any order and regular thoughts, [5] and Bertrand Russell defines it as the effort to find the laws that connect the phenomena of the world through observation and reasoning based on observation [6] .
For centuries , humanity's curiosity about the living environment on earth has begun to take on an activity that will raise living standards. The effort to understand seemingly ordinary events has actually led to the fact that the world is a place full of mysteries and that they need to be analyzed. Although traditional science only requires understanding and solving, the types of science that have reached advanced stages include not only solving but also progress beyond solution. Some of the branches of science that are considered to be the most important in retrospect are mathematics , geometry , astronomy , and medicine . Since the early days when a wide variety of mathematical analysis systems were developed, new formulas, systems and theories have been developed, which is an example of the continuity of science.
Science attaches great importance to experimentation and the scientific method is based on experimentation. This phase not only makes the subject more believable but also puts it into a certain framework. If an assumption (hypothesis) is confirmed as a result of various tests, it can acquire the status of theory and become a cornerstone. The change of science in an endless process is an undeniable situation. Science, which has been divided into sub-branches over time, has taken on separate topics in numerical and social fields; but it continued to serve the same purpose in terms of quality. The universe is represented as multiple disk-shaped slices, expanding and evolving from left to right.
The universe is represented as multiple disk-shaped slices, expanding and evolving from left to right.
History of science
 Aristotle .
Aristotle .
It is known that science appeared before writing. [7] For this reason, archeology has an important place in examining scientific discoveries, opinions and discoveries, especially in ancient times . For example, when various archaeological discoveries are examined, it has been determined that people in prehistoric times made various observations; for example, they followed the seasons. Various findings found in Africa and dating back to 35000 BC and 20000 BC [8] bear traces of various attempts to measure time. [9]
However, it has been determined that, in addition to technological development, scientific activities intensified and gained momentum, especially around 2500 BC. [7] Many examples of this, especially architectural , can still be seen today; Great structures such as Stonehenge are monuments that could not have been built without certain scientific and technological development, especially a variety of advanced mathematical knowledge. [7] For example, most of the structures in this period were structures that could not be built without at least the Pythagorean theory ; Based on this and other similar findings, it has been determined that the Pythagorean theory was known to people thousands of years before Pythagoras. [7] As a matter of fact, mathematical activities are observed in many nations, such as the ancient Egyptians, at very early times. Just as the ancient Egyptians produced a 365-day calendar in 4200 BC, it was seen that a system was used to express millions numerically in a mace dated 3100 BC. [10] The existence of mathematical activity and development in ancient Mesopotamia is known with the help of clay tablets obtained by archaeological research. [11] Evidence of mathematical activity survives from almost all of the different kingdoms that came to power in Mesopotamia over time; It belongs to the Sumerians from the 3rd millennium BC , to the Akkadian and Babylonians from the 2nd millennium BC , and to the Assyrians from the 1st millennium BC . [11] In addition to these, there are also findings dating back to the 6th century BC to the 4th century, belonging to the Persians who later dominated the region. [11] Mathematical activities in Mesopotamia were very diverse and often went beyond practical problems; Algebra studies involving the solution of linear and quadratic equations and various number theory studies have been carried out. [11] In addition, the number system was greatly developed over time by the different kingdoms in these lands. The Sumerians established and used a number system with decimal suffixes similar to that used by the ancient Egyptians. [11] This system was developed by different governments in later periods, and a base 60 system was reached by the Babylonians. [11th] Archimedes' screw
Archimedes' screw
It is known that mathematics was practiced and mathematical calculations were made in the Indian subcontinent in the 3rd millennium BC. [12] In addition, this mathematical activity largely included topics such as measuring tables, weight and measurements in general. [13] It has been suggested that mathematical activities in this period were generally related to astronomy . [12]
As a matter of fact, astronomy studies, which also include religious aspects and are often carried out together with other branches of science such as mathematics, were of great importance and place in ancient times. [7] Mathematical manifestations of astronomy-related phenomena can be found in scientific activities in ancient Mesopotamia. [7] Just as there were astronomy activities in China to meet calendar needs, in Mesopotamia, calculations were made regarding the cycles and positions of the planets using mathematical development. [7] Apart from mathematical development, astronomy studies and understanding found their place in the Mayan civilization based in Central America; Especially calendar studies and calculation of solar and lunar eclipses played an important role. [7]
It is possible to find the origins of sciences other than these in ancient times. For example, biology played an important role in society long before the development of civilization, there were various developments especially in agriculture, and people domesticated many animals. [14] Many things have been discovered as a result of the study of plants; For example, archaeological findings discovered that the Babylonian palm tree reproduced sexually, and proved that pollen was male and that reproduction could be achieved by transferring pollen to female plants. [14] In ancient times, medical studies were also carried out along with biology, and various civilizations in China, Egypt and the Indian subcontinent used different medicinal plants for certain medical and anatomical problems, and sometimes expressed their uses in writing. [14] Besides medicine, sciences such as chemistry , geography , and geology are also greatly developed, especially in China. [7]
Science and philosophy
The philosophers' attempts to understand the world and the environment in ancient times and their sense of curiosity led to the emergence of certain criteria and their transformation into various ideologies. Until the foundations of science were laid, the phenomenon of discussion and experimentation was developed by people and it turned into a quest. In the early periods, there was no clear distinction between philosophy and science, and many great scientists were also philosophers. The fact that the experiment and the result have become clichés has enabled science to reach a desirable level. Science, which developed until the 19th century , actually fought a war within itself, and many original researchers were defeated by medieval leaders who acted with plain logic. Galileo , who had different ideas from Aristotle 's physics , began to disagree with the scientists of his time. Science has constantly witnessed such scenes throughout its history, and the laws that collapsed as a result of experiment and observation were replaced by others.
Philosophy, which investigates the truth and the purpose of existence, requires systematic thinking. Beginning with the philosophy of classical antiquity , Thales , [15] Anaximenes , [16] Pythagoras , [17 ] Democritus , [18] Gorgias , [19] Empedocles , [20] Heraclitus , [21] Parmanides , [22] Socrates , Plotinus , [ 23] Philosophers such as Plato , [24] and Aristotle [25] have helped shape philosophical questions that gradually develop and take shape. In the religion-oriented medieval philosophy , the philosophy that Christianity used as a tool for itself was used extensively on the axes of God , knowledge and belief. Reason came to the fore in the philosophy of the Age of Enlightenment . The basic view in the thought system is to move towards definitive truths and knowledge enlightened by the human mind. Renaissance philosophy , known as transitional philosophy , covers a period in which new developments in science and thought systems took place. Renaissance , which means rebirth , is the bridge of transition to a system of thought that is very different from previous ages.
The separation of science and philosophy has become more evident as we approach the modern age, however, philosophy and science are not completely separated from each other, and both philosophy of science, which is the philosophy of science in general, and branches of philosophy in which branches of science are examined philosophically one by one (for example, philosophy of physics ) continue to exist and exist in both science and philosophy fields. play important roles.
Development of branches of science
Astronomy and physics
 The equation discovered by Albert Einstein .
The equation discovered by Albert Einstein . Simple drawing of a non-spinning black hole
Simple drawing of a non-spinning black hole
Astronomy is one of the oldest branches of science and is a science that was practiced most intensively, especially in ancient times, and is seen as the mother of sciences. [7] People's interest in the sky led them to examine objects suspended above, and with the invention of the telescope , these observations became more effective. Compared to Babylonian factual astronomers , Greek astronomers formed the basic points in the development of this science by assimilating mathematical details.
Ptolemy, who lived in Egypt under the rule of the Roman Empire, has an important position especially in the history of astronomy and the history of science in general. His work on astronomy called Hè Megalè Syntaxis , or "Great Compilation", which would later be known as el-Mejisti by Islamic astronomers, was a generally accepted astronomy work throughout the Middle Ages, and Ptolemy, as its author, was given an almost mythical status. [26] Ptolemy's model of the universe was geocentric , and the transition from this system, which was accepted for many years, to a heliocentric system caused controversy. Radiography
Radiography
Nikolas Copernicus , a Polish astronomer , explained that the earth and other planets revolve around the sun ; He proposed a heliocentric, or sun-centered, system. He introduced Copernicus' system to his friends in a treatise called Commentariolus , and later, he introduced his system to Pope Paul III. He explained it in detail in his work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, which can be considered his masterpiece, which he dedicated to Paulus . This opened a new era in the science of astronomy. Italian scientist Galileo Galilei , known for his development of the telescope, his astronomical observations, and his support for Copernicus' system, is also an important person for the history of astronomy and physics, and over time , he has been referred to as the father of modern observational astronomy [27] and the father of modern physics [28]. . Mathematician and physicist Isaac Newton, who built the first reflecting telescope in 1671, contributed greatly to the development of the branches of science he was interested in and laid the foundations of differential and integral calculus. In addition, Newton's book Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy ( Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ) , published on July 5, 1687, includes important topics such as Newton's laws of motion and gravity, which form the foundations of classical mechanics . German theoretical physicist Albert Einstein proved that energy is equal to the square of the speed of light and mass with the formula E=mc² . With the theory of general relativity and the theory of relativity, he proved that mass bends space-time and that time, space and motion are interdependent, and proved the existence of the atom with Brownian motion . It includes the book Evolution of Physics , which he wrote together with Leopold Infeld, and topics such as quantum and space
Chemistry [ edit | change source ]
 Bunsen burner .
Bunsen burner .
Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the structure and behavior of matter . It may involve seeing if any chemical reactions occur. Physical chemistry , biochemistry , analytical chemistry , inorganic chemistry and organic chemistry are the basic branches. Organic chemistry is the most well-known branch of chemistry, which is an auxiliary of many branches of science such as medicine, due to its use in the fields of food , medicine , paint , cosmetics and textiles .
In ancient times, matter was thought to consist of certain basic elements, and in many cultures these included air , water , fire and earth . However, some of the ancient Greek philosophers put forward the idea of atoms and suggested that everything consists of very small building blocks. These philosophers were later called atomist philosophers. Since ancient times, people have been dealing with metallurgy and using chemical events and their resulting products in the production of various goods; for example in the production of glassware. Towards the Middle Ages, the tradition of alchemy emerged. The alchemical tradition is the predecessor of chemistry and consists of a mixture of elements such as mysticism, philosophy and various chemical researches.
Over time, interest in alchemy became more scientific and the science of chemistry emerged, separate from alchemy. Robert Boyle is a name that made important contributions to the separation of modern chemistry from alchemy and to laying its foundations . Boyle, who is known today especially for the Boyle law named after him, was a scientist who defended the atomic idea. French scientist Antoine Lavoisier took an important step in the history of both chemistry and science with the law of conservation of mass, and he is also known as the father of chemistry . [29] He is also the one who identified and named oxygen and hydrogen . Until the beginning of the 19th century , the induction aspect of chemistry was more dominant than the deduction aspect, unlike other physical sciences, causing it to be closer to the biological sciences. However, Wilhelm Ostwald , [30], Van't Hoff [31] and Arrhenius [32] played a major role in the birth of a new branch of science, namely physical chemistry, as a result of the application of mathematical and physical methods to chemistry . Physicochemistry, which deals with the physical changes of chemical substances and the explanation of physical events by using the properties of chemical substances and is divided into branches such as electrochemistry , colloid chemistry, nuclear chemistry and polymer chemistry, became a separate branch from chemistry in the scientific world when these scientists published the science journal Zeitschrift Für Physikalische Chemie in 1881. has taken its place. A modern chemistry laboratory
A modern chemistry laboratory
People's curiosity for learning and research led to the emergence of analytical chemistry over time, which paved the way for the development of coordination chemistry and industrial analytical chemistry over time. The discovery of analytical methods expanded the use of chemistry in medicine, biology and genetics . In addition to the fact that chemistry improved the quality of life of humans with the discovery of penicillin and vitamins , the use of developing technology in production processes caused environmental problems, which resulted in reckless consumption of natural resources. For this reason , sub-branches such as environmental chemistry and water chemistry have also developed.
Mathematics and Geometry
 Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein
It is known that mathematics played an important role in scientific activities in ancient times , and that various tribes such as the ancient Egyptians, Mesopotamians and Indians dealt with mathematics.
The development continued as a result of Tales , one of the most important names of Greek mathematics, learning geometry during his stay in Egypt and teaching this science to those around him. The famous theorem [33] of Pythagoras , who is known as the father of numbers, brought him to a considerable place among the greatest scientists of his time. A yupana ( "counting instrument" in Quechua ); A type of calculator used by the Incas . According to the researchers' predictions, calculations in this device were made based on Fibonacci numbers . [34]
A yupana ( "counting instrument" in Quechua ); A type of calculator used by the Incas . According to the researchers' predictions, calculations in this device were made based on Fibonacci numbers . [34]
Another mathematician, Omer Khayyam, who lived in the 12th century, criticized Euclid 's work and laid the foundations of analytic geometry and non-Euclidean geometry. He is also the first mathematician to provide a general, geometric solution to cubic equations. [35]
One of the most important mathematicians in the West in the Middle Ages was Fibonacci . Fibonacci introduced the Arabic numeral system to Europe and helped spread it, and popularized the number sequence known today as Fibonacci numbers . In fact, he was not the first to discover this number sequence, but they became famous in the West after being used as an example in his book. [36] [37]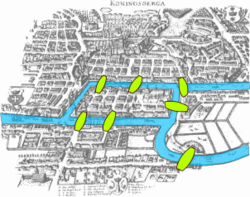 The seven bridges of Königsberg problem, posed by Euler , formed the basis of graph theory .
The seven bridges of Königsberg problem, posed by Euler , formed the basis of graph theory .
In the 17th and 18th centuries, mathematics rose in the West and many important mathematical discoveries took place. Scotsman John Napier researched natural logarithms , Kepler revealed the mathematical laws of planetary motion, and René Descartes developed the Cartesian coordinate system , which is still widely used today, and thus analytical geometry. German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz developed calculus with his many studies on calculus and laid the foundations of the notation used in calculus today. Pierre de Fermat and Blaise Pascal laid the foundations of probability theory and thus discovered the relevant rules of combinatorics . Pascal is also the developer and namesake of Pascal theory and the Pascal triangle (although it was known and used in the East before him [38] ) . In the 18th century, mathematician Leonhard Euler developed the concept of functions and numerous notations in mathematics (for example, the notation e as the base of the natural logarithm ). He produced important works and made important discoveries in a wide variety of fields such as number theory , graph theory , and geometry .
Carl Friedrich Gauss, a German mathematician who lived in the 19th century, achieved significant success in both mathematics and many other sciences; He proved the basic theory of algebra (or the fundamental theorem of algebra ), put forward and proved the Theorema Egregium , and had important works on functions of complex variables. George Boole, who also lived in the 19th century, introduced a new type of algebra, Boolean algebra, of which he is the father.
Medicine
 The heart is located in the center of the chest. Muscle mass is greater on the left side and is pointed from the apex to the left of the heart.
The heart is located in the center of the chest. Muscle mass is greater on the left side and is pointed from the apex to the left of the heart.
The first developments in the field of science and medicine took place in the Asian continent. Medicine began to develop systematically in India , Egypt , China , Iran and Greece , and developments in the field of health , which is one of the biggest problems of humanity as a branch of science , continued for centuries.
Medicine and dentistry have existed in the Indian subcontinent since the Indus Valley civilization. As a matter of fact, Ayurveda , the Indian medical tradition, continues to exist alongside contemporary medicine even today. Ayurveda, which was the main medical system in the region until the British colonized the Indian subcontinent, used mercury-sulfur-based drugs in its early periods. Apart from this, various plants such as turmeric, which is known for its various medicinal benefits today, have also been used in classical Indian medicine in treatments.
There is a traditional medical tradition in China that has survived from ancient times to the present day. Traditional Chinese medicine, which is the result of Chinese thought and empirical observations of disease and illness by Taoist physicians, has a wide range of practical methods such as herbal treatment, acupuncture and massage. Apart from these, mental therapies such as nutritional therapy and Feng Shui are also included in traditional Chinese medicine.
The fact that Hippocrates began to apply treatment methods with proven healing effects, instead of offering patients a treatment laced with magic and superstitions , led to the understanding of the importance of patients in medical science. Treatment methods, which initially differed by region, have begun to modernize in the last two centuries and have generally turned into a common effort. Medical science, which has progressed further after the epidemics in Europe, has reached very high levels today with the development of genetic studies.
Biology
Biology is the study of the human body and living organisms . Biology , which developed as a branch of science with its current sub-branches until the 19th century , is a system that studies all the characteristics of living things . It is divided into sub-branches such as botany , which studies plants , especially humans , zoology , which studies animals , and microbiology ( cell ) , which studies microorganisms .
Aristotle did many studies on nature, examined and categorized many plant and animal species. Aristotle's views, together with the additions made by some scientists after him, have been an authority for a long time, especially in the West. In the Middle Ages, Muslim scientists such as Ibn Nefis , Ibn Jahiz and Ibn Baytar contributed to the field of biology. Ibn Cahiz , who particularly contributed to early evolution thought [40] , is also the person who first put forward the idea of the food chain . [41] Al-Dinaveri, who lived in the 9th century , examined plant evolution and the development of plants and contributed to botany by describing many species in his work titled Kitâb'ün-Nebat . [42] Ibn Baytar, a student of another scientist, al-Nabati, prepared a pharmaceutical encyclopedia and described many plants, foods and medicines in his work. The Latin translation of this work was later used by European scholars in the 18th and 19th centuries. [43] Ibn Nafis correctly identified the pulmonary [44] and coronary circulation [45] [46] and defined the concept of metabolism . [47] cell types
cell types
The modern theory of evolution , considered one of the foundations of biology, is built on the views of Charles Darwin [48] . Darwin expressed his views in his works : The Origin of Species , [49] The Descent of Man, and Selection Due to Sex , [50] [51] The Expression of Emotions in Man and Animals, [52] . Gregor Mendel, who laid the foundations of genetic science by matching peas in the garden of the monastery , created the building blocks of classical genetic laws.
Pregnancy and fetal development
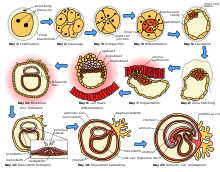 First stages of amniote embryogenesis
First stages of amniote embryogenesis
The sperm and egg cell released from one of the female's two ovaries combine in one of the two Fallopian tubes . The fertilized egg, known as the zygote , then moves towards the uterus, a journey that can take up to a week to complete. Cell division begins approximately 24 to 36 hours after the union of female and male cells. Cell division continues at a rapid pace and the cells then develop into what is known as a blastocyst . The blastocyst reaches the uterus and attaches to the uterine wall, a process known as implantation .
The modern theory of evolution , considered one of the foundations of biology, is built on the views of Charles Darwin [48] . Darwin expressed his views in his works : The Origin of Species , [49] The Descent of Man, and Selection Due to Sex , [50] [51] The Expression of Emotions in Man and Animals, [52] . Gregor Mendel, who laid the foundations of genetic science by matching peas in the garden of the monastery , created the building blocks of classical genetic laws. The development of the cell mass that will become a baby is called embryogenesis in approximately the first ten weeks of pregnancy . During this time, cells begin to differentiate into various body systems. The basic outlines of the organ, body and nervous systems have been established. At the end of the embryonic stage, the beginnings of features such as fingers, eyes, mouth, and ears become visible. Also during this time, there is development of structures important for supporting the embryo, including the placenta and umbilical cord . The placenta attaches the developing embryo to the uterine wall, allowing nutrient intake, waste excretion, and gas exchange through the mother's blood. The umbilical cord is the connecting cable from the embryo or fetus to the placenta.
After approximately ten weeks of gestational age (the same as eight weeks after conception), the embryo is known as a fetus . [53] At the beginning of the fetal stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases sharply. [54] At this stage, a fetus is approximately 30 mm (1.2 in) long, its heartbeat is visible through ultrasound, and the fetus makes involuntary movements. [55] During ongoing fetal development, early body systems and structures established during the embryonic stage continue to develop. Sexual organs begin to appear in the third month of pregnancy. Although most physical growth occurs in the final weeks of pregnancy, the fetus continues to grow in both weight and length.
The development of the cell mass that will become a baby is called embryogenesis in approximately the first ten weeks of pregnancy . During this time, cells begin to differentiate into various body systems. The basic outlines of the organ, body and nervous systems have been established. At the end of the embryonic stage, the beginnings of features such as fingers, eyes, mouth, and ears become visible. Also during this time, there is development of structures important for supporting the embryo, including the placenta and umbilical cord . The placenta attaches the developing embryo to the uterine wall, allowing nutrient intake, waste excretion, and gas exchange through the mother's blood. The umbilical cord is the connecting cable from the embryo or fetus to the placenta.
- Embryo 4 weeks after fertilization
-
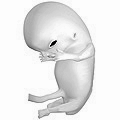
- Fetus 8 weeks after fertilization
-

- Fetus 18 weeks after fertilization
-
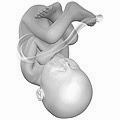
- Fetus 38 weeks after fertilization

- Relative size in month 1 (simplified example)
-

- Relative size at month 3 (simplified example)
-

- Relative size at month 5 (simplified example)
-
- Relative size at month 9 (simplified example)
Sociology
Although it is defined as a relatively new branch of science compared to other branches of science, sociology , that is, sociological studies and observations, have existed since ancient times. It is possible to come across sociological observations and evaluations in the works of names such as Herodotus and Thucydides .
Although the term sociology was used before him, [56] it was Auguste Comte , who independently introduced the term again [57] and was also known as the father of sociology over time, seeing sociology as the 'queen of positive sciences' [57] . [57] However, Comte is not generally considered the founder of sociology. [58] The first names in the field of sociology in the West were generally influenced by Darwin's theory of evolution, and they especially compared living organisms and society analogically. [58] To give examples of these names, names such as Herbert Spencer and Lewis Henry Morgan can be mentioned. [58] In the 19th and early 20th centuries, classical sociologists such as Émile Durkheim , Vilfredo Pareto , and Max Weber made important contributions to science.
Psychology
 Biopsychosocial Model
Biopsychosocial Model
Many concepts, events and phenomena discussed in the science of psychology today also received philosophical attention in civilizations such as ancient India, China and Egypt.
Philosopher René Descartes contributed to establishing the foundations of the modern philosophical form of psychology in the West. [59] Descartes, who dealt with important psychological issues in his various works, is known to have conducted various anatomy studies, although he was not a physician himself. British physician Thomas Willis played an important role in introducing psychology as a medical discipline and made great contributions to psychology, whether it was his approach to psychology in line with brain functions or his intensive anatomical studies. In addition, philosophers such as John Locke and David Hume had a great influence on the later development of experimental psychology . [59]
Branches such as hypnotism and phrenology , which emerged as the modern age approached and emerged as a treatment especially in cases of psychological disorders, have been the subject of debate; In particular, it has been discussed whether these methods are really effective and whether they have any scientific basis. The German experimental psychology movement that emerged later made important contributions to psychology. The anatomical and physiological discoveries that took place at this time, especially regarding the neurological structure, had a positive impact on psychology. German physician Wilhelm Wundt broke new ground by opening the first experimental psychology laboratory in 1879. [60] Starting in the 1890s, Austrian physician Sigmund Freud brought a new direction to psychology with the approach he called psychoanalysis . Although the scientific position of psychoanalysis is still controversial [61] [62], various propositions and concepts of psychoanalysis have gained an important place in Western culture in general. Again, in the 1890s, Ivan Pavlov successfully demonstrated classical conditioning with his experiments on dogs . As a matter of fact , various animals such as non-human primates , cats and dogs were later used in psychology experiments.