The Role of Bees in Pollination: A Foundation for Biodiversity and Food Security
The Essential Connection Between Bees and Plant Life
Bees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of natural ecosystems and sustaining global agriculture. These small yet industrious insects are among the world’s most efficient pollinators, carrying pollen from one flower to another and facilitating plant reproduction. The process of pollination, critical for plant genetic diversity, is responsible for the growth of fruits, vegetables, and seeds.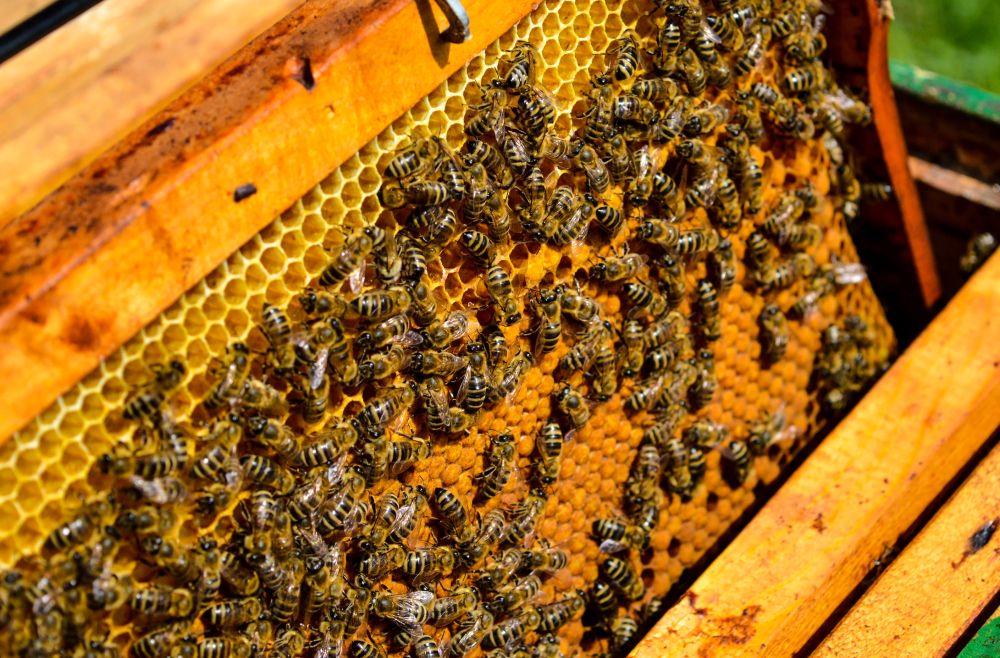 
Without bees, agricultural industries would face severe challenges, affecting food security and biodiversity. This interdependence between bees and plants underlines the profound impact these insects have on both natural and cultivated environments.
Pollination by bees is a sophisticated process influenced by factors like plant biology, bee behavior, and environmental conditions. As bees move through gardens, forests, and farmlands, they transfer pollen grains from the male part of a flower (anther) to the female part (stigma), enabling fertilization and subsequent fruit or seed formation. Beyond the visible agricultural impact, bees support entire ecosystems, making them essential for numerous plant species that serve as habitats and food sources for various organisms. Thus, protecting and understanding the role of bees in pollination is vital for ecological stability.
Bees as Keystone Pollinators and Their Impact on Agriculture
In the agricultural sphere, bees are invaluable for crop production and yield quality. Approximately 75% of the world’s leading food crops rely to some degree on animal pollination, with bees responsible for pollinating about 35% of these crops. This reliance on bee pollination spans many of the foods we consume daily, including almonds, apples, and blueberries, which depend almost exclusively on bee pollination to produce optimally. Moreover, bees' role in agriculture goes beyond quantity; they enhance crop quality by improving fruit size, flavor, and nutritional value.
The economic value of pollination provided by bees is staggering. Studies estimate that the annual contribution of bee pollination to global agriculture is worth hundreds of billions of dollars. Farmers often employ managed bee populations, such as honeybees, to maximize crop yields, while wild bees also play a critical role in ensuring crop diversity and resilience. However, the over-reliance on managed bee populations can create vulnerabilities, as these bees are highly susceptible to diseases and environmental stressors. Recognizing and preserving wild bee species is as essential as sustaining managed populations to foster a stable agricultural system.
Threats to Bee Populations and the Consequences for Pollination
Despite their importance, bee populations face numerous threats that compromise their pollination abilities and survival. Habitat loss due to urbanization, agricultural expansion, and deforestation reduces the floral diversity that bees depend on for nutrition. Climate change further exacerbates this issue by altering blooming seasons and disrupting the alignment between bee activity and flower availability, leading to mismatches that can hinder effective pollination.
Pesticide use, particularly neonicotinoids, has been implicated in declining bee health, causing neurotoxic effects that impair bees’ ability to forage and navigate. Additionally, exposure to pesticides weakens their immune systems, making them more vulnerable to diseases and parasites, such as the Varroa destructor mite. Pathogens like Nosema fungi and Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD) have decimated bee populations worldwide, with ripple effects on pollination and food supply chains.
As bee numbers dwindle, the global agriculture industry faces increased costs, as farmers must find alternative ways to pollinate crops or face yield declines. The consequences of these threats extend beyond agriculture to entire ecosystems, as plants that rely on bee pollination fail to reproduce effectively, affecting biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Practices to Protect Bee Populations
Protecting bees requires coordinated conservation efforts that address habitat preservation, sustainable agriculture, and policy reforms. Initiatives to create pollinator-friendly environments, such as planting wildflowers, conserving natural habitats, and reducing pesticide usage, are vital in supporting bee populations.
Many countries have implemented pollinator strategies aimed at restoring wild habitats and encouraging farmers to adopt bee-friendly practices, such as integrated pest management, which minimizes pesticide use while controlling agricultural pests.
Public awareness campaigns also play a significant role in conservation, educating individuals and communities on the importance of bees and encouraging actions like supporting local beekeepers, planting pollinator gardens, and reducing lawn areas to create more wildflower-rich habitats.
Furthermore, scientific advancements are aiding conservation through breeding programs designed to enhance disease resistance among bees and developing innovative monitoring systems to track bee health and behavior. The synergy of these approaches can foster environments where bees thrive, ultimately supporting food production and ecological diversity.
Conclusion
Bees are indispensable to the global ecosystem, underpinning both agricultural productivity and ecological stability. Their role as primary pollinators fosters biodiversity, strengthens food security, and supports rural economies. However, the decline in bee populations due to human-driven environmental pressures presents a critical challenge. Addressing this requires robust conservation strategies, a commitment to sustainable agricultural practices, and a collective effort to reduce environmental threats to bees. By safeguarding bees, we protect not only our food systems but also the intricate web of life that sustains our planet.
Sources
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). "Pollinators Vital to Our Food Supply Under Threat."
- National Geographic. "Bee Decline Threatens US Crop Production and Food Security."
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). "Global Initiative on Pollinators." Link.
- Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation. "Pollinator Conservation." Link.
- ScienceDaily. "Impact of Neonicotinoids on Bee Populations." Link.
- USDA. "The Economic Impact of Pollinators on Agriculture." Link.
- Bee Informed Partnership. "Bee Health and Best Practices." Link.
- European Commission. "Bees and Pollinators: Essential for Our Ecosystems and Agriculture." Link.
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. "Link Between Pesticides and Bee Decline." Link.
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF). "Why We Need to Protect Pollinators." Link.