Comparing and Contrasting Proof of Work and Proof of Stake Consensus Mechanisms
 Source: google
Source: google
Decentralized cryptocurrencies rely on consensus mechanisms to confirm and validate transactions. Two popular consensus mechanisms, Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), have emerged as leading contenders in the blockchain community. In this article, we will be comparing and contrasting these two mechanisms to shed light on their advantages and drawbacks.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
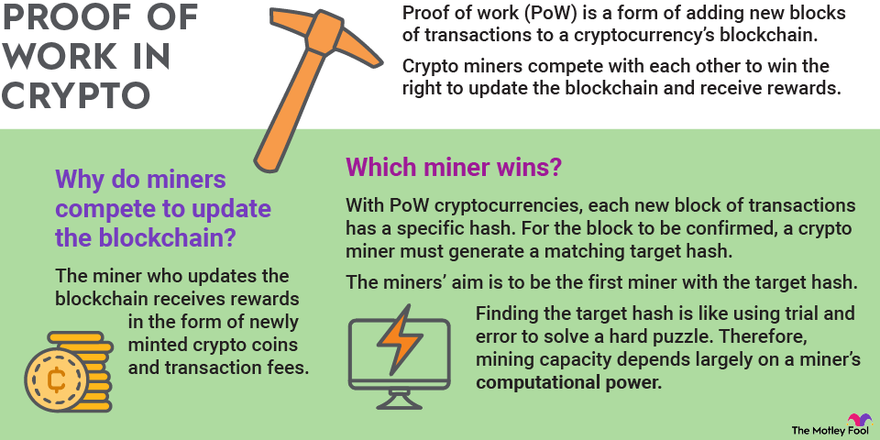
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism, utilized by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. It involves solving complex mathematical puzzles, requiring significant computational power and energy consumption. This process, known as mining, is performed by miners who compete to solve the puzzle and add a new block to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the puzzle is rewarded with newly minted coins as an incentive for their computational work.
The primary goal of PoW is to ensure that the majority of the network agrees on the state of the blockchain. By requiring miners to solve complex puzzles, PoW makes it computationally expensive to attack the network. This creates a high level of security, as an attacker would need to control a majority of the network's computational power to manipulate the blockchain.
However, PoW also has its drawbacks. The computational power required for mining consumes a significant amount of energy, leading to environmental concerns. Additionally, the high competition among miners can lead to centralization, as those with greater computational power have a higher chance of being rewarded.
How does Proof of Work (PoW) work?
To understand how PoW works, let's delve into the process of mining. Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle by repeatedly hashing a combination of the block's data and a random number. The goal is to find a hash that meets certain criteria, such as having a specific number of leading zeros. This requires a trial-and-error approach, as the only way to find a valid hash is through brute force computation.
Once a miner discovers a valid hash, they broadcast it to the network, along with the solution to the puzzle. Other nodes in the network can then verify the validity of the solution by applying the same hash function to the block's data and the provided solution. If the hash matches the criteria, the block is considered valid and added to the blockchain. The miner who found the valid hash is rewarded with newly minted coins and transaction fees.
The difficulty of the puzzle is adjusted dynamically to maintain a consistent block creation rate. This ensures that blocks are added to the blockchain at a regular interval, typically every 10 minutes for Bitcoin. The adjustment is based on the total computational power of the network, with the goal of keeping the average time to find a valid hash constant.
However, as more miners join the network, the computational power increases, making it harder to find a valid hash. This leads to the need for more powerful hardware and increased energy consumption.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work has several advantages that have made it the preferred consensus mechanism for many cryptocurrencies. Firstly, PoW provides a high level of security. The computational power required to solve the puzzles makes it difficult for attackers to manipulate the blockchain. Additionally, the decentralized nature of PoW ensures that no single entity has control over the network.
Another advantage of PoW is its fairness. Miners compete on an equal footing to solve the puzzles and add blocks to the blockchain. The randomness in finding a valid hash ensures that no miner can predict or manipulate the outcome. This fairness contributes to the overall security and trustworthiness of the network.
However, PoW also has its drawbacks. The energy consumption associated with mining is a significant concern. As the computational power required for mining increases, so does the energy consumption, leading to environmental concerns. Furthermore, the high competition among miners can result in centralization, as those with greater computational power have a higher chance of being rewarded. This can lead to a concentration of mining power in the hands of a few major players, potentially undermining the decentralized nature of the cryptocurrency.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
Proof of Stake is an alternative consensus mechanism that provides an energy-efficient approach to validating transactions and securing the blockchain. In PoS, participants are required to "stake" a certain amount of their coins to become validators. The higher the stake, the higher the chances of being selected as a validator and earning rewards.
Unlike PoW, where computational power is the deciding factor, PoS selects validators based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to stake. This means that the probability of being chosen as a validator is directly proportional to the amount of coins staked. This concept is often referred to as "economic finality," as the economic stake of participants determines the consensus.
How does Proof of Stake (PoS) work?
In a PoS system, validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on their stake. The selection process is typically random, but weighted by the amount of stake each validator holds. Validators are incentivized to act honestly and follow the protocol rules, as any attempt to manipulate the blockchain would result in the loss of their stake.
To participate in PoS, users need to lock up a certain number of coins as collateral. This collateral acts as a guarantee for their honest behavior. If a validator is found to have acted maliciously, their stake can be slashed, resulting in a financial penalty. This economic punishment serves as a deterrent against fraudulent activities.
Once selected, validators create new blocks by bundling a set of valid transactions together. They then broadcast the newly created block to the network for verification. Other validators in the network can attest to the validity of the block by cross-checking the included transactions and ensuring that they adhere to the protocol rules. If the block is deemed valid by a sufficient number of validators, it is added to the blockchain.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake offers several advantages over Proof of Work. Firstly, PoS is more energy-efficient since it doesn't require the computational power needed for mining. Validators are chosen based on their stake, eliminating the need for energy-intensive computations. This makes PoS a more environmentally friendly consensus mechanism.
Another advantage of PoS is its potential for scalability. In PoW systems, the block creation rate is fixed, leading to potential bottlenecks as the number of transactions increases. In PoS, the block creation rate can be adjusted dynamically based on network demand, allowing for greater scalability.
However, PoS also has its drawbacks. One of the main concerns is the potential for a "nothing at stake" problem. In PoS, validators are incentivized to follow the longest chain and validate transactions on that chain. However, if multiple chains are valid, validators have nothing to lose by validating on all of them. This can lead to network forks and potential double-spending attacks.
Comparison between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS)
When comparing PoW and PoS, several key differences emerge. In terms of security, PoW is considered more robust due to the computational power required to attack the network. PoS, on the other hand, relies on economic incentives and penalties to deter malicious behavior.
Energy consumption is another area of comparison. PoW is notorious for its high energy consumption, as mining requires significant computational power. PoS, on the other hand, is more energy-efficient since validators are selected based on their stake rather than computational power.
Scalability is also a differentiating factor. PoW systems often face challenges in scaling due to the fixed block creation rate. PoS, on the other hand, can adjust the block creation rate dynamically based on network demand, allowing for greater scalability.
Real-world examples of Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin is the most notable example of a cryptocurrency that utilizes PoW as its consensus mechanism. The mining process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles, and miners are rewarded with newly minted coins for their computational work.
Ethereum, on the other hand, is in the process of transitioning from PoW to PoS. The upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade aims to replace the energy-intensive mining process with a more energy-efficient PoS mechanism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Proof of Work and Proof of Stake have their advantages and drawbacks. PoW provides robust security but faces challenges with energy consumption. PoS offers energy efficiency and potential scalability but can be susceptible to certain attacks.
Understanding the differences between these consensus mechanisms is crucial for making informed decisions about which mechanism best suits specific use cases. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the trade-offs between security, energy consumption, and scalability to ensure the sustainable growth of decentralized networks.
































