Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake: Powering the Cryptocurrency Realm
Introduction
Proof of Work (PoW): The OG Security Guard
The Merits of PoW
· Decentralization: Anyone with the necessary hardware can participate in mining, fostering a distributed network with no single point of failure.
· Security: PoW boasts a robust security model. The high computational power required for mining makes it incredibly difficult and expensive for attackers to tamper with the blockchain.
· Battle-Tested: Having been around since the birth of Bitcoin, PoW has a proven track record of securing blockchains.
The Demerits of PoW
· Energy Consumption: The relentless computational power needed for mining translates to a massive energy footprint. This raises environmental concerns and criticisms of PoW's sustainability.
· Scalability Issues: As the number of transactions on a PoW network increases, so does the mining difficulty. This can lead to slow transaction processing times.
· Centralization Risks: The high cost of mining hardware can lead to mining pools, where individuals combine resources. While these pools enhance security, they also raise concerns about centralization if a single pool gains too much dominance.
Proof of Stake (PoS): A Greener Alternative
The Advantages of PoS
· Energy Efficiency: PoS eliminates the need for complex computations, resulting in a significantly lower energy footprint compared to PoW.
· Faster Transaction Speeds: Since there's no competition involved, PoS blockchains can typically process transactions much faster than PoW networks.
· Potential for Lower Barriers to Entry: Staking typically requires less investment compared to mining hardware, making participation more accessible.
The Considerations of PoS
· Security Concerns: While staking discourages malicious activity, some argue that PoS blockchains might be more vulnerable to attacks if a large stakeholder attempts to manipulate the network.
· Centralization Risks: If a small number of users hold a large portion of the staked coins, it could lead to centralization of power within the network.
· Wealth Concentration: Staking rewards favor those who already hold a significant amount of cryptocurrency, potentially exacerbating wealth inequality within the network.
The Great Debate: Choosing the Right Consensus Mechanism
The choice between PoW and PoS depends on the specific goals of a cryptocurrency. PoW offers unparalleled security and decentralization, making it ideal for established currencies like Bitcoin. However, its energy consumption is a growing concern. PoS, on the other hand, is a greener and faster alternative, but questions regarding security and potential centralization remain.
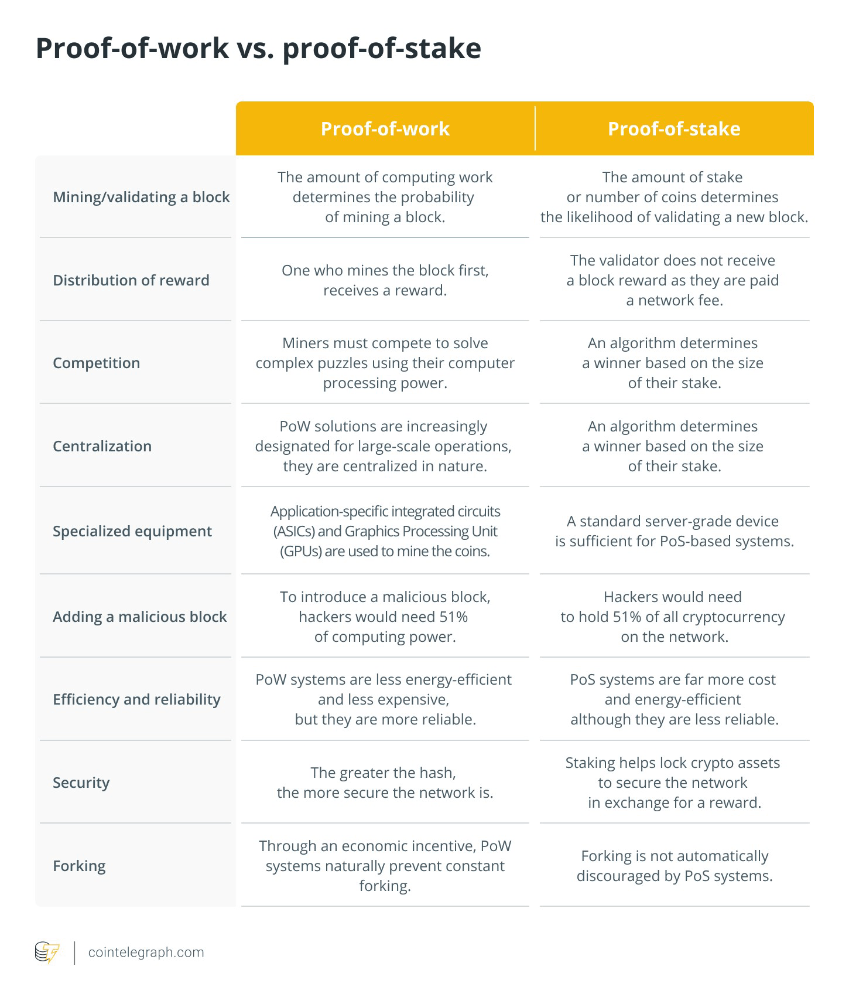
Proof-of-work vs. proof-of-stake
It is evident from the preceding explanations that both consensus mechanisms have advantages and disadvantages. They all have the same essential aim as the ones listed above, but they use different methods to achieve it.
The critical distinction between various consensus mechanisms is how they delegate and reward transaction verification. Other differences are explained in the table below.
The Future of Crypto Consensus
The cryptocurrency landscape is constantly evolving. Hybrid models that combine elements of PoW and PoS are emerging, aiming to leverage the strengths of both. Additionally, innovative consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Authority (PoA) are being explored for specific use cases. As the crypto world matures, the search for the most secure, efficient, and sustainable consensus mechanism will continue.
Conclusion
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake represent two distinct approaches to achieving consensus in blockchain networks, each with its own set of advantages and trade-offs. While PoW has established itself as the gold standard for security and decentralization, PoS offers promising solutions to scalability and energy concerns. Understanding the differences between these consensus mechanisms is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology.
https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/Proof-of-work-vs-proof-of-stake-Whats-the-difference
https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/investing/proof-of-work-vs-proof-of-stake
https://cointelegraph.com/learn/proof-of-stake-vs-proof-of-work:-differences-explained
https://www.coindesk.com/learn/proof-of-work-vs-proof-of-stake-what-is-the-difference/
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/proof-of-work-vs-proof-of-stake/