DIN Type Fuse & BS Type Fuse for Industrial Use: A Complete Expert Guide
In modern industrial environments, electrical safety is not optional—it is foundational. From manufacturing plants and power distribution units to automation systems and heavy machinery, protecting electrical circuits against overloads and short circuits is critical for operational continuity and human safety. Among the most widely adopted protective devices are DIN Type Fuse and BS Type Fuse, both known for their reliability, standardization, and suitability for demanding industrial conditions.
This in-depth guide explores the role of DIN Type Fuse and BS Type Fuse for industrial use, explaining how they work, where they are applied, their key differences, and how engineers and facility managers can select the right fuse for global industrial applications. Written from a technical and practical perspective, this article is designed to provide real value to professionals, consultants, and decision-makers.
Understanding Industrial Fuse Protection
Industrial electrical systems operate under high loads, fluctuating currents, and often harsh environmental conditions. Without proper circuit protection, faults can lead to:
- Equipment damage
- Production downtime
- Fire hazards
- Safety risks to personnel
Fuses act as sacrificial safety devices. When excessive current flows through a circuit, the fuse element melts and breaks the circuit, preventing damage to downstream components. Unlike resettable devices, fuses provide a highly reliable and fast-acting form of protection.
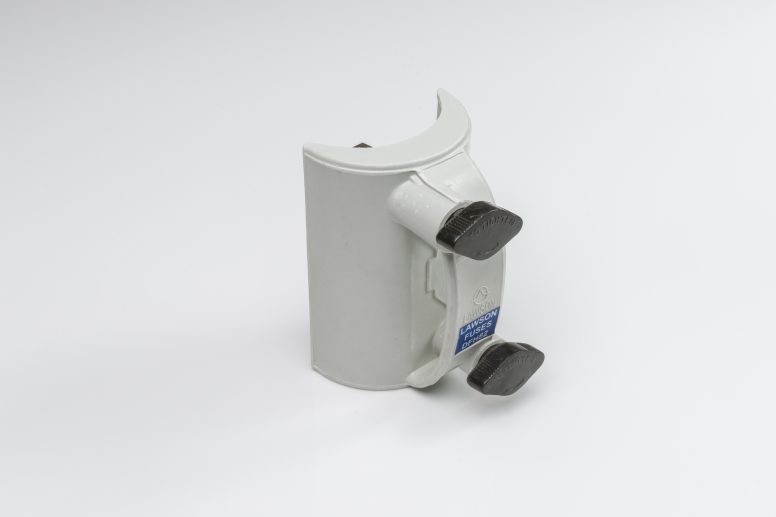
What Is a DIN Type Fuse?
A DIN Type Fuse is a fuse designed in accordance with DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) standards, commonly used across Europe and globally in industrial electrical installations. These fuses are known for their modular design, compatibility with DIN rail-mounted systems, and precise performance characteristics.
Key Characteristics of DIN Type Fuse
- Designed to meet DIN and IEC standards
- Compact and modular construction
- Suitable for DIN rail fuse holders
- Available in multiple current and voltage ratings
- High breaking capacity for industrial fault levels
DIN Type Fuse solutions are widely used in control panels, switchgear, motor protection circuits, and industrial distribution boards.
Common Types of DIN Type Fuse
DIN fuses are available in several formats, each designed for specific applications:
1. NH DIN Type Fuse
Used in high-power industrial applications, NH fuses offer excellent short-circuit protection and are commonly found in power distribution systems.
2. D-Type (Diazed) DIN Fuse
Often used in legacy or semi-industrial systems, these fuses provide reliable protection with screw-type holders.
3. D0 (Neozed) DIN Fuse
A more compact and modern alternative to Diazed fuses, D0 DIN fuses are widely used in industrial control panels.
What Is a BS Type Fuse?
A BS Type Fuse is manufactured according to British Standards and is commonly used in systems that follow UK-origin electrical design practices. These fuses are prevalent in industrial, commercial, and infrastructure projects across many regions worldwide.
Key Characteristics of BS Type Fuse
- Designed to meet British Standard specifications
- Known for consistent performance and safety compliance
- Suitable for a wide range of industrial voltages
- Commonly used in switchgear and power distribution
BS Type Fuse designs focus on robustness and reliability, making them suitable for both legacy systems and modern industrial installations.
Popular Variants of BS Type Fuse
1. BS88 Fuse
One of the most widely used industrial fuses, BS88 fuses offer high rupturing capacity and are suitable for motor protection, transformers, and distribution circuits.
2. BS1361 Fuse
Primarily used in industrial cut-outs and service equipment, this fuse type provides dependable overcurrent protection.
DIN Type Fuse vs BS Type Fuse: Technical Comparison
Understanding the differences between DIN Type Fuse and BS Type Fuse is essential when designing or maintaining industrial electrical systems.
Standards and Compatibility
- DIN Type Fuse follows European DIN and IEC standards.
- BS Type Fuse follows British Standards, often aligned with IEC but with distinct form factors.
Design and Mounting
- DIN Type Fuse systems are highly modular and optimized for DIN rail mounting.
- BS Type Fuse systems are often integrated into switchgear assemblies designed around BS standards.
Application Scope
- DIN Type Fuse is dominant in European-style industrial panels and automation systems.
- BS Type Fuse is widely used in systems designed under British electrical practices.
Global Usage
Both fuse types are used globally, but selection often depends on project specifications, regulatory requirements, and system design standards.
Why DIN Type Fuse Is Preferred in Industrial Use
The DIN Type Fuse has become a preferred choice in industrial environments due to its adaptability, standardization, and performance reliability.
Advantages of DIN Type Fuse
1. High Precision Protection
DIN fuses are engineered with precise time-current characteristics, ensuring accurate response to overloads and short circuits.
2. Modular System Integration
Their compatibility with DIN rail systems allows easy installation, replacement, and expansion in industrial panels.
3. Space Efficiency
Compact design helps optimize panel space, which is critical in modern industrial control cabinets.
4. High Breaking Capacity
DIN Type Fuse units can safely interrupt very high fault currents, making them suitable for heavy industrial loads.
Role of BS Type Fuse in Industrial Systems
While DIN Type Fuse dominates many modern installations, BS Type Fuse remains highly relevant, particularly in regions and systems aligned with British standards.
Advantages of BS Type Fuse
- Proven reliability in high-load applications
- Strong performance in motor and transformer protection
- Widely accepted in industrial infrastructure projects
- Long history of safe operation in demanding environments
BS Type Fuse solutions are often selected during system upgrades or when maintaining compatibility with existing installations.
Industrial Applications of DIN Type Fuse & BS Type Fuse
Both fuse types are used across a wide range of industrial sectors:
Manufacturing Plants
Protecting CNC machines, conveyors, welding equipment, and automated production lines.
Power Distribution Systems
Used in low-voltage and medium-voltage distribution boards for fault protection.
Motor Control Centers
Essential for protecting motors against overloads and short circuits.
Renewable Energy Systems
Applied in solar and wind power installations to safeguard inverters and distribution circuits.
Infrastructure and Utilities
Used in water treatment plants, transport systems, and industrial utilities.
Selecting the Right Fuse for Industrial Use
Choosing between a DIN Type Fuse and a BS Type Fuse depends on several technical and regulatory factors.
Key Selection Criteria
1. System Standards
Always match the fuse type to the electrical standards followed by the system design.
2. Current and Voltage Rating
Ensure the fuse rating matches the circuit requirements to avoid nuisance tripping or inadequate protection.
3. Breaking Capacity
Industrial systems require fuses capable of handling high fault currents safely.
4. Environmental Conditions
Consider temperature, humidity, and vibration levels common in industrial settings.
5. Maintenance and Replacement
Select fuse systems that allow easy inspection and replacement to reduce downtime.
Safety and Compliance Considerations
Proper fuse selection and installation are critical for compliance with global safety regulations. Incorrect fuse usage can lead to:
- Reduced protection effectiveness
- Increased fire risk
- Equipment damage
- Non-compliance with electrical safety audits
Both DIN Type Fuse and BS Type Fuse are designed to meet stringent safety standards when correctly applied within their specified parameters.
Future Trends in Industrial Fuse Technology
As industrial systems evolve, fuse technology continues to adapt:
- Integration with smart monitoring systems
- Improved materials for higher efficiency
- Enhanced coordination with circuit breakers
- Compact designs for high-density panels
Despite advances in electronic protection devices, fuses remain irreplaceable due to their simplicity, speed, and reliability.
Conclusion: The Importance of DIN Type Fuse in Modern Industry
In today’s complex industrial environments, reliable circuit protection is essential. The DIN Type Fuse stands out as a globally accepted, highly adaptable solution that meets the demands of modern industrial systems. When combined with the proven reliability of BS Type Fuse, engineers and system designers have robust options for ensuring electrical safety across diverse applications.
By understanding the characteristics, applications, and differences between DIN Type Fuse and BS Type Fuse for industrial use, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance system reliability, safety, and long-term performance. Selecting the right fuse is not just a technical choice—it is a critical investment in operational continuity and industrial safety.
For More Details: Lawson Fuse