The Renaissance of Urban Agriculture: Cultivating Sustainable Cities
Introduction: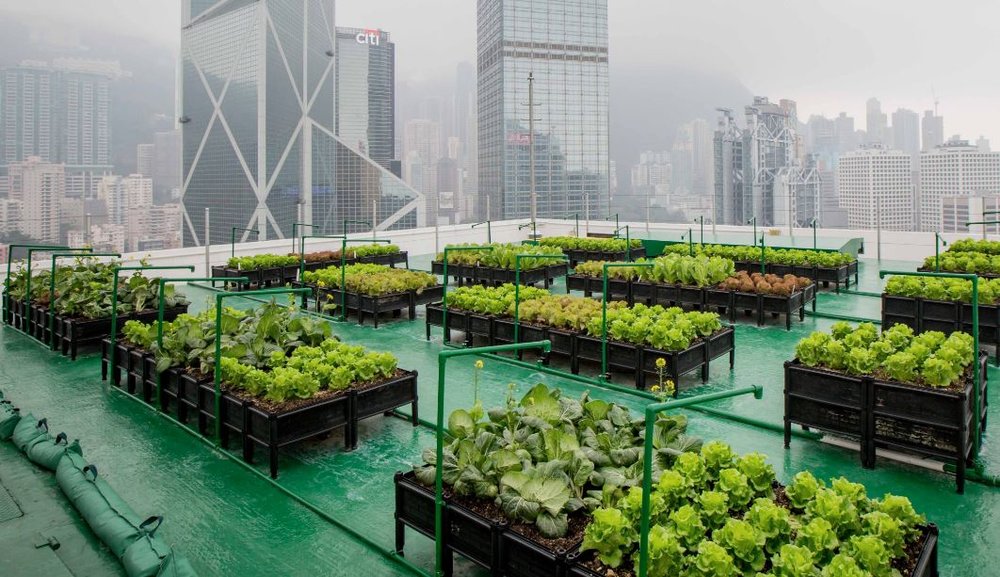
In an era where urbanization is rapidly transforming the global landscape, cities face an array of challenges ranging from food insecurity to environmental degradation. However, amidst these challenges, a promising movement has emerged—urban agriculture. This article delves into the resurgence of urban agriculture, exploring its multifaceted benefits, innovative practices, and its transformative potential in shaping sustainable cities.
The Rise of Urban Agriculture:
Urban agriculture encompasses a spectrum of practices, from rooftop gardens to aquaponic systems, collectively reshaping urban landscapes and fostering local food sovereignty. What once may have been considered a fringe movement has now evolved into a mainstream phenomenon, driven by the desire for sustainable living, community resilience, and equitable access to fresh produce. Across the globe, urban farmers are reclaiming vacant lots, repurposing rooftops, and embracing innovative growing techniques to cultivate food in the heart of the city.
Benefits of Urban Agriculture: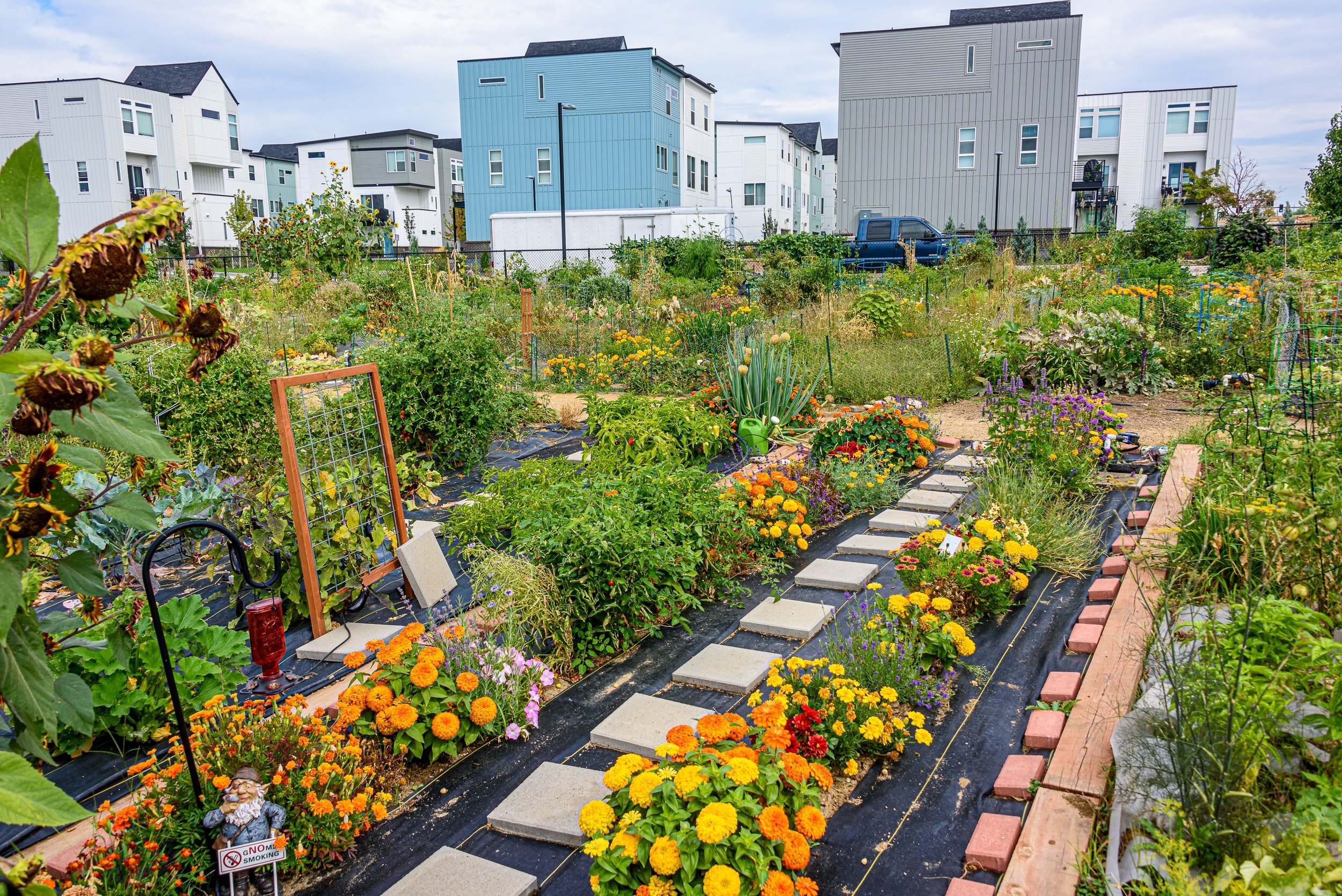
The benefits of urban agriculture extend far beyond the mere production of food. By integrating green spaces into urban environments, urban agriculture mitigates the adverse effects of urbanization, such as air and noise pollution, while enhancing biodiversity and ecological resilience. Moreover, by shortening the distance between farm and fork, urban agriculture reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. Additionally, urban farms and community gardens serve as vibrant hubs of social interaction, fostering a sense of belonging and empowerment among residents.
Addressing Food Insecurity: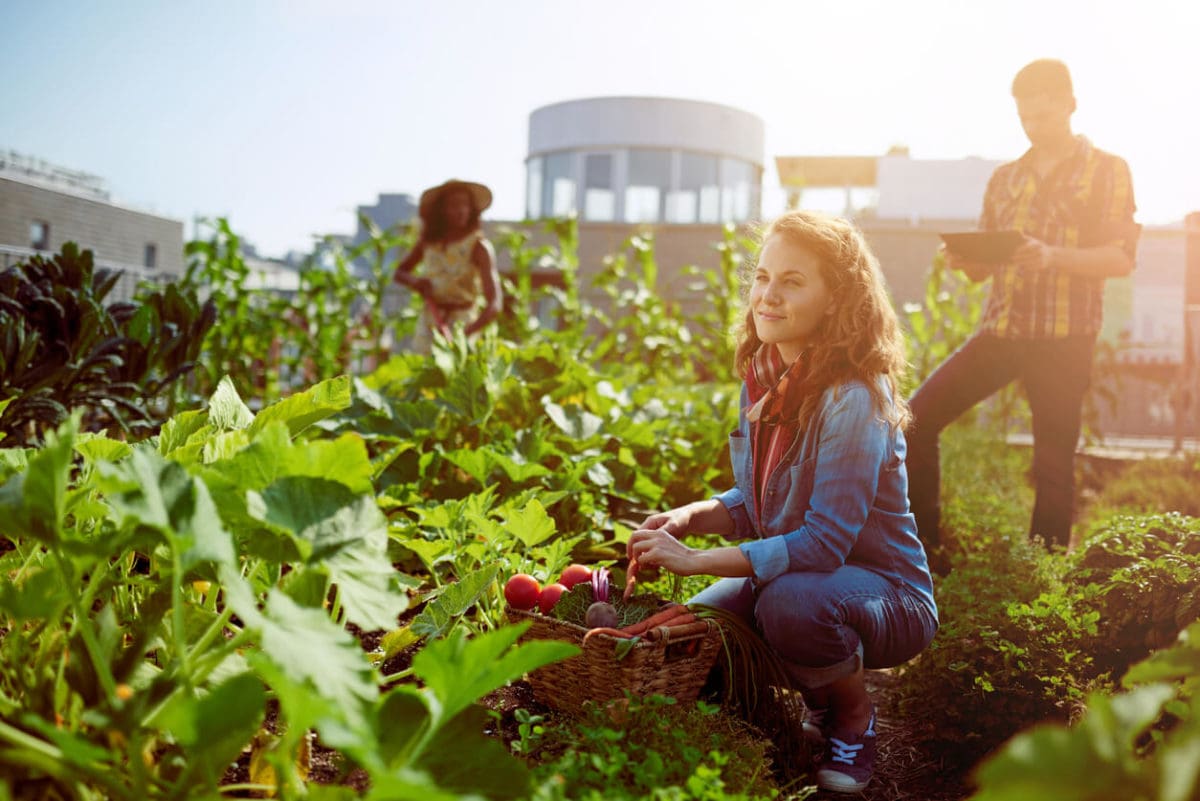
One of the most pressing challenges facing cities today is food insecurity, particularly in underserved communities. Urban agriculture plays a crucial role in addressing this challenge by providing fresh, locally grown produce to neighborhoods lacking access to healthy food options. Community gardens, urban farms, and food forests serve as sources of nutritious food, empowering residents to take control of their diets and improve their overall health. Furthermore, urban agriculture initiatives often incorporate educational components, teaching valuable skills such as gardening and nutrition, and fostering a deeper connection to food and the environment.
Promoting Resilience and Self-Sufficiency:
In an increasingly interconnected world, the importance of local resilience and self-sufficiency cannot be overstated. Urban agriculture offers cities a means to enhance their resilience by diversifying food sources, reducing dependency on global supply chains, and building community networks. In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or economic disruptions, locally grown food can serve as a lifeline, ensuring food security for vulnerable populations. Moreover, urban agriculture contributes to economic resilience by creating opportunities for entrepreneurship and job creation, particularly in marginalized communities.
Challenges and Opportunities: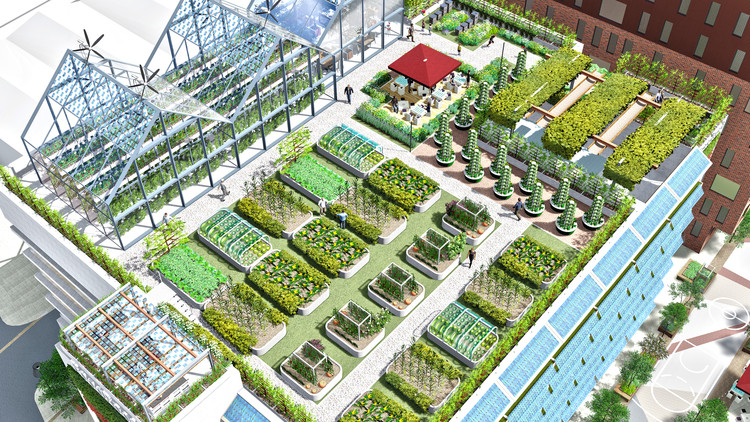
Despite its numerous benefits, urban agriculture faces several challenges, including limited access to land, regulatory barriers, and financial constraints. Zoning regulations often restrict the use of land for agricultural purposes, making it difficult for urban farmers to secure suitable growing spaces. Moreover, the high cost of land in urban areas can pose a significant barrier to entry for aspiring farmers. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Cities can support urban agriculture through policy initiatives such as zoning reforms, land-use incentives, and funding opportunities for community-based projects. By fostering partnerships between government agencies, community organizations, and private stakeholders, cities can create an enabling environment for urban agriculture to thrive.
Empowering Communities:
Urban agriculture is not merely about growing food; it's about empowering communities and fostering social cohesion. Community gardens and urban farms serve as gathering spaces where people from diverse backgrounds come together to share knowledge, resources, and experiences. These spaces promote social interaction, bridge cultural divides, and strengthen community bonds. Moreover, urban agriculture projects often engage residents in decision-making processes, giving them a sense of ownership and agency over their neighborhoods. By fostering a sense of collective responsibility and solidarity, urban agriculture contributes to the social fabric of cities and promotes a culture of collaboration and mutual support.
Educational Opportunities: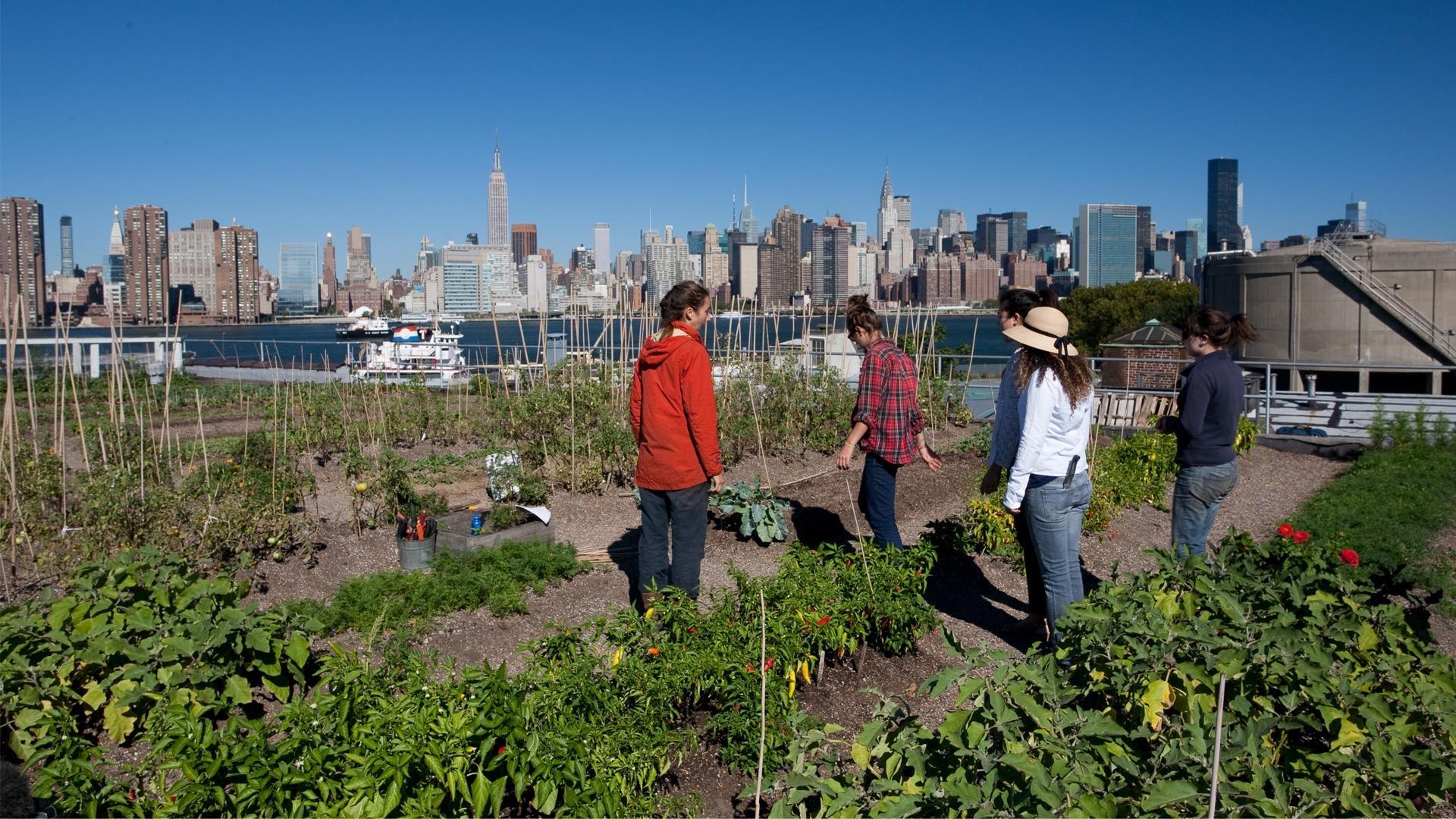
Urban agriculture provides valuable educational opportunities for people of all ages, from school children to seniors. Community gardens and urban farms serve as outdoor classrooms where individuals can learn about plant biology, ecology, and sustainable farming practices. Hands-on experiences in gardening and food production foster environmental literacy and empower individuals to make informed choices about their food and lifestyle habits. Moreover, urban agriculture initiatives often incorporate nutrition education and cooking classes, teaching people how to prepare healthy meals using fresh, locally grown ingredients. By integrating food production into educational curricula, urban agriculture promotes lifelong learning and fosters a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
Innovative Practices:
The field of urban agriculture is continually evolving, driven by innovation and experimentation. From vertical farming to aquaponics, urban farmers are exploring novel growing techniques that maximize space, conserve resources, and minimize environmental impact. Vertical farms, for example, utilize stacked growing systems to produce high yields in small urban spaces, while aquaponic systems integrate fish farming with hydroponic vegetable cultivation, creating closed-loop ecosystems that recycle nutrients and water. Moreover, advances in technology, such as precision agriculture and remote sensing, enable urban farmers to monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and increase productivity. By embracing innovation and collaboration, urban agriculture has the potential to revolutionize food production and reshape urban landscapes in the years to come.
Policy and Advocacy:
As urban agriculture gains momentum, there is a growing recognition of the need for supportive policies and regulations to enable its growth and sustainability. Cities around the world are implementing measures to promote urban agriculture, such as updating zoning ordinances to allow for agricultural land use, providing financial incentives for urban farming initiatives, and establishing urban agriculture task forces to coordinate efforts across government agencies. Moreover, grassroots advocacy efforts are raising awareness about the importance of urban agriculture and mobilizing support from policymakers, community leaders, and the public. By advocating for policies that prioritize food security, environmental sustainability, and social equity, urban agriculture advocates are driving positive change at the local, regional, and global levels.
Conclusion: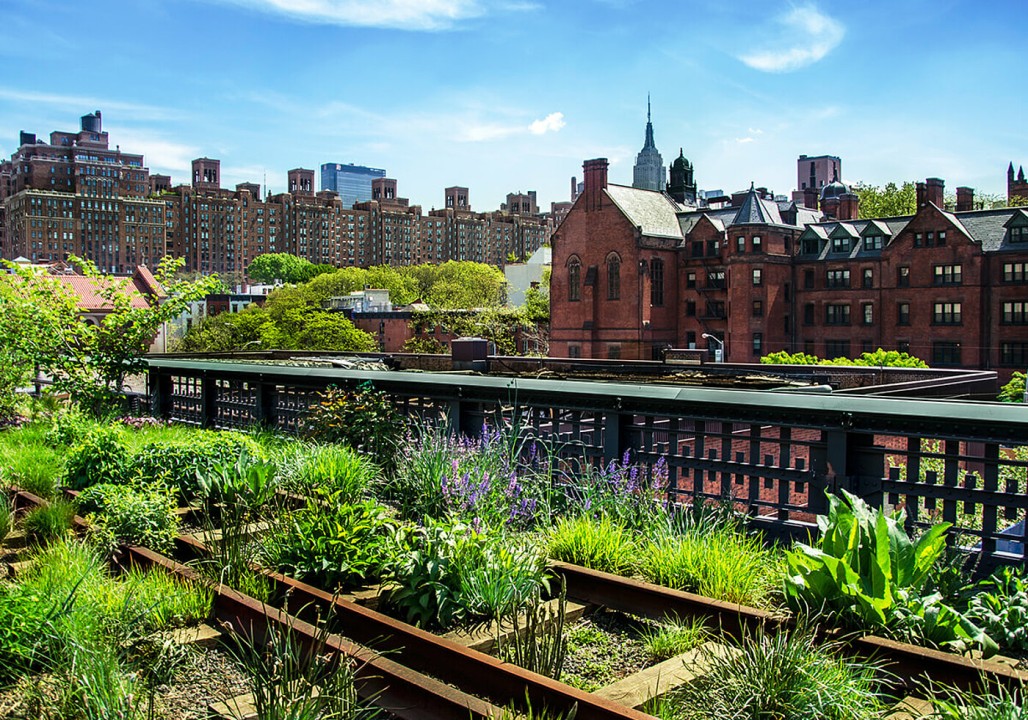
Urban agriculture represents a paradigm shift in how we think about food, cities, and sustainability. By integrating food production into the fabric of urban life, we can create healthier, more resilient, and more equitable cities for all. From rooftop gardens to community farms, urban agriculture offers a blueprint for transforming concrete jungles into vibrant, green oases of sustainability and self-sufficiency. As cities continue to grapple with the challenges of the 21st century, urban agriculture offers a beacon of hope, demonstrating that by harnessing the power of nature and community, we can cultivate a brighter future for generations to come.