Beginner Guide - Cryptography Demystified: Protecting Your Digital Privacy
Today’s digital space has become flooded with doubts regarding the safety of personal information and privacy, in general. Some of these concerns have been taken care of, thanks to the adoption of cryptography and encryption. Here, you will learn about cryptography and the various aspects of it. The topics covered in this tutorial on ‘What is Cryptography’ are:
- What is the need for Cryptography?
- What is Cryptography?
- What are the Applications of Cryptography?
- What are the Different Categories in Cryptography?
- Historical Significance of Cryptography
- Demo on Cryptography
What Is the Need for Cryptography?
Take a look at the following story to understand the need for Cryptography.
Take the example of Anne. Anne wants to look for a discount on the latest iPhone. After browsing the internet, she comes across a questionable website willing to offer a 50% discount on the first purchase.
However, a few moments after she provides her payment details, the website withdraws a huge chunk of money from her account. Anne then wonders how she had failed in realizing that the website was a scam. She then notices that the website is an HTTP webpage instead of HTTPS.
The payment information submitted was not encrypted and visible to anyone keeping an eye, including the website owner.
If she had chosen to use a reputed website, which has encrypted transactions and employs cryptography, this iPhone enthusiast could have avoided this particular incident. This is why it's never recommended to visit unknown websites or share any personal information on them.
This is where Cryptography comes to play, and is so essential. Now you’ll go through exactly what cryptography is.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the science of encrypting or decrypting information to prevent unauthorized access. In cryptography, you transform data and personal information to make sure only the correct recipient can decrypt the message. As an essential aspect of modern data security, using cryptography allows the secure storage and transmission of data between willing parties.
Here are a few terminologies which will help you understand what cryptography is, with better clarity.
There are two primary aspects of cryptography, they are:
1. Encryption
Encryption is the process of scrambling the information, to avoid third parties from comprehending the message even if it is intercepted. This scrambling is done using specific mathematical calculations and steps, often collectively known as ciphers. Along with the cipher, it uses an encryption key to encrypt the message.
2. Decryption
The second part of the cryptography process is decryption. Decryption is the process of reversing the work done by encryption. It converts the scrambled information into its original form so that the data is readable again. Usually, the encryption key which is used to scramble the data can decrypt the data, but that varies depending on the type of cryptography used. Irrespective of whether or not they are the same, a key is mandatory for both the encryption and decryption of data.
In the next section of this tutorial titled ‘what is cryptography’, you will go through an example as to how you can use keys to encrypt data.
For example, jumble up the alphabets in the word ‘Simplilearn’ and someone without the necessary information cannot guess the original message just by looking at the ciphertext.
You can only understand the word if you know how to decrypt the coded word, thereby reversing the work done by encryption to get back the plaintext.
Taking the above example as reference, before the original message is encrypted, it is called cleartext or plaintext. After it encrypts the plaintext using the encryption key, the coded message is called the ciphertext. It can then pass the same ciphertext through the decryption key and return to the cleartext/plaintext format.
What Are the Applications of Cryptography?
Cryptography finds use in many areas, ranging from safety in payment portals, to secure messaging platforms like WhatsApp. A few of those applications are as follows -
1. SSL/TLS Encryption:
Browsing the internet is secure today primarily because cryptography has allowed you to encrypt your data flow. Starting from browser identification to server authentication, encryption and cryptography, in general, have simplified online browsing.
2. Digital Signatures:
With digital contracts gaining prominence, the world was in the need of a secure channel to pass critical documents through. Cryptography helps provide a layer of authentication so you can be certain regarding the origin, confidentiality, and integrity of your documents.
3. Safe Online Banking:
Online banking services and payment applications would be an afterthought, if not for encryption of data. Cryptography has enabled authentication systems to verify the identity of certain individuals before allowing them to hold transactions and help reduce credit card fraud in the process.
4. Secure Chatting Services:
Messaging applications like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Signal have now adopted an end-to-end encryption protocol, which guarantees that no one other than the sender and receiver can read the messages. This is a huge step up from SMS days, where security was always a toss-up. Thanks to cryptography, there are a plethora of communication platforms to make use of.
5. Encrypted Emails:
With a vast amount of private information passing through your inbox, having a secure method of communication is an absolute necessity. Thanks to encryption algorithms like PGP (Pretty Good Privacy), your emails are now encrypted at all times.
6. Crypto-Currency:
With blockchain technology, cryptocurrency has seen an astronomical increase in interest rates and is still one of today’s most sought-after trade markets. A completely decentralized, secure, and tamper-proof system has found its way into today’s digital sphere, thanks to cryptography.
With so many different avenues where cryptography has found its place, its implementation is distinct. In the next section on ‘what is cryptography’, you will understand how to go ahead with it.
What Are the Different Categories in Cryptography?
Cryptography can be broadly classified into three different types -
- Symmetric Key Cryptography
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography
- Hashing
1. Symmetric Key Cryptography
Symmetric key cryptography is the category where the same key is used for both the encryption and decryption of information.
This type of encryption is used when data rests on servers and identifies personnel for payment applications and services. The potential drawback with symmetric encryption is that both the sender and receiver need to have the key, and it should be secret at all times.
For example, as seen from the image below, if Alice wants to send a message to Bob, she can apply a substitution or shift cipher to encrypt the message, but Bob must be aware of the same key so that he can decrypt it when necessary.
Symmetric key algorithms use one of the two types of Ciphers -
- Stream Ciphers - The plaintext is converted to ciphertext bit-by-bit, one at a time.
- Block Ciphers - The plaintext is broken down into blocks/chunks of data encrypted individually and later chained together.
The most widely used Symmetric Key Algorithms are AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard), 3DES (Triple DES), Twofish, etc.
2. Asymmetric Key Cryptography
In asymmetric key cryptography, there are two keys at play. A public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt the data pre-transit, and the private key is used to decrypt the data post-transit.
If Alice wants to communicate with Bob using Asymmetric encryption, she encrypts the message using Bob's public key. After receiving the message, Bob uses his private key to decrypt the data. This way, nobody can intercept the message in between transmissions, and they don’t need a secure key exchange for this to work.
RSA encryption is the most widely used asymmetric encryption standard today. Named after its founders (Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman), it uses block ciphers that separate the data into blocks and obscure the information.
On many occasions, it is advised to use a combination of symmetric and asymmetric to achieve better speed and security. In the image below, you see the process of using both symmetric and asymmetric encryption to transfer information and secret keys privately.
Follow the procedure as explained below:
Step 1: Encrypt the original message using symmetric key cryptography.
Step 2: Encrypt the key used in step one using the receiver’s public key i.e. using asymmetric key cryptography.
Step 3: Send both the encrypted message and encrypted symmetric key to the receiver.
Step 4: The receiver uses his private key to decrypt the symmetric key used to encrypt the original message.
Step 5: The decrypted key is used to convert the encrypted message back to plaintext.
3. Hashing
Hashing is the branch of cryptography that scrambles data beyond recognition. However, unlike symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography, hashing isn’t designed to be reversible. It gives an output of a fixed size, known as the hash value of the original data.
You can use hash functions to scramble the data. They are not reversible and the output size of a hash function is always the same, irrespective of the size of the plaintext.
It is to be noted that cryptography isn’t entirely limited to the 21st century. There have been several occasions in history where cryptography has helped create secure channels of communication. This tutorial on ‘what is cryptography’ will take you through two such examples in the next section.
Historical Significance of Cryptography
The two most famous examples of cryptography in ancient times are -
- Caesar Cipher
- Enigma Machine
1. Caesar Cipher:
Julius Caesar used a substitution shift to move alphabets a certain number of spaces beyond their place in the alphabet table. A spy cannot decipher the original message at first glance.
For example, if he wanted to pass confidential information to his armies and decides to use a substitution shift of +2, A becomes A+2=C, B becomes B+2=D, and so on. This cipher has been appropriately named Caesar cipher, which is one of the most widely used algorithms.
2. Enigma Machine:
The Nazi German armies used to have a machine called the Enigma during the era of the world wars. It was used to protect confidential political, military, and administrative information. It consisted of 3 or more rotors that scramble the original message typed, depending on the machine state at the time.
The decryption process is similar, but it needs both machines to stay in the same state before passing the ciphertext to give out the plaintext message.
Now you will go through how modern-day cryptography has helped in keeping the data secure on the internet with a demonstration of what is cryptography.
Demo on Cryptography
For this demo on what is cryptography, there is a web-based tool (https://www.devglan.com/online-tools/rsa-encryption-decryption) that will help you understand the process of RSA encryption. As you already probably know, the RSA encryption algorithm falls under the umbrella of asymmetric key cryptography, which implies that you have two keys at play here, the public key and the private key.
You have the choice of key size in RSA, which allows you to prioritize either speed or added complexity, depending on the requirements. Here, choose the key size as 1028 bits and generate the key pair for this example.
Now, try and encrypt the word Simplilearn in this example. You have to select if the key which is being used for encryption is private or public. Since that affects the process of scrambling the information. Since you are using the public key, select the same. You also have the option of using modified ciphers, but stick to plain RSA for the time being.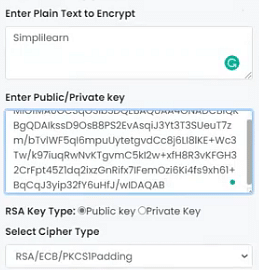 With the above parameter set, encrypt the data.
With the above parameter set, encrypt the data.You have to generate your ciphertext that is to be sent to the recipient of the message.
The receiver must already possess the private key generated from the same pair. No other private key can be used to decrypt the message. You must paste the private key here and select the same.
The cipher must also match the one used during the encryption process.
Once you click decrypt, you can see the original plaintext.
This sums up the entire process of RSA encryption and decryption.
Here, you are going to use the software called Wireshark, which helps in analyzing network traffic from your system, so you can see what kind of data enters and leaves the machine.
Consider the website Wikipedia. Pretty standard HTTPS website where the S stands for secured. Analyze the traffic passing through the network when you use the website.
You can see that there are a lot of applications running, and you see a lot of requests, so you apply a filter that only shows results for the requests generated and requested by Wikipedia. Once done, analyze some of the data packets.