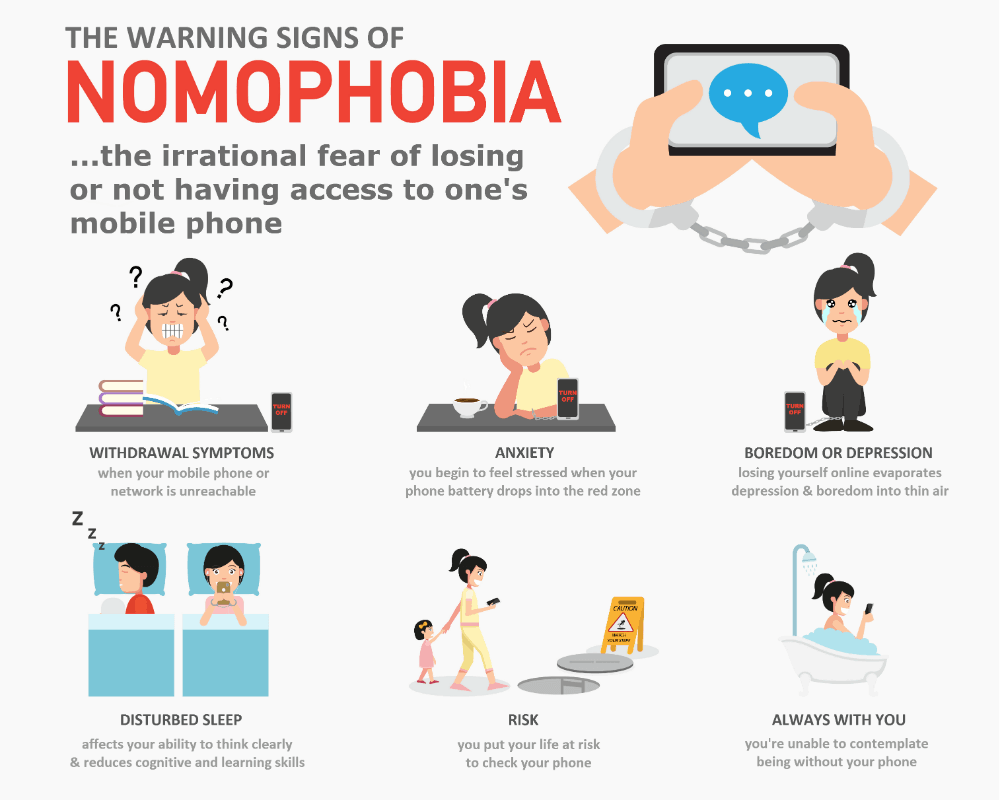
[Great]Nomophobia: Navigating the Fear of Being Disconnected in the Digital Age
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the term "nomophobia" has emerged to describe a modern affliction – the fear of being without a mobile phone or unable to use it. As we delve into the intricate realms of psychology and neuroscience, exploring nomophobia reveals a complex interplay of emotions, neurobiology, and societal influences, shedding light on the challenges individuals face in an increasingly digitized world.
Defining Nomophobia:
Nomophobia, a portmanteau of "no mobile phone phobia," encompasses the anxiety and fear individuals experience when separated from their smartphones or unable to access them. This phenomenon has become increasingly prevalent in a society where smartphones have become indispensable tools for communication, information access, and social connection.
Psychological Aspects of Nomophobia:
- Dependency on Connectivity:
Nomophobia often stems from a profound dependency on smartphones for social interaction, information retrieval, and a sense of connectedness. Individuals may experience anxiety at the thought of being cut off from these digital lifelines.
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO):
The fear of missing out on social events, news, or updates contributes significantly to nomophobia. Social media platforms, in particular, amplify this fear, creating a sense of urgency to stay constantly connected to avoid being left out.
- Identity and Self-Worth:
Smartphones have become extensions of individuals' identities, and nomophobia can be linked to a fear of losing a part of oneself when disconnected. The constant connectivity provides a platform for self-expression and validation, influencing self-worth and self-esteem.
Neurobiological Insights:
- Dopaminergic System Activation:
The use of smartphones, particularly social media apps, triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with reward and pleasure. The anticipation of notifications and the subsequent rewards contribute to the addictive nature of smartphone use.
- Amygdala and Stress Response:
Nomophobia can activate the amygdala, a key player in the brain's stress response. The fear of being disconnected may trigger a "fight or flight" response, leading to increased cortisol levels and heightened physiological arousal.
- Prefrontal Cortex Implications:
Prolonged smartphone use and the associated fear of disconnection may impact the prefrontal cortex, affecting decision-making, impulse control, and emotional regulation. This can contribute to difficulties in managing nomophobia-related behaviors.
Societal and Cultural Factors:
- Technological Integration:
The integration of smartphones into various aspects of daily life intensifies the fear of disconnection. Smartphones serve not only as communication devices but also as tools for work, education, and entertainment, further amplifying the impact of nomophobia.
- Social Expectations:
Societal norms and expectations around constant connectivity can contribute to nomophobia. The pressure to respond promptly to messages and notifications creates a sense of obligation and anxiety when disconnected.
Addressing Nomophobia:
- Digital Detox Strategies:
Encouraging individuals to engage in periodic digital detoxes can help break the cycle of nomophobia. Scheduled breaks from smartphones allow for reflection, reduced stress, and increased awareness of one's dependence on digital devices.
- Mindfulness Practices:
Incorporating mindfulness practices can help individuals become more aware of their smartphone usage patterns. Mindful engagement with technology encourages intentional and purposeful interactions, reducing the anxiety associated with constant connectivity.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT, a therapeutic approach, can be effective in treating nomophobia by addressing irrational thought patterns and behaviors related to smartphone use. Cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy are common techniques used to alleviate anxiety.
Conclusion:
In the intricate dance of psychology and neuroscience, nomophobia emerges as a poignant reflection of our digitally interconnected society. As we navigate the complexities of this fear, understanding its psychological underpinnings and neurobiological correlates becomes paramount. Acknowledging nomophobia as a valid concern allows for the development of strategies and interventions that promote a healthier relationship with technology, fostering well-being in an era dominated by the omnipresence of smartphones.
[Great] Articles I've Published Before
The Neurological Essence of Resilience: Unveiling the Power of Human Adaptability
The Intersection of Artificial Intelligence and Art
Minimalist Bir Yaşamın Rahatlatıcı Dokunuşu: Stresle Başa Çıkmanın Yolu
The Amygdala: Unraveling the Enigma of Emotional Processing in the Human Brain