Enterprise Metaverse: How Nvidia Omniverse Is Transforming Industrial Design
A New Era of Industrial Digitalization
The metaverse in 2025 is no longer just a playground for gamers or a speculative vision for futurists; it has evolved into a transformative force reshaping industries through enterprise-grade platforms like Nvidia Omniverse. While metaverse crypto coins like Decentraland’s MANA and The Sandbox’s SAND fuel virtual economies in consumer spaces, Nvidia Omniverse is carving a distinct path in the enterprise metaverse, blending creative ecosystems with industrial precision. Positioned as a “middle ground” between broad consumer platforms like Roblox and specialized industrial tools, Omniverse integrates 3D design, spatial computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to redefine product design and industrial workflows. With a projected market size of $936.57 billion for the metaverse by 2030, according to Grand View Research, Nvidia’s platform is driving a revolution in how enterprises create, simulate, and optimize digital twins. This essay explores Omniverse’s unique features, its transformative impact on industrial applications, and its cross-platform compatibility, with real-world examples like ABB’s industrial metaverse platform illustrating its potential.
The Rise of the Industrial Metaverse
Defining the Enterprise Metaverse
The enterprise metaverse, unlike its consumer counterpart, focuses on practical applications in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and logistics. It leverages digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems—to simulate, optimize, and monitor real-world operations. Nvidia Omniverse, launched in 2022, has emerged as a cornerstone of this space, offering a platform of APIs, software development kits (SDKs), and services that integrate Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD) and Nvidia RTX rendering technologies. Unlike consumer platforms that prioritize entertainment, Omniverse is built for precision, enabling engineers and designers to collaborate on complex 3D workflows in real time. Deloitte’s 2025 Tech Trends report highlights the industrial metaverse’s potential to generate $100 billion in revenue by 2030, driven by platforms like Omniverse that streamline design and automation.
Omniverse’s Role in the Ecosystem
Nvidia Omniverse occupies a unique “middle ground,” as described by ABI Research, bridging creative ecosystems and enterprise-grade tools. It supports a wide range of industries by enabling interoperability across design, simulation, and rendering tools from vendors like Siemens, Autodesk, and Adobe. This flexibility distinguishes Omniverse from more rigid enterprise platforms like Siemens’ Immersive Engineering or consumer-focused platforms like Meta Horizon. By 2025, Omniverse has been adopted by major corporations, including BMW and Foxconn, to create digital twins for factory planning and product design, showcasing its ability to unify fragmented workflows.
Omniverse’s Core Features: Powering Industrial Design
OpenUSD and RTX Rendering
At the heart of Nvidia Omniverse is OpenUSD, a standardized 3D scene description format developed by Pixar, which enables seamless data exchange across over 50 3D file formats. This interoperability eliminates the siloing of design tools, allowing teams to work collaboratively on complex projects. Nvidia’s RTX rendering technology complements OpenUSD by delivering photorealistic, real-time visualizations, critical for simulating physical properties like lighting and material textures. In 2025, Omniverse’s integration of generative AI further enhances its capabilities, enabling automated 3D asset creation and simulation. For instance, the Nvidia Edify SimReady model reduces 3D asset labeling time by 97.5%, from 40 hours to minutes for 1,000 objects, streamlining workflows.
Mega Omniverse Blueprint
The Mega Omniverse Blueprint, announced at CES 2025, is a game-changer for industrial applications. This reference architecture enables enterprises to simulate and test multi-robot fleets in digital twins before real-world deployment. Key features include:
- Robot Fleet Simulation: Tests diverse robot fleets in virtual environments to ensure seamless coordination.
- Sensor Simulation: Generates realistic sensor data for accurate robot perception, using Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX APIs.
- AI Integration: Incorporates video analytics AI agents via Nvidia Metropolis for operational insights.
Companies like KION Group, collaborating with Accenture and Nvidia, use the Mega Blueprint to optimize warehouse operations, simulating autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and robotic arms in digital twins to enhance efficiency.
Enterprise Support and Scalability
Omniverse Enterprise, available for $4,500 per year, provides robust support for production environments, including 24/7 access to Nvidia’s technical experts and prioritized bug fixes. The platform’s cloud-based deployment options, supported by AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, ensure scalability for large-scale industrial projects. The deprecation of Omniverse Launcher by October 1, 2025, reflects Nvidia’s shift toward cloud-native solutions like the Enterprise Nucleus Server, which is free for testing but requires a license for production use.
Industrial Applications: Redefining Product Design
Digital Twins in Manufacturing
Digital twins are the backbone of the industrial metaverse, enabling enterprises to design, simulate, and optimize products and processes virtually before physical implementation. Omniverse’s ability to create physically accurate digital twins has transformed product design in industries like automotive and electronics. For example, BMW uses Omniverse to simulate its electric vehicle factory in Hungary, launched in 2025, optimizing production logistics and reducing costs. By integrating computer-aided design (CAD) files, lidar scans, and AI-generated data, BMW’s digital twin mirrors real-world conditions, allowing engineers to test scenarios without disrupting operations.
Foxconn, the world’s largest electronics manufacturer, employs the Fii Digital Twin platform, built with Omniverse and Siemens technologies, to design and simulate robot work cells and assembly lines. In 2025, Foxconn uses the Mega Blueprint to test large robotic fleets, including AMRs and humanoid robots, before deployment. By integrating Nvidia’s Isaac GR00T model and cuOpt for optimization, Foxconn achieves 150x faster thermal simulations, reducing energy risks and enhancing factory efficiency.
ABB’s Industrial Metaverse Platform
ABB, a leader in industrial automation, has embraced Omniverse to develop its industrial metaverse platform, focusing on robotics and factory automation. In 2025, ABB uses Omniverse to create digital twins of its robotic systems, enabling real-time simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes. For instance, ABB’s platform integrates Omniverse’s OpenUSD and RTX rendering to simulate robotic arms in automotive assembly lines, ensuring precision and safety. This approach has reduced deployment times by 30%, according to ABB’s internal reports, by allowing engineers to test configurations virtually before physical implementation. ABB’s collaboration with Nvidia also leverages the Omniverse Cloud Sensor RTX APIs to simulate sensor data, enhancing robot perception in complex environments.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Unifying Workflows
Seamless Integration with Industry Tools
Omniverse’s cross-platform compatibility is a key strength, enabling integration with leading design and simulation tools. Partnerships with Siemens, Autodesk, Adobe, and Bentley Systems ensure that Omniverse supports workflows across CAD, computer-aided engineering (CAE), and geographic information systems (GIS). For example, Siemens’ Teamcenter X, powered by Omniverse APIs, allows engineers to create photorealistic digital twins for real-time collaboration, reducing errors in product design. In 2025, Siemens announced the Teamcenter Digital Reality Viewer, built on Omniverse libraries, enhancing its Xcelerator platform for industrial automation.
Ecosystem Growth and OpenUSD
The adoption of OpenUSD as a universal format has fostered a growing ecosystem of developers and vendors. Over 200 extensions, ranging from simple utilities to complex simulation frameworks, are available through the Nvidia OpenUSD Ecosystem Catalog. This ecosystem enables seamless data sharing across domains, from automotive to entertainment. For instance, TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor manufacturer, collaborates with an AI-powered digital twins startup to transform 2D CAD designs into interactive 3D layouts using Omniverse libraries. This approach, enhanced by Nvidia cuOpt and Isaac Lab, generates multilevel piping systems in seconds, streamlining fab construction.
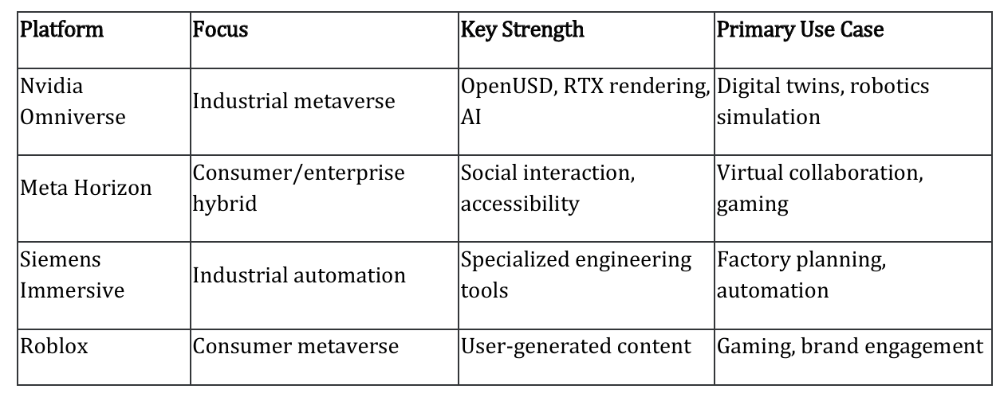
Comparison of Key Metaverse Platforms
Challenges and Opportunities
Overcoming Adoption Barriers
Despite its strengths, Omniverse faces challenges in widespread adoption. The high cost of enterprise licenses ($4,500 annually) and the need for advanced hardware, such as RTX GPUs, can be prohibitive for smaller firms. Additionally, the complexity of integrating Omniverse with existing workflows requires significant upskilling, as noted in a 2025 Forbes report. Data privacy and security concerns also loom large, particularly when deploying cloud-based digital twins that handle sensitive industrial data. Nvidia is addressing these issues by offering cloud deployment options through major providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure, ensuring scalability and security.
Future Potential
The opportunities for Omniverse are vast. Its integration with generative AI and platforms like Nvidia Cosmos, a world foundation model for photoreal synthetic data, positions it to lead the next wave of industrial AI. The Mega Blueprint’s ability to simulate robotic fleets at scale opens new possibilities for autonomous warehouses and smart factories. Collaborations with industry leaders like Accenture, which uses Omniverse for its AI Refinery for Simulation and Robotics, highlight its potential to transform supply chain management. By 2030, Gartner predicts that digital twins will be integral to 70% of manufacturing processes, with Omniverse at the forefront.
Conclusion
Nvidia Omniverse is redefining the enterprise metaverse by blending creative ecosystems with industrial precision, offering a “middle ground” that bridges consumer and enterprise applications. Its core features—OpenUSD, RTX rendering, and the Mega Blueprint—enable unparalleled collaboration and simulation, transforming product design and industrial workflows. Real-world applications, from BMW’s virtual factory to ABB’s robotic simulations, demonstrate its impact on efficiency and innovation. Despite challenges like cost and complexity, Omniverse’s cross-platform compatibility and growing ecosystem position it as a leader in the industrial metaverse. As enterprises embrace digital twins and AI-driven automation, Nvidia Omniverse is not just shaping industrial design but paving the way for a smarter, more connected future.
#Metaverse #NvidiaOmniverse #IndustrialMetaverse #DigitalTwins #ProductDesign #ABB #OpenUSD #RTXRendering #GenerativeAI #EnterpriseMetaverse