Empowering Decentralized Innovation: The Internet Computer Protocol (ICP)
What is Internet Computer Protocol? (ICP)
Summary of Internet Computer Protocol
The Internet Computer Protocol is an efficient blockchain that enables decentralized Web3 services. It utilizes innovative technologies like chain key cryptography. Its goal is to bring greater efficiency, speed, and decentralization to computation and data storage. The Internet Computer stands out from other blockchains in three ways: it allows anyone to create dApps through a user-friendly interface, it runs on a decentralized network with dedicated hardware, and it does not rely on centralized data servers.
Who created Internet Computer (ICP)?
The DFINITY project, headed by Dominic Williams and founded in 2015, developed the Internet Computer blockchain. The DFINITY Foundation, established in 2016 in Switzerland, raised funds through a public ICO in 2017 and subsequent funding rounds in 2018, accumulating over $150 million. The foundation operates research centers in Zürich, California, and remote locations.
What is the Internet Computer and ICP?
"The Internet Computer Protocol enables decentralized Web3 services."
A Web3 enabler
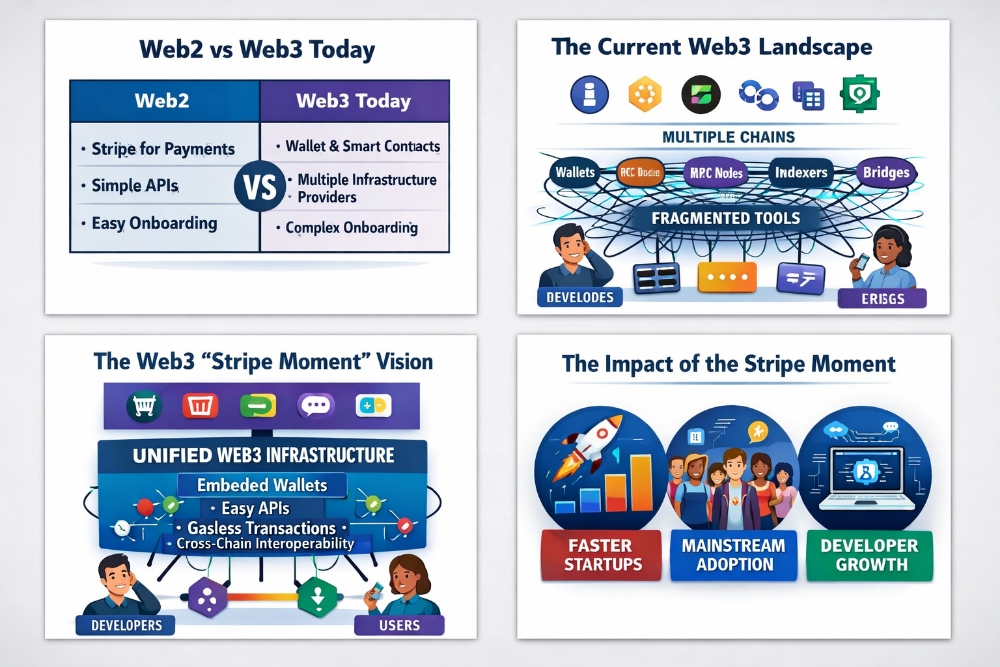
Traditional social networks have privacy issues, share sensitive data with corporations, and bombard users with advertisements. Users cannot influence the terms and conditions of these networks. However, decentralized social networks on the Internet Computer blockchain offer features like cryptographic logins with Face ID or fingerprint sensors, fast file storage and sharing, instant transfer of NFTs and cryptocurrencies through chat, and the opportunity for users to become owners and team members by earning governance tokens. These services are being developed on the Internet Computer blockchain, a powerful platform for hosting Web3 services.
The world computer
The Internet Computer blockchain allows for complete decentralization by enabling developers to create online services without relying on traditional IT resources such as cloud computing services, databases, and web servers. These traditional methods are centralized, insecure, susceptible to censorship, and often unreliable. Instead, developers utilize smart contract software called "canisters" to interact with the web and other blockchains directly, without the need for bridges. In cases where Web3 services have already been established using different blockchain ecosystems, the Internet Computer smart contracts can replace the traditional IT infrastructure, potentially offering more efficient decentralized data storage and processing capabilities. This enables developers to enhance existing blockchain services and create various Web3 services like SocialFi, GameFi, metaverse platforms, DeFi rails, and enterprise systems by utilizing Internet Computer smart contracts. Additionally, on the Internet Computer, smart contracts are able to independently cover the costs of computation, known as "reverse gas".
Why does Internet Computer (ICP) have value?
ICP has three main uses. First, it fuels smart contracts by providing cycles. Second, it can be staked in the Network Nervous System DAO to create voting neurons. Third, it serves as a store of value for investing in decentralization sales.
How does Internet Computer Protocol work?
The Internet Computer blockchain operates on a network of dedicated "node machines," similar to how the internet relies on network routers. These machines are run by independent providers globally and connect via the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) to form a public World Computer.
Chain Key Cryptography
ICP introduces "chain key cryptography," enabling blockchains to generate public "chain keys" and authenticate messages using distributed private key material, unlike traditional blockchains that need excessive data for verification.
Subnet Blockchains
The Internet Computer features multiple "subnet blockchains," independent blockchain entities that collaborate to boost capacity. These transparent subnets, akin to internet subnets, merge to create a seamless, limitless blockchain for smart contracts. Subnet blockchains employ an innovative consensus system and cryptographic framework, enabling secure interactions without local nodes. Applications verify security through chain key signatures on exchanged messages, ensuring message integrity and the correct functioning of the subnet blockchain.
Controlled by a master subnet blockchain, the Internet Computer network operates under the Network Nervous System (NNS) DAO. The NNS, with a constant chain key, guides network structure. Nodes authenticate instructions by checking the validity chain key signature. Nodes dynamically join or leave subnets without altering chain keys due to cryptographic mechanisms.
Subnet blockchains exchange messages directly, obviating the need for state copies for validation. New subnets can be seamlessly added to augment network capacity. For application interaction, knowledge of the NNS subnet's chain key suffices, as it signs the subnets' chain keys, with subnets providing proofs of NNS signatures with their own signatures.
Canister Smart Contracts
When interactive web content operates in a browser, it verifies chain key signatures on content and responses served by "canister" smart contracts hosted on the Internet Computer.
Canister smart contracts are software entities consisting of WebAssembly bytecode and persistent memory pages, enabling parallel and deterministic execution of multiple smart contracts on a single subnet. They are versatile, capable of handling complex tasks such as multi-block transactions and automatic periodic invocations through daemon smart contracts.
A recent development extends the chain key cryptography framework to empower smart contracts to manage accounts and sign transactions on other blockchains. For instance, Internet Computer smart contracts can create and handle Bitcoin addresses, facilitating the development of native decentralized finance (DeFi) systems for the Bitcoin network.
This extension also allows the creation of decentralized web experiences for Ethereum. Internet Computer smart contracts can generate and sign Ethereum transactions, subsequently querying the results using HTTP outcalls.