The Need for Menstruation in the Female Body
Menstruation is a normal and natural part of a woman's reproductive cycle. It occurs when the lining of the uterus (endometrium) sheds each month if there is no pregnancy. This shedding is triggered by a drop in hormone levels at the end of the menstrual cycle.
Menstruation is important for the following reasons:
- It helps to prepare the body for pregnancy. The endometrium thickens during the menstrual cycle to provide a nutrient-rich environment for a fertilized egg.
- It helps to remove old and damaged cells from the uterus. This helps to keep the uterus healthy and functioning properly.
- It helps to regulate hormone levels. The hormones that regulate menstruation also play a role in other important bodily functions, such as mood, sleep, and appetite.
Menstruation typically begins between the ages of 12 and 15 and continues until menopause, which usually occurs around the age of 51. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days long, but it can vary from woman to woman.
Each menstrual cycle has three phases:
- Follicular phase: This phase begins on the first day of menstruation and ends when an egg is released from the ovary. During this phase, the endometrium thickens and the egg prepares to be released.

- Ovulatory phase: This phase occurs when the egg is released from the ovary. The egg can then be fertilized by a sperm and implant in the endometrium.
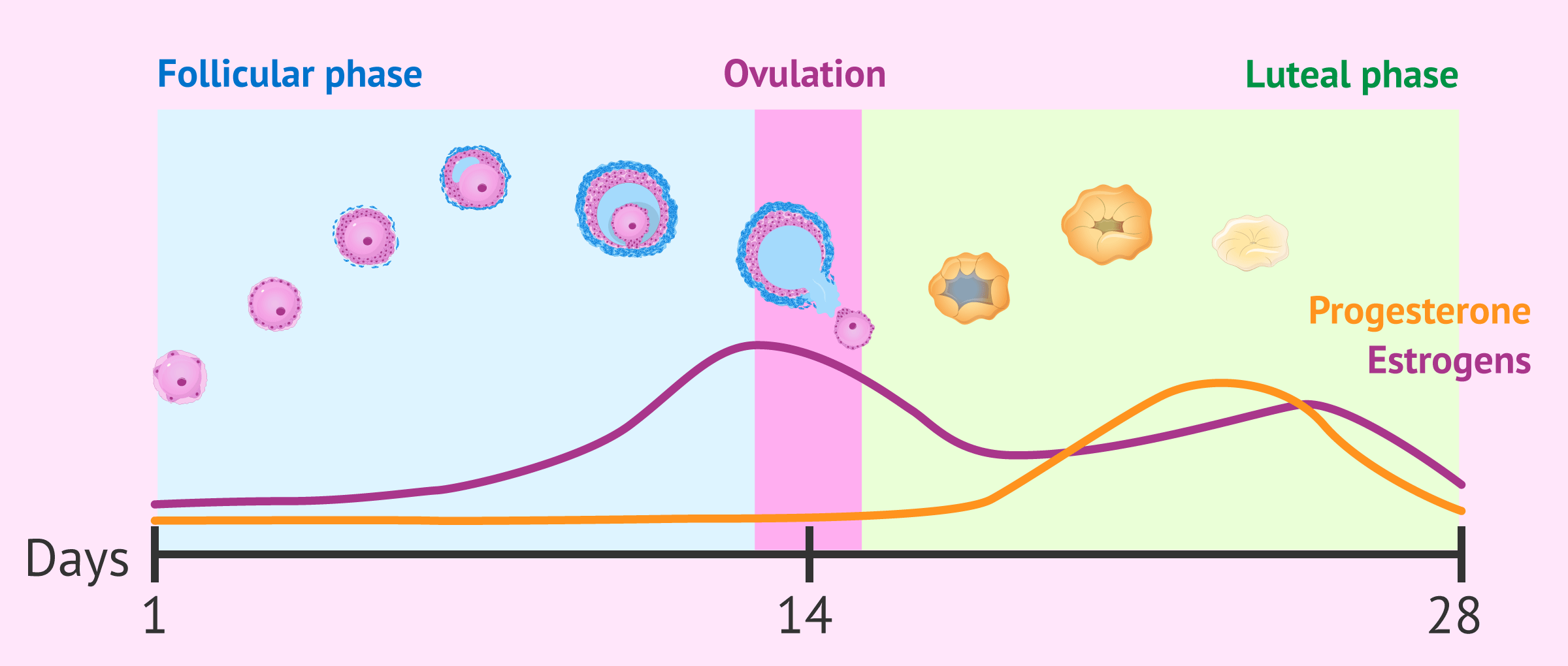
- Luteal phase: This phase begins after ovulation and ends on the last day of the menstrual cycle if there is no pregnancy. During this phase, the endometrium prepares to support a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the endometrium sheds and menstruation begins.
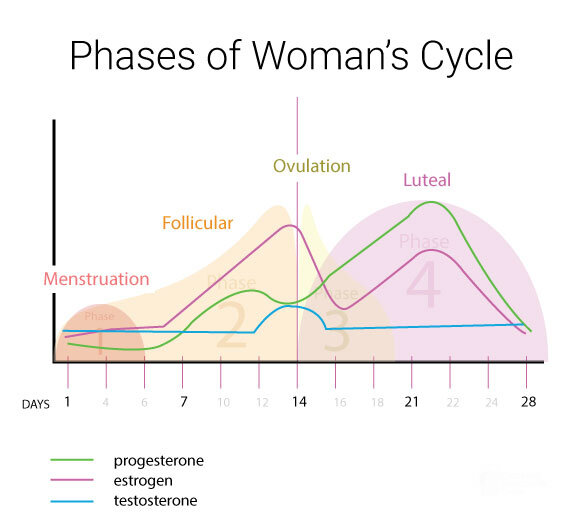 Menstruation can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms, such as cramps, bloating, mood swings, and breast tenderness. These symptoms are caused by changes in hormone levels. Most women find that these symptoms are mild and go away on their own within a few days.
Menstruation can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms, such as cramps, bloating, mood swings, and breast tenderness. These symptoms are caused by changes in hormone levels. Most women find that these symptoms are mild and go away on their own within a few days.
However, some women experience heavy menstrual bleeding, severe cramps, or other painful symptoms. These conditions may be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as endometriosis or fibroids. If you are experiencing any severe or unusual menstrual symptoms, it is important to see a doctor.
Menstruation is an important part of a woman's reproductive health. It is important to understand the menstrual cycle and to be aware of the symptoms that are normal and those that may be a sign of a problem.
There are a number of cases where a woman may not have menstruation. Some of the most common causes include:
- Pregnancy: When a woman is pregnant, the fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus and begins to develop. This prevents the endometrium from shedding, so menstruation does not occur.
- Menopause: Menopause is the natural end of menstruation. It typically occurs around the age of 51, but it can vary from woman to woman. During menopause, the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of estrogen and progesterone decline. This decline in hormones causes the endometrium to thin and menstruation to stop.
- Primary amenorrhea: Primary amenorrhea is a condition in which a woman has never had a menstrual period. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic disorders, hormonal imbalances, and structural problems with the reproductive organs.
- Secondary amenorrhea: Secondary amenorrhea is a condition in which a woman has had at least one menstrual period, but then her menstruation stops for at least three months. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, weight loss, eating disorders, excessive exercise, and certain medical conditions.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions can also cause amenorrhea. These conditions include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and pituitary gland problems.
- Certain medications: Some medications can also cause amenorrhea. These medications include chemotherapy drugs, birth control pills, and certain antidepressants.
- Extreme stress: Extreme stress can also cause amenorrhea. This is because stress can cause the body to release hormones that can interfere with menstruation.
- Extreme weight loss or gain: Extreme weight loss or gain can also cause amenorrhea. This is because the body needs a certain amount of body fat in order to produce the hormones necessary for menstruation.
- Excessive exercise: Excessive exercise can also cause amenorrhea. This is because excessive exercise can lower estrogen levels and interfere with ovulation.
If you are concerned about amenorrhea, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
In addition to the above, there are a number of other, less common causes of amenorrhea. These include:
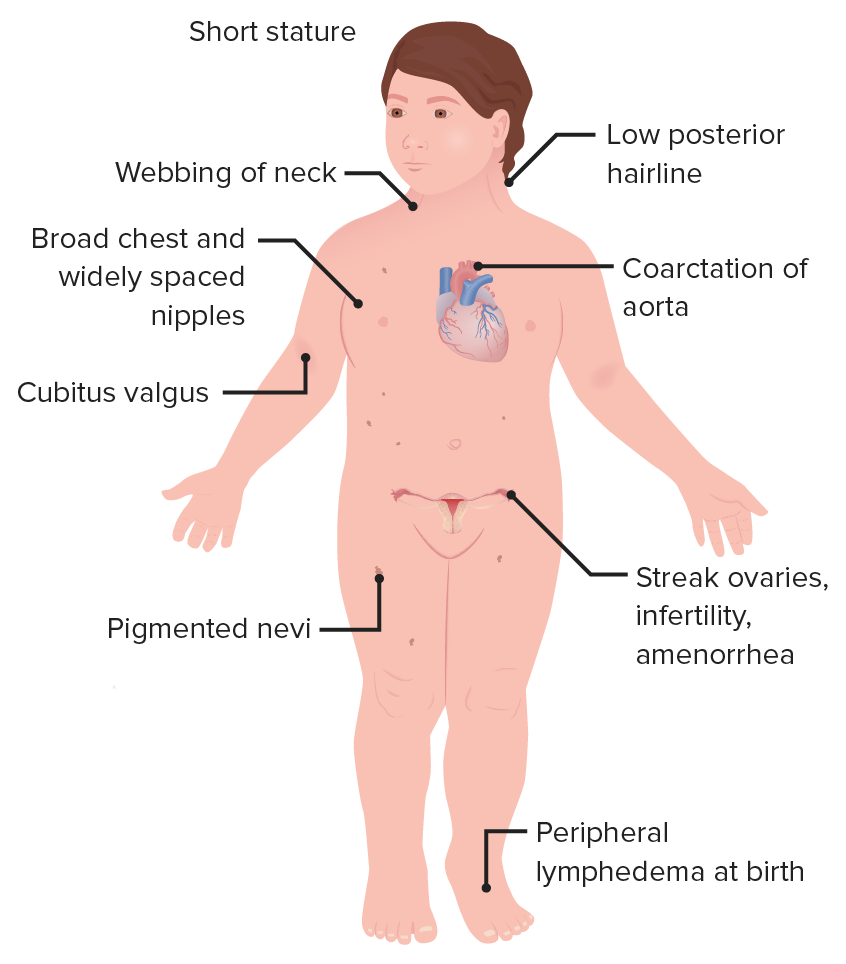
- Turner syndrome: Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that occurs when a female is missing one or both X chromosomes. Women with Turner syndrome often have delayed puberty and amenorrhea.
- Kallmann syndrome: Kallmann syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the development of the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate menstruation. Women with Kallmann syndrome often have delayed puberty and amenorrhea.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of the uterus. Endometriosis can cause a variety of symptoms, including amenorrhea.
- Fibroids: Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can develop in the uterus. Fibroids can cause a variety of symptoms, including amenorrhea.
- Asherman's syndrome: Asherman's syndrome is a condition in which scar tissue forms in the uterus. This scar tissue can block the opening to the cervix and prevent menstruation from occurring.
 If you are experiencing amenorrhea, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
If you are experiencing amenorrhea, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.