What is Bipolar? What are the symptoms of Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder, formerly known as manic-depressive disorder, is a bipolar psychological disorder in which two separate illness periods occur. Unlike the ups and downs that occur in the flow of daily life, people with bipolar may experience serious problems in the work environment, school life, and family and friend relationships due to sharp ups and downs. He may even have delusional and paranoid thoughts that have no connection with reality. Specialist Clinical Psychologist Gizem Mine Çölümlü from Memorial Hospital Psychology Department gave information about bipolar disorder and its treatment.
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar describes bipolar disorder in people who have diametrically opposed "manic" and "depressive" moods. While mania, which is seen in two different disease periods, refers to an enthusiastic, exuberant and energetic mood, depressive refers to a sad depression that can extend to suicide.
Bipolar disorder, which is seen in 1-2% of every 100 people in the society, often occurs in young adulthood, between the ages of 15-35, and is seen equally in men and women.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/379962-bipolar-disorder-symptoms-and-diagnosis-5b1150af3418c60037552e47.png)
What is mania?
The person who is in mania (i.e. the 'manic' patient) is extremely cheerful. He laughs, sings and chats with everyone, but although the patient is cheerful, he can also get angry easily. People with bipolar disease ( mood disorder ) may become very angry when you try to criticize their ideas or prevent their rambunctious behavior. Mania is an 'abnormal' condition and although the person is cheerful, happy, humorous and energetic, the person's entire social harmony is disrupted.
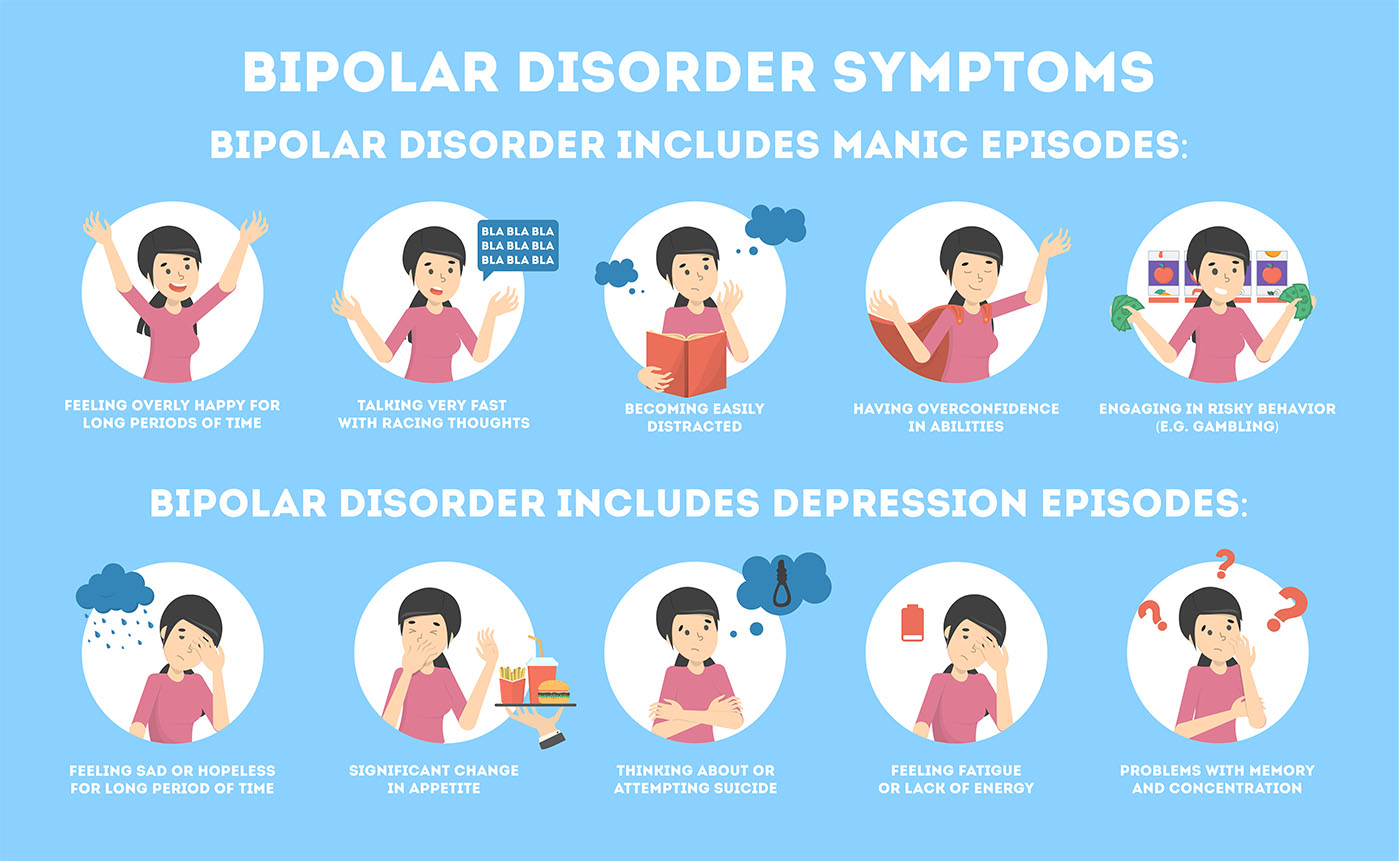
What are the symptoms of Bipolar Disorder?
People with bipolar disorder experience a shift from extremely high mood to extremely low mood. While manic symptoms include increased energy, being very happy and cheerful, feeling important and agitation, depressive symptoms include lack of energy, feeling worthless, low self-confidence and suicidal thoughts.
Manic symptoms include:
- Feeling happy, joyful and enthusiastic
- Don't feel important
- Jabber
- Decreased concentration and distraction
- Increase in sexual desire
- Making risky decisions
- Sleep problems (decreased need for sleep)
- don't spend a lot of money
- Decreased capacity to judge
- Increased thinking and speaking content
- Increase in provocative, inappropriate behavior
- Increase in alcohol and substance use
Depressive symptoms also include:
- Feeling sad and unhappy
- Being angry and tense
- lack of energy
- Don't believe you are worthless
- Don't be in despair
- Anorexia
- Having suicidal thoughts
Three or more of the bipolar symptoms must occur every day and last for a week or longer. Mania begins suddenly and can last for weeks if left untreated. The person usually does not realize that he is sick or tends to refuse treatment while experiencing a manic episode.
Another condition that can occur at the beginning of a manic attack or as an independent attack is hypomania. The hypomania phase is a period when productivity increases but manic symptoms are milder. In the hypomania phase, symptoms are usually seen to a degree that does not affect the person's relationships with school, work and social environment.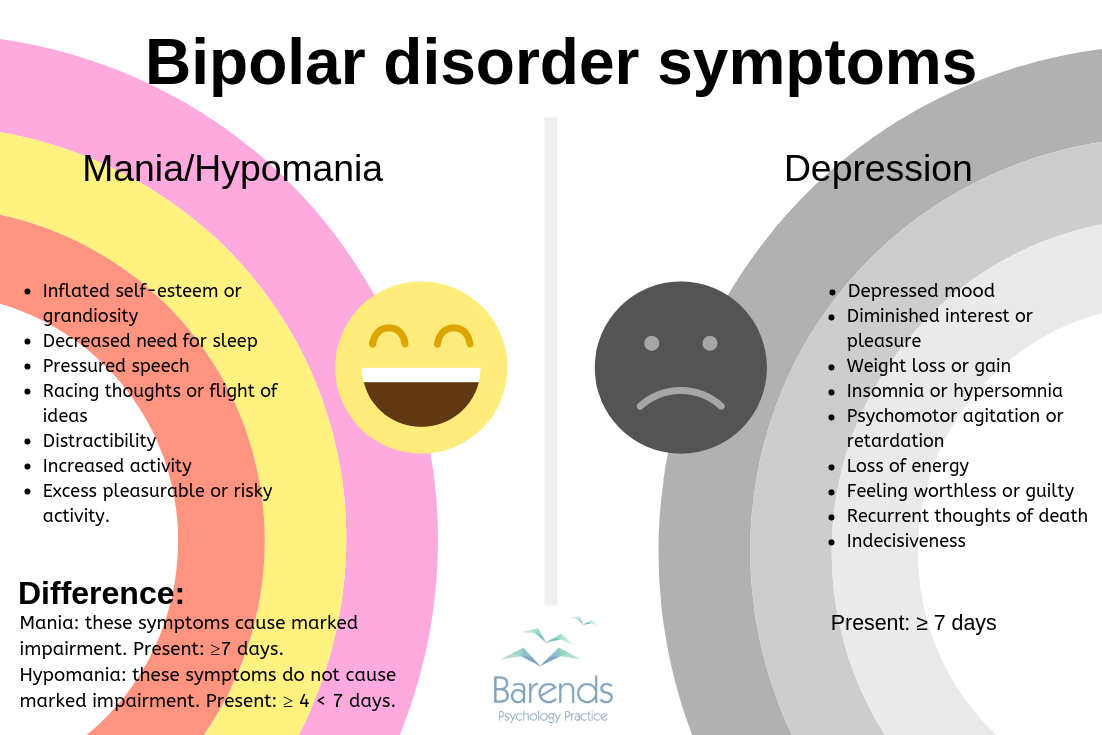
What are Bipolar Disorder Attacks?
Periods of highs and lows that lead to dramatic changes in a person's mood are described as depressive and manic 'attacks'. While some people are more prone to depression or mania, in some people the symptoms may fluctuate between two extreme emotional states (mixed episode). The stages of bipolar disorder are as follows:
1.manic episode
It is a period in which the person feels extremely energetic, talkative, active, and defines himself/herself as strong.
2.depressive episode
It is a period when the person starts not to enjoy life, constantly complains and is unhappy.
3.mixed period
It is the period when manic and depressive symptoms occur simultaneously and in a mixed manner.
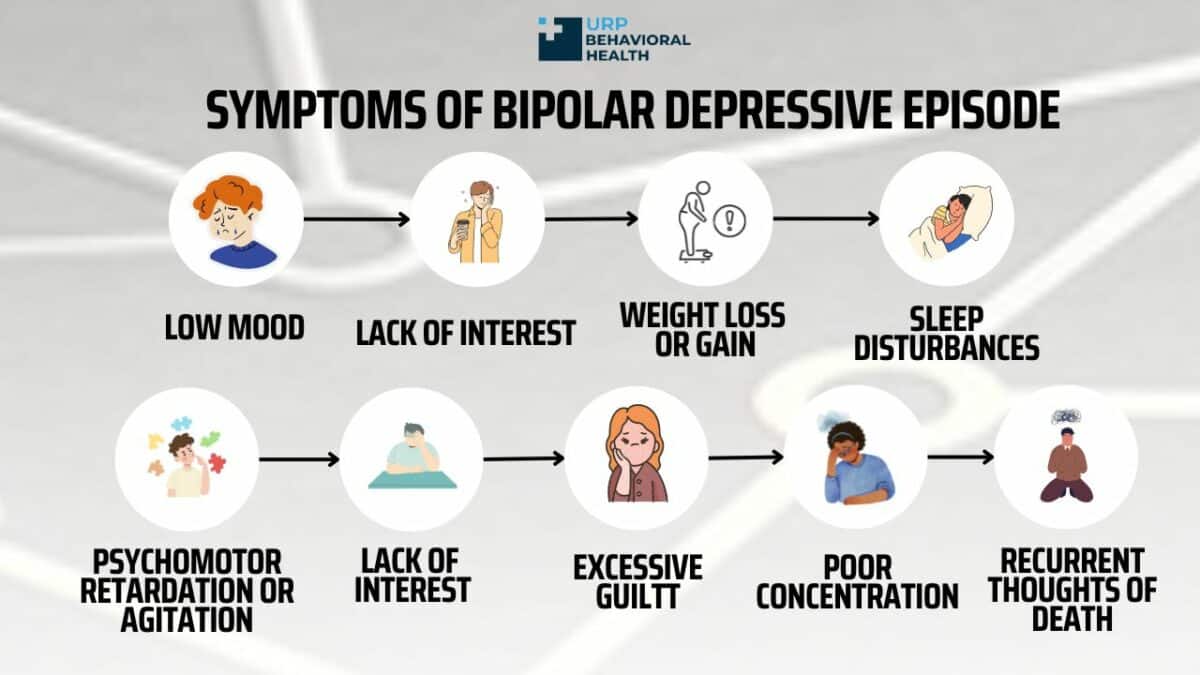
What are the symptoms of a bipolar depressive episode (period)?

- Don't be hopeless and pessimistic
- Feeling sad, anxious and unhappy
- Inability to enjoy life
- lack of energy
- Forgetfulness
- difficulty concentrating
- feeling of worthlessness
- Change in appetite; weight loss or weight gain
- Oversleeping, difficulty falling asleep, frequent waking at night
- Feelings of helplessness and worthlessness
- Thoughts of death or suicide
During a depressive episode, at least five symptoms are expected to last for two weeks or more. In cases where depressive and manic attacks are severe, psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions may also be observed.
What are the Risk Factors that Play a Role in the Development of Bipolar Disorder?
- Not doing enough physical activities
- bad eating habits
- Side effects of medications
- business problems
- stressful life
- Changes in adrenaline, insulin, stress hormone and cortisol systems
- Living in a high crime area
- financial problems

Frequently Asked Questions About Bipolar Disorder
Who gets bipolar disease?
Bipolar disorder, which increases especially in the spring months, can be seen between the ages of 15-35. The most common ages start from 20.
Does bipolar disorder treatment last a lifetime?
In the treatment of bipolar disorder, preventive treatment must be continued in the long term. In bipolar treatment, the application of mood-stabilizing medications (bipolar disorder medications) planned by the physician, as well as supportive psychotherapy and psychosocial therapies, is important for the control of bipolar disease.
How does a bipolar crisis occur?
Bipolar disorder shows different subtypes, severity, intensity and frequency in each person. Periods of highs and lows that lead to dramatic changes in a person's mood are described as depressive and manic 'attacks'. While some people are more prone to depression or mania, in some people the symptoms may fluctuate between two extreme emotional states (mixed episode).
How is bipolar disorder diagnosed?
A patient showing symptoms of bipolar disorder should be tested by a specialist physician and the appropriate treatment should be chosen after a psychiatric diagnosis is made.
Does bipolar disorder go away?
While some patients with bipolar disorder respond positively to treatment and recover, some patients may experience attacks at various periods of their lives. Apart from attacks, they can continue their lives without any problems.
At what age does bipolar disorder usually begin?
Bipolar disorder most often occurs in young adulthood, between the ages of 15 and 35, and is seen equally in men and women.
SOURCE:
https://www.acibadem.com.tr/ilgi-alani/bipolar-bozukluk/
https://www.medicalpark.com.tr/bipolar-bozukluk/hg-1880
https://psikiyatri.org.tr/halka-yonelik/22/bipolar-bozukluk-ikiuclu-bozukluk-manik-depresif-hastalik







































