Rise of Open-Source AI Models
💡 TL;DR
- Open-source foundation models like LLaMA, Mistral, Qwen, IBM Granite, and Sarvam are challenging proprietary giants, with performance gaps shrinking to ~1–2 % on benchmarks (medium.com, artificialanalysis.ai).
- Cost-wise, inference for open-weight models equivalent to GPT‑3.5 dropped 280‑fold (Nov 2022–Oct 2024), with hardware cost and energy efficiency improving ~30–40 % annually (hai.stanford.edu).
- Use cases span from finance (FinGPT) to legal (Sarvam AI), fostering reusability, transparency, and niche applications (arxiv.org).
- A heated debate is underway: advocates (Andreesen, Eric Schmidt) warn that China may lead open‑source if the U.S. doesn't act; policymakers are calling for national strategies .
- Major challenges include security, model maintenance, governance, misuse, and ensuring long-term support (mckinsey.com).
1. Why Open‑Source AI Models Are on the Rise
1.1 Democratizing Access & Cost Efficiency
Open-source models put advanced AI in the hands of developers, researchers, and small businesses without licensing overhead. McKinsey's survey shows over 50% of enterprises are using open-source AI, driven by lower costs (~60%) and transparency (mckinsey.com).
1.2 Rapid Innovation & Customization
The open model ecosystem fosters experimentation. From general-purpose LLaMA to domain-specific FinGPT and Sarvam AI, developers can fine-tune models for specialized tasks—something closed models don't always allow (hai.stanford.edu).
1.3 Technological Parity with Closed Models
Benchmarks show open-source models closing the performance gap—within ~1.7% of closed models—and reasoning-capable releases like Mistral’s Magistral series are performing strongly (hai.stanford.edu).
2. Key Open‑Source Models & Ecosystems
2.1 Meta’s LLaMA Family
LLaMA (7B–405B) was a breakthrough in 2023. Meta released LLaMA 3 in April 2024, followed by LLaMA 3.1 with advanced instruction tuning (en.wikipedia.org).
2.2 Mistral AI
France’s Mistral AI made headlines with their open reasoning models Magistral Small & Medium, rivaling LLaMA and GPT‑3.5 (en.wikipedia.org).
2.3 Alibaba’s Qwen
Alibaba Cloud’s Apache‑licensed Qwen 3 (Apr 2025) delivers multilingual performance, ranking national benchmarks in China (en.wikipedia.org).
2.4 IBM Granite
Released under Apache 2.0, Granite’s code models outperform LLaMA 3 in code tasks, proving open-source viability for enterprise-grade workloads (en.wikipedia.org).
2.5 Indian Efforts: Sarvam AI
Sarvam’s first Indic model supports vernacular languages and legal-domain functions, showing how open-source helps address regional needs (en.wikipedia.org).
2.6 Community & Multi-domain Models
- FinGPT: Specialized finance models (arxiv.org)
- GPT4All: Compresses capability into local models (arxiv.org)
- h2oGPT: Multi-size models under Apache 2.0 (arxiv.org)
- EleutherAI: Grassroots research collective & dataset creator (en.wikipedia.org)
3. The Technology & Economics Behind the Rise
3.1 Efficiency Gains
Inference cost dropped 280× between Nov 2022 and Oct 2024; hardware LM costs fell ~30% and energy use ~40% per year (hai.stanford.edu).
3.2 Benchmark Competitiveness
The performance gap with closed models is almost gone (~1.7% difference). Models like DeepSeek R1, LLaMA 4, Gemini 2.5 Pro are within striking distance (hai.stanford.edu).
3.3 Open Ecosystem Dynamics
Open-source AI benefits from developer friendliness, transparency, and customizability. Enterprises mix open and closed, but open models often win in niche tasks and compliance cases .
4. Benefits & Applications by Sector
- Finance: FinGPT offers robo‑advisory and trading pipelines (arxiv.org).
- Legal & Regional AI: Sarvam targets Indic languages and legal docs .
- Software Dev: IBM Granite code models rival LLaMA on developer tasks (en.wikipedia.org).
- Generic Development: GPT4All enables offline, compressed models (arxiv.org).
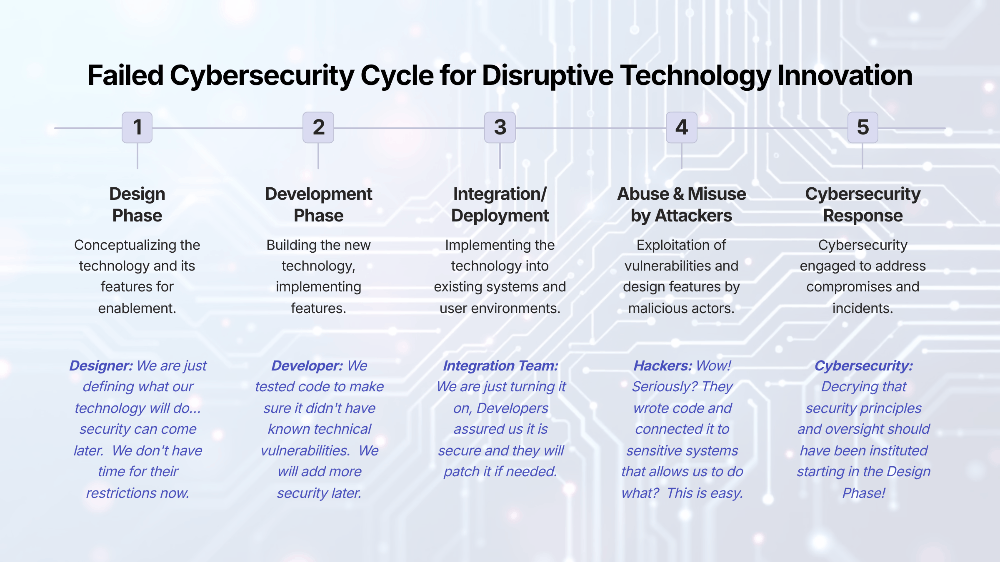
5. Governance, Security & Ethical Concerns
5.1 Misuse Potential
Open weights can be repurposed for harmful ends, from disinformation to biothreat engineering. LLaMA sparked debates over "open-source" ethics (en.wikipedia.org).
5.2 Security & Maintenance
Enterprises worry about compliance and support. McKinsey notes 56% cite security as a barrier, and 45% worry about ongoing updates (mckinsey.com).
6. Geopolitics & Strategic Competition
6.1 U.S. vs China
Marc Andreessen and Eric Schmidt warn that China (e.g., DeepSeek R1) leads in open-source, urging the U.S. to invest (businessinsider.com).
6.2 National Sovereignty & Security
Open-source AI offers transparency and aligns with sovereign interests versus reliance on U.S.-based closed models (businessinsider.com).
7. Community Voices & Perspectives
From Reddit’s LocalLLaMA:
“With open source I can make a model just for my niche… don’t need Italian, only JSON output.” (reddit.com)
These grassroots voices highlight the value of custom, efficient solutions.
8. Future Outlook & Strategic Imperatives
- Governance frameworks for open models to prevent misuse.
- Enterprise support ecosystems: documentation, updates, vulnerability monitoring.
- Public investment: US needs open‑source funding to counter foreign dominance (reddit.com).
- Blended deployment: combining open for niche needs and closed for general purpose (mckinsey.com).
- Ethical stewardship: community-led safety norms and standards.
9. Final Thoughts
The rise of open-source AI models marks a pivotal shift from proprietary control toward collective innovation, transparency, and customization. As technical and economic viability improves, open models are no longer fringe—they're mission-critical for enterprises, governments, and innovators.
But alongside widespread access comes responsibility: from ethical guardrails to national investment strategies, the ecosystem must mature to ensure benefits outweigh risks.
Open-source AI isn't just an alternative—it's becoming the foundation of democratized, sovereign, and adaptable AI in the coming decade.
Would you like this as a PDF, slide deck, or include a country/model comparative table or open-source deployment roadmap?





























![[Honest Review] The 2026 Faucet Redlist: Why I'm Blacklisting Cointiply & Where I’m Moving My BCH](https://cdn.bulbapp.io/frontend/images/4b90c949-f023-424f-9331-42c28b565ab0/1)