Victor Hugo: A Literary Genius and Social Advocate
Victor Hugo, one of the most illustrious figures in French literature, was born on February 26, 1802, in Besançon, France. Renowned as a poet, novelist, playwright, and political activist, Hugo's influence extends far beyond his literary achievements. His works, including "Les Misérables" and "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame," have left an indelible mark on world literature, exploring themes of justice, love, redemption, and the human condition.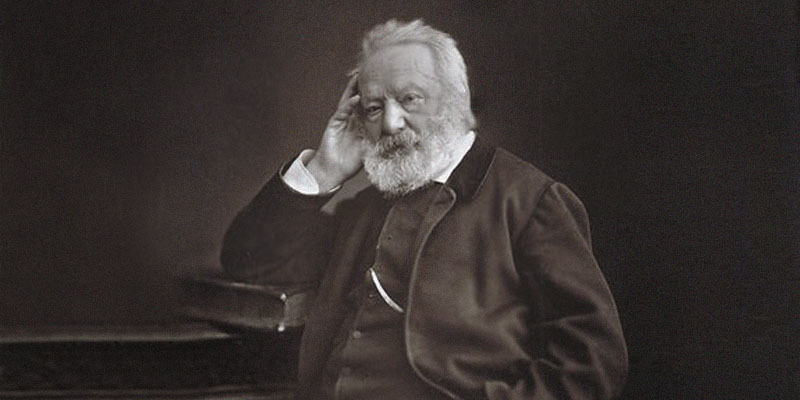 Hugo was born into a prominent family, his father being an officer in Napoleon's army. His upbringing was marked by privilege and exposure to literature and the arts. From a young age, Hugo displayed a precocious talent for writing, publishing his first poetry collection, "Odes et poésies diverses," at the age of 20.
Hugo was born into a prominent family, his father being an officer in Napoleon's army. His upbringing was marked by privilege and exposure to literature and the arts. From a young age, Hugo displayed a precocious talent for writing, publishing his first poetry collection, "Odes et poésies diverses," at the age of 20.
Throughout his life, Hugo was deeply engaged with the social and political issues of his time. He was a fervent supporter of Republican ideals and championed causes such as the abolition of the death penalty, freedom of the press, and the rights of the poor and marginalized. His political activism often found expression in his writing, as he used his literary talents to advocate for social justice and reform. Hugo's literary career began in earnest with the publication of his first novel, "Han d'Islande" (Han of Iceland), in 1823. However, it was his historical novel "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831) that catapulted him to fame and established him as one of the leading literary figures of his time. Set in medieval Paris, the novel tells the story of Quasimodo, the hunchbacked bell-ringer of Notre-Dame Cathedral, and Esmeralda, the beautiful gypsy girl he loves. Through its vivid characters and evocative portrayal of medieval society, the novel explores themes of love, prejudice, and the search for redemption.
Hugo's literary career began in earnest with the publication of his first novel, "Han d'Islande" (Han of Iceland), in 1823. However, it was his historical novel "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831) that catapulted him to fame and established him as one of the leading literary figures of his time. Set in medieval Paris, the novel tells the story of Quasimodo, the hunchbacked bell-ringer of Notre-Dame Cathedral, and Esmeralda, the beautiful gypsy girl he loves. Through its vivid characters and evocative portrayal of medieval society, the novel explores themes of love, prejudice, and the search for redemption.
Following the success of "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame," Hugo turned his attention to poetry and theater. His poetry collections, including "Les Contemplations" (1856) and "Les Châtiments" (1853), are celebrated for their lyrical beauty and emotional depth. Hugo's poetry often reflects his humanitarian values and his concern for the plight of the oppressed and downtrodden.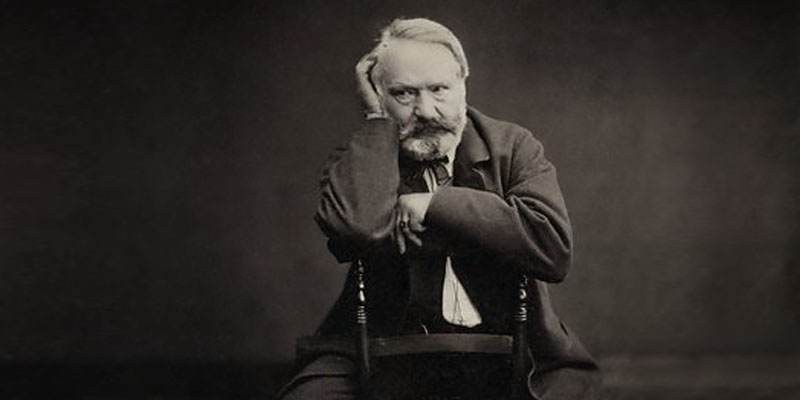 In addition to his poetry, Hugo was also a prolific playwright, with his plays "Hernani" (1830) and "Ruy Blas" (1838) causing scandal and controversy for their innovative use of language and dramatic techniques. "Hernani," in particular, sparked a literary revolution known as the "battle of Hernani," with Hugo and his supporters clashing with conservative critics over the direction of French theater.
In addition to his poetry, Hugo was also a prolific playwright, with his plays "Hernani" (1830) and "Ruy Blas" (1838) causing scandal and controversy for their innovative use of language and dramatic techniques. "Hernani," in particular, sparked a literary revolution known as the "battle of Hernani," with Hugo and his supporters clashing with conservative critics over the direction of French theater.
However, it was Hugo's magnum opus, "Les Misérables" (1862), that solidified his reputation as one of the greatest novelists of the 19th century. A sprawling epic that spans decades and continents, "Les Misérables" tells the story of Jean Valjean, a former convict who seeks redemption after being released from prison. Through its richly drawn characters and sweeping narrative, the novel explores themes of justice, love, sacrifice, and the struggle for social change.
"Les Misérables" is not only a literary masterpiece but also a powerful indictment of social injustice and inequality. Hugo's portrayal of poverty, oppression, and the suffering of the poor resonated deeply with readers, inspiring empathy and compassion for the less fortunate. The novel's enduring popularity has led to numerous adaptations in various artistic mediums, including stage musicals, films, and television series. Throughout his life, Hugo remained committed to his political ideals and continued to advocate for social reform. He was a vocal critic of the authoritarian regime of Napoleon III and went into exile in 1851 after speaking out against the government's crackdown on civil liberties. Hugo spent much of his exile in Guernsey, where he continued to write and campaign for political change.
Throughout his life, Hugo remained committed to his political ideals and continued to advocate for social reform. He was a vocal critic of the authoritarian regime of Napoleon III and went into exile in 1851 after speaking out against the government's crackdown on civil liberties. Hugo spent much of his exile in Guernsey, where he continued to write and campaign for political change.
Hugo's political activism culminated in his involvement in the Paris Commune of 1871, a revolutionary government that briefly governed Paris before being suppressed by the French army. Despite his advanced age, Hugo threw himself into the cause of the Communards, using his influence to advocate for amnesty and clemency for the insurgents.
Victor Hugo's legacy as a writer, poet, and political activist is immense. His works continue to be studied, celebrated, and adapted for new generations, inspiring readers with their timeless themes and universal truths. Hugo's commitment to social justice, his advocacy for the oppressed and marginalized, and his unwavering belief in the power of literature to effect change remain as relevant today as they were during his lifetime. As one of the towering figures of French literature, Victor Hugo's influence will endure for centuries to come, reminding us of the enduring power of art to illuminate the human experience and inspire hope for a better world. Victor Hugo's impact extends beyond his literary and political endeavors; he also played a significant role in cultural and intellectual circles of his time. As a leading figure of the Romantic movement in literature, Hugo helped shape the artistic landscape of the 19th century.
Victor Hugo's impact extends beyond his literary and political endeavors; he also played a significant role in cultural and intellectual circles of his time. As a leading figure of the Romantic movement in literature, Hugo helped shape the artistic landscape of the 19th century.
The Romantic movement, which emerged in Europe in the late 18th century and flourished throughout the 19th century, emphasized individualism, emotion, and the sublime in art and literature. Rejecting the rationalism and order of the Enlightenment, Romantic writers and artists sought to evoke intense emotional responses and explore the mysteries of the human psyche and the natural world. Hugo's works embody many of the key characteristics of Romanticism, including a focus on the individual's inner life, a fascination with nature and the supernatural, and a celebration of passion and emotion. His poetry, in particular, is characterized by its lyrical beauty, vivid imagery, and emotional intensity, capturing the essence of the Romantic sensibility.
Hugo's works embody many of the key characteristics of Romanticism, including a focus on the individual's inner life, a fascination with nature and the supernatural, and a celebration of passion and emotion. His poetry, in particular, is characterized by its lyrical beauty, vivid imagery, and emotional intensity, capturing the essence of the Romantic sensibility.
In addition to his literary achievements, Hugo was also a central figure in the cultural and intellectual life of 19th-century France. He was a member of the prestigious Académie Française and a frequent participant in literary salons and intellectual debates. His views on art, politics, and society were widely respected and debated, and his influence extended far beyond the literary world.
Hugo's impact on French culture and society is perhaps most evident in his advocacy for social justice and his commitment to the rights of the poor and marginalized. Throughout his life, Hugo used his platform as a writer and public figure to speak out against injustice and inequality, championing causes such as the abolition of the death penalty, the rights of workers, and the education of the poor.
Hugo's humanitarian values and his belief in the power of literature to effect change continue to inspire readers and thinkers around the world. His works remind us of the enduring importance of compassion, empathy, and solidarity in the face of oppression and injustice, and his legacy serves as a reminder of the transformative potential of art and literature to shape hearts and minds. In conclusion, Victor Hugo's life and work epitomize the ideals of the Romantic movement and the enduring power of literature to illuminate the human experience and inspire social change. His novels, poetry, and plays continue to captivate readers with their timeless themes, vivid characters, and evocative imagery, while his advocacy for social justice and his commitment to the rights of the oppressed serve as a model of courage and compassion for future generations. As one of the greatest writers and thinkers of the 19th century, Victor Hugo's influence will continue to be felt for centuries to come, reminding us of the enduring power of art to touch hearts, provoke thought, and inspire action.
In conclusion, Victor Hugo's life and work epitomize the ideals of the Romantic movement and the enduring power of literature to illuminate the human experience and inspire social change. His novels, poetry, and plays continue to captivate readers with their timeless themes, vivid characters, and evocative imagery, while his advocacy for social justice and his commitment to the rights of the oppressed serve as a model of courage and compassion for future generations. As one of the greatest writers and thinkers of the 19th century, Victor Hugo's influence will continue to be felt for centuries to come, reminding us of the enduring power of art to touch hearts, provoke thought, and inspire action.