How To Effectively Manage Labor Pain: A Guide for Every Mother
 The experience of labor is a profound journey marked by intense physical and emotional sensations. Among these, pain stands out as one of the most significant and challenging aspects. For centuries, women have sought ways to manage and alleviate the pain of childbirth, each method reflecting the cultural, medical, and personal contexts of the time. Today, modern medicine and holistic practices offer a diverse array of pain management strategies, empowering women to navigate labor with greater comfort and control. This comprehensive guide explores the myriad approaches to labor pain management, critically analyzing their efficacy and impact. By understanding the intricate dynamics of labor pain and the available relief methods, expectant mothers and their caregivers can craft personalized, effective strategies that transform the childbirth experience into a more manageable and empowering event.
The experience of labor is a profound journey marked by intense physical and emotional sensations. Among these, pain stands out as one of the most significant and challenging aspects. For centuries, women have sought ways to manage and alleviate the pain of childbirth, each method reflecting the cultural, medical, and personal contexts of the time. Today, modern medicine and holistic practices offer a diverse array of pain management strategies, empowering women to navigate labor with greater comfort and control. This comprehensive guide explores the myriad approaches to labor pain management, critically analyzing their efficacy and impact. By understanding the intricate dynamics of labor pain and the available relief methods, expectant mothers and their caregivers can craft personalized, effective strategies that transform the childbirth experience into a more manageable and empowering event.
Managing pain during labor is a critical aspect of the childbirth experience. Here is an outline of both non-pharmacological and pharmacological methods that mothers can use to manage labor pain, including their advantages and potential limitations.
Non-Pharmacological Methods
Breathing and Relaxation Techniques
 Description: Deep, rhythmic breathing and relaxation exercises are designed to help mothers reduce tension and manage pain during labor by focusing on controlled breathing patterns. These techniques can significantly alter pain perception, making the experience more manageable.
Description: Deep, rhythmic breathing and relaxation exercises are designed to help mothers reduce tension and manage pain during labor by focusing on controlled breathing patterns. These techniques can significantly alter pain perception, making the experience more manageable.
Advantages: These methods are easy to learn and can be practiced by anyone. They do not have any side effects and contribute to overall relaxation, which can help in reducing the intensity of labor pain.
Key Point: To utilize these techniques effectively, practice slow, deep breathing by concentrating on inhaling deeply through the nose and exhaling slowly through the mouth. This can be complemented by listening to guided relaxation tapes or participating in childbirth classes where these techniques are taught. By regularly practicing these breathing exercises, expectant mothers can better prepare for labor, helping to maintain calm and control during the process.
Hydrotherapy
 Description: Hydrotherapy involves the use of warm water, such as in a bath or shower, to soothe and relax the body during labor. The warmth and buoyancy of the water help to alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
Description: Hydrotherapy involves the use of warm water, such as in a bath or shower, to soothe and relax the body during labor. The warmth and buoyancy of the water help to alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
Advantages: The buoyancy of the water supports the body, reducing the strain on muscles and joints, while the warmth helps to relax muscles and ease tension. This combination can significantly reduce the sensation of pain and provide a comforting environment for labor.
Key Point: During labor, spend time in a birthing pool or take a warm shower. The water should be comfortably warm, not hot, to ensure safety and effectiveness. Immersing yourself in a birthing pool allows you to take advantage of the buoyancy and warmth, while a warm shower can provide similar relief through the steady flow of water over your body.
Massage and Acupressure
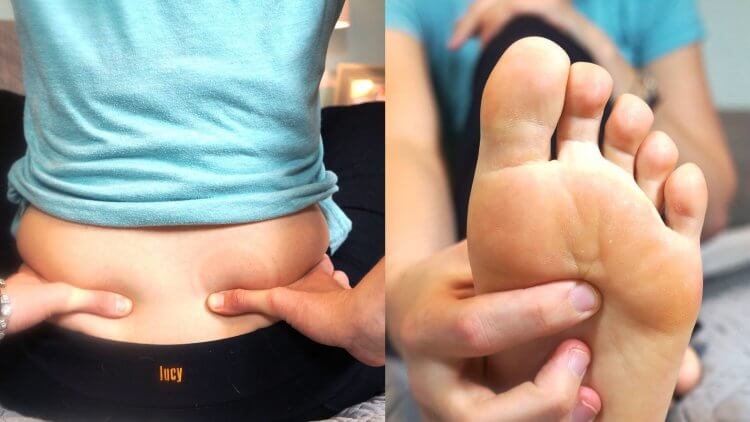 Description: Gentle massage and the application of pressure to specific points on the body, known as acupressure, are effective techniques for relieving pain during labor. These methods work by providing counter-stimulation to the pain signals and helping to relax tense muscles.
Description: Gentle massage and the application of pressure to specific points on the body, known as acupressure, are effective techniques for relieving pain during labor. These methods work by providing counter-stimulation to the pain signals and helping to relax tense muscles.
Advantages: Massage and acupressure offer immediate pain relief and can significantly reduce muscle tension. These techniques are non-invasive and can be easily performed by a partner, doula, or other support persons. They help to foster a sense of connection and support during labor.
Key Point: During labor, have your partner or support person gently massage areas such as your back, shoulders, or feet to help alleviate discomfort. Additionally, learning and applying acupressure points, such as those on the lower back, hands, or feet, can be particularly effective in reducing labor pain. Attending a prenatal class or consulting with a healthcare provider can provide guidance on the most effective massage techniques and acupressure points to use during labor.
Hypnosis and Visualization
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/labor-pain-management-f7ac3619df70492ba8f7178c27c2b3fd.jpg) Description: Hypnosis and visualization involve mental techniques that use guided imagery or hypnotic suggestions to change the perception of pain during labor. These methods help the mind focus away from pain and create a sense of calm.
Description: Hypnosis and visualization involve mental techniques that use guided imagery or hypnotic suggestions to change the perception of pain during labor. These methods help the mind focus away from pain and create a sense of calm.
Advantages: These techniques can significantly reduce anxiety, helping to promote relaxation and a sense of control over the labor process. They can enhance the overall childbirth experience by making it more positive and manageable.
Key Point: To effectively use hypnosis and visualization during labor, consider attending hypnobirthing classes where you can learn these techniques from a trained instructor. Practice visualization exercises regularly, imagining yourself in a calm and peaceful place. During labor, use these learned techniques to focus your mind on soothing and positive imagery, helping to distract from the pain and reduce overall stress.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
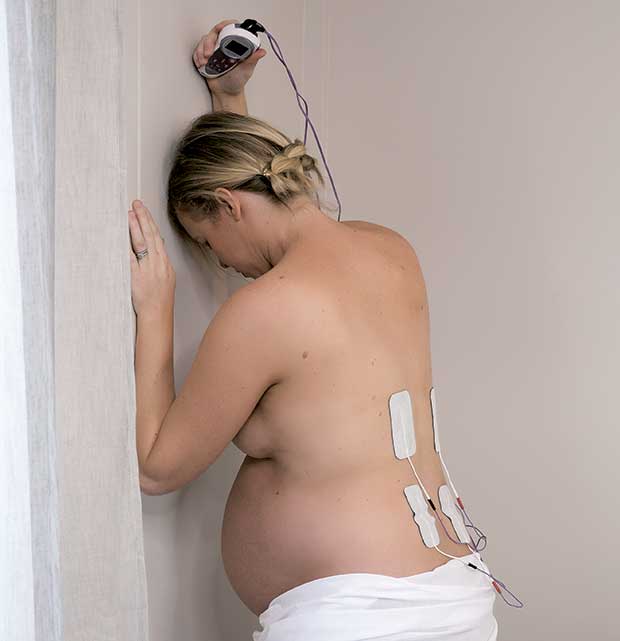 Description: TENS involves using a device that delivers mild electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin, typically on the lower back. These impulses help to block pain signals from reaching the brain and stimulate the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers.
Description: TENS involves using a device that delivers mild electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin, typically on the lower back. These impulses help to block pain signals from reaching the brain and stimulate the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers.
Advantages: This method is non-invasive and offers the advantage of being controlled by the mother, allowing for adjustments in intensity to suit her comfort level. It can be a useful tool for managing labor pain without the need for medications.
Key Point: To use a TENS unit during labor, start by placing the electrodes on your lower back, where the pain is most intense. Turn on the device and gradually increase the intensity of the electrical impulses until you find a level that is effective but comfortable. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before labor to learn the proper placement and use of the TENS device. This consultation will ensure that you are using the device safely and effectively.
Pharmacological Methods
Pharmacological methods are more direct in their approach to pain relief, they include;
Analgesics
Opioids
 Description: Opioids such as morphine, fentanyl, and meperidine are powerful pain-relieving medications that can be administered intravenously or through intramuscular injections. They work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord to reduce the perception of pain.
Description: Opioids such as morphine, fentanyl, and meperidine are powerful pain-relieving medications that can be administered intravenously or through intramuscular injections. They work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord to reduce the perception of pain.
Advantages: Opioids provide effective pain relief and can be administered relatively quickly. They are useful for managing moderate to severe labor pain when other methods are insufficient.
Note: Despite their effectiveness, opioids can cause several side effects, including sedation, nausea, and respiratory depression in both the mother and baby. This can lead to a need for additional monitoring and intervention during labor and delivery. They may also affect the baby’s breathing and feeding behaviors after birth.
Usage: Opioids are administered by a healthcare provider, typically in a hospital setting. Dosages and specific medications will be chosen based on the mother’s needs and medical history. Continuous monitoring of the mother and baby is essential to manage potential side effects.
Non-Opioids
Description: Non-opioid analgesics, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, are generally less commonly used during labor due to concerns about their effects on fetal circulation and other potential risks.
Advantages: In contexts outside of labor, NSAIDs are effective for managing mild to moderate pain and have anti-inflammatory properties.
Note: During labor, the use of NSAIDs is limited due to their potential to cause adverse effects on fetal circulation and kidney function. Therefore, they are rarely used for pain management in this setting.
Usage: If non-opioid analgesics are considered, their use will be carefully evaluated and monitored by a healthcare provider to ensure the safety of both the mother and baby. This might involve alternative dosing strategies or using these medications in conjunction with other pain relief methods.
Epidural Anesthesia
 Description: Epidural anesthesia involves the injection of an anesthetic medication into the epidural space surrounding the spinal nerves in the lower back. This numbs the nerves that carry pain signals from the uterus and birth canal to the brain, providing significant pain relief during labor.
Description: Epidural anesthesia involves the injection of an anesthetic medication into the epidural space surrounding the spinal nerves in the lower back. This numbs the nerves that carry pain signals from the uterus and birth canal to the brain, providing significant pain relief during labor.
Advantages: One of the primary advantages of epidural anesthesia is its ability to offer profound pain relief while allowing the mother to remain awake and alert. This enables the mother to actively participate in the birthing process and make informed decisions about her care.
Usage: Epidural anesthesia is administered by an anesthesiologist, a specialized physician, in a hospital setting. The procedure involves placing a small catheter into the epidural space through which the anesthetic medication is continuously delivered. This ensures a consistent level of pain relief throughout labor.
Note: Despite its effectiveness, epidural anesthesia is not without potential risks and considerations. It may lead to a drop in blood pressure, which can be managed with intravenous fluids and medication if necessary. Epidurals have also been associated with a potential increase in the duration of labor and an increased likelihood of needing interventions such as instrumental delivery (forceps or vacuum extraction). Continuous monitoring of the mother and baby, including blood pressure, heart rate, and fetal heart rate, is essential to identify and manage any complications that may arise.
Spinal Anesthesia
 Description: Spinal anesthesia is a type of regional anesthesia similar to an epidural but with some distinct differences. It involves the injection of anesthetic medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid in the lower back, numbing the nerves responsible for sensation in the lower half of the body.
Description: Spinal anesthesia is a type of regional anesthesia similar to an epidural but with some distinct differences. It involves the injection of anesthetic medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid in the lower back, numbing the nerves responsible for sensation in the lower half of the body.
Advantages: One of the primary advantages of spinal anesthesia is its rapid onset and effectiveness in providing pain relief. It is often the preferred choice for cesarean sections or other surgical procedures due to its quick action.
Usage: Spinal anesthesia is administered by an anesthesiologist in a surgical setting, typically in the operating room. The anesthetic medication is injected into the spinal canal using a fine needle, numbing the lower half of the body almost immediately.
Note: While spinal anesthesia offers rapid and effective pain relief, it is limited to certain procedures such as cesarean sections and is not typically used for labor pain management. It shares some similar side effects with epidural anesthesia, including a potential drop in blood pressure and the risk of complications such as headache or nerve damage.
Local Anesthesia
 Description: Local anesthesia involves the administration of anesthetics directly into specific areas of the body to numb sensation and relieve pain. This can include procedures such as a pudendal block for perineal pain relief during childbirth.
Description: Local anesthesia involves the administration of anesthetics directly into specific areas of the body to numb sensation and relieve pain. This can include procedures such as a pudendal block for perineal pain relief during childbirth.
Advantages: One of the primary advantages of local anesthesia is its ability to target specific areas of pain with minimal systemic effects. By numbing only the intended region, local anesthesia can provide effective pain relief while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Usage: Local anesthesia is typically administered by a healthcare provider, such as an obstetrician or midwife, during the second stage of labor or for procedures such as an episiotomy. The anesthetic medication is injected directly into the area requiring pain relief, providing rapid and localized numbing.
Note: While local anesthesia offers targeted pain relief, it is limited to specific regions of the body and may not provide comprehensive pain relief for all types of labor pain. Additionally, its effectiveness can vary depending on factors such as the individual's pain threshold and the specific procedure being performed.
Choosing the Right Pain Management Method
Choosing the most suitable pain management method during labor is a crucial decision that depends on several factors. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed choice.
Personal Preferences: Your preferences and comfort level with different pain management techniques play a significant role. Consider what methods resonate with you and align with your birthing goals. Some women may prefer non-pharmacological methods, while others may opt for pharmacological options.
Medical History: Your medical history, including any pre-existing conditions or previous experiences with anesthesia or pain management, can influence your options. Certain medical conditions or allergies may limit the use of specific medications or techniques.
Stage of Labor: The stage of labor can also impact the choice of pain management. Non-pharmacological methods like breathing techniques and massage may be more effective in early labor, while pharmacological options such as epidural anesthesia may be preferred as labor progresses and pain intensifies.
Progression of Labor: Labor can be unpredictable, and the intensity of pain may vary throughout the process. It's essential to remain flexible and open to adjusting your pain management plan based on the progression of labor and your changing needs.
Availability of Resources: Consider the availability of resources and facilities at your chosen birthing location. Not all hospitals or birthing centers may offer certain pain management options, so it's essential to discuss available options with your healthcare provider in advance.
Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Discussing pain management options with your healthcare provider is crucial. Your provider can offer personalized guidance based on your medical history, preferences, and the specific circumstances of your labor. They can also help you understand the benefits, risks, and potential side effects of each method.
Developing a Birth Plan: Developing a birth plan in collaboration with your healthcare provider can help ensure that your preferences for pain management are respected during labor. Your birth plan should outline your preferred pain management techniques, any medications or interventions you wish to avoid, and any additional support you may need during labor.
Flexibility: Labor is a dynamic process, and it's essential to remain flexible and open-minded about your pain management options. What works for one woman may not work for another, and it's okay to adjust your plan based on your individual needs and preferences as labor progresses.
By considering these factors and discussing your options with your healthcare provider, you can make an informed decision about the most suitable pain management method for your labor experience. Remember that the goal is to ensure your comfort, safety, and satisfaction during this transformative journey.
Conclusion
The management of pain during labor is a complex aspect of childbirth, with a range of non-pharmacological and pharmacological options available to mothers. By understanding the diverse array of pain management techniques and their respective advantages and limitations, expectant mothers can make informed decisions that align with their individual preferences and needs.
Throughout this article, we have examined the various methods of pain management, from breathing techniques and massage to epidural anesthesia and opioids. Each method offers unique advantages and considerations, allowing mothers to tailor their pain management approach to suit their preferences and circumstances.
By actively engaging with healthcare providers, discussing available options, and developing a personalized birth plan, mothers can enhance their childbirth experience and overall satisfaction. Effective pain management not only alleviates discomfort but also promotes a sense of empowerment, control, and confidence during labor.
As labor is a dynamic and unpredictable process, flexibility is key. Being open to adjusting pain management strategies based on the progression of labor ensures that mothers receive the support and relief they need throughout this transformative journey.
Finally, effective pain management in labor is essential for optimizing the childbirth experience and promoting the well-being of both mothers and babies. By embracing a holistic approach that integrates both non-pharmacological and pharmacological methods, mothers can navigate labor with greater comfort, confidence, and satisfaction.