The Plastic Crisis and Marine Life: Efforts to Protect Oceans

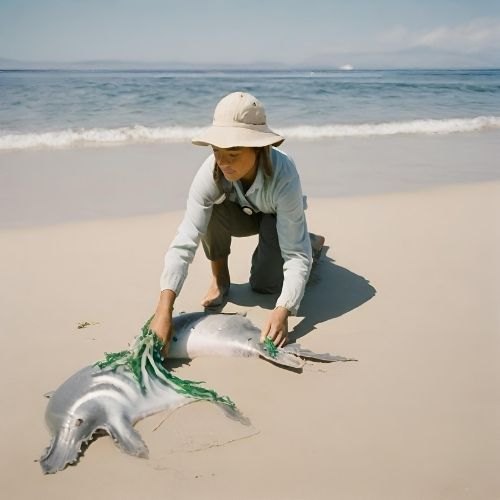
The influx of plastic waste into oceans mainly originates from terrestrial regions. Through rivers, these wastes are transported to seas and accumulate predominantly in the oceans. Due to the slow decomposition process of plastics in nature, they can persist in oceans for years, causing harm to ecosystems. The breakdown of plastics results in the formation of microplastics—tiny particles that can be ingested, inhaled, or absorbed by marine organisms, affecting the food chain.
Several key strategies are crucial to solving this problem. Firstly, changing consumer habits and promoting sustainable packaging materials are essential to reduce plastic waste at its source. Encouraging waste recycling and organizing regular cleanup campaigns to clear coastal areas are also effective solutions.
International cooperation and agreements are critically important for solving the plastic crisis. Collaborative actions between countries can prevent the leakage of plastic waste into oceans and facilitate the development of effective solutions. Establishing marine protection areas stands out as an effective strategy for conserving marine life.
Furthermore, technological innovations can contribute to addressing the plastic crisis. Devices for marine cleanup, systems that filter microplastics, and technologies accelerating biological decomposition processes are making progress in this field.
Plastic Crisis: Origins and Dimensions
In today's world, the widespread use of plastic and the mismanagement of plastic waste have triggered a serious global environmental issue known as the plastic crisis. This article will delve into the origins and dimensions of the plastic crisis, shedding light on the complexity of the problem.
1. The Origin of Plastic
At the core of the plastic crisis is the rapid increase in plastic production dating back to the late 19th century. Initially widely used in industrial production due to its lightweight, durable, and inexpensive nature, the discovery of plastic facilitated the emergence of consumer societies and the production of single-use plastic items.
2. Consumption Habits and Single-Use Plastics
One of the main contributing factors to the growth of the plastic crisis is the change in consumption habits. The popularity of single-use plastic products has increased due to fast-paced lifestyles and the convenience of single-use items. This has led to a rapid accumulation of plastic waste and exacerbated the negative effects on the environment.
3. Waste Management Issues
The ineffective management of plastic waste is another crucial factor deepening the crisis. Inadequate recycling facilities lead to the reaching of waste into oceans and natural habitats. Developing effective waste management strategies is crucial to prevent the toxic effects on marine life and the disruption of ecosystems.
4. Marine Plastic Pollution
Arguably one of the most visible dimensions of the plastic crisis is marine plastic pollution. Oceans contain millions of tons of plastic waste, posing threats to marine life, diminishing water quality, and disrupting ecosystems. International efforts need to be intensified to reduce plastic waste in the seas.
5. Health and Economic Impacts
In addition to the environmental effects of plastic waste, its impacts on human health and the economy cannot be ignored. Potential health risks of chemicals in plastic products and the costs incurred for waste cleanup require a broader perspective on the plastic crisis.
The plastic crisis is a complex and multifaceted issue. Factors such as the origin of plastic, consumption habits, waste management issues, marine plastic pollution, and health-economic impacts shape the crisis. Addressing this problem requires global collaboration, promoting sustainable production and consumption practices. The battle against the plastic crisis is a critical task to ensure environmental sustainability and protect our planet for future generations.
Impacts on Marine Life

1. Marine Pollution and Its Effects on Organisms
Marine pollution, especially the deposition of plastic waste into oceans, significantly impacts marine life. Plastic particles can enter the digestive systems of fish and other marine organisms, disrupting the entire marine ecosystem by affecting the food chain. Additionally, marine pollution threatens the habitats of marine life by reducing water quality.
2. Climate Change and Marine Life
Climate change affects marine life deeply by increasing sea temperatures. Changes in ocean acidification and oxygen levels negatively impact ecosystems such as coral reefs, marine algae, and fish species. This phenomenon disrupts the distribution and migration patterns of marine life, posing a threat to marine biodiversity.
3. Overfishing and Marine Biodiversity
Another significant factor affecting marine life is overfishing and excessive fishing practices. Overfishing can disturb the balance of ecosystems and lead to the extinction of some species. The pressure on marine biodiversity emphasizes the need for adopting sustainable fishing methods and the conservation of marine resources.
4. Marine Pollution and Seabirds
Marine pollution, especially oil spills, can have severe consequences for seabirds. The spread of oil on the sea surface can lead to the loss of water-resistant properties of birds' feathers and contamination of their food sources. This situation can result in the death of seabirds and a decrease in their populations.
5. Restoration of Marine Ecosystems
To address the negative impacts on marine life, the restoration of marine ecosystems is crucial. Global solutions, such as promoting sustainable fishing practices, preventing marine pollution, and combating climate change, need to be developed. Additionally, international collaboration and the establishment of conservation areas are necessary to protect and enhance marine biodiversity.
The impacts on marine life are shaped by the interaction of various factors. Marine pollution, climate change, overfishing, and other human activities threaten marine ecosystems. However, conscious environmental policies, sustainable fishing practices, and global cooperation can protect and restore marine life. Implementing these measures is vital for future generations to have a healthy marine environment.
Conservation Efforts for the Oceans
Oceans play a crucial role in our world, regulating climate and sustaining biodiversity. However, threats such as human activities, climate change, and marine pollution pose challenges to ocean ecosystems. In this article, we will examine global efforts to protect oceans and discuss sustainable marine management practices.
1. Marine Protected Areas
One key effort in ocean conservation is the establishment of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs). MPAs aim to protect specific marine areas by limiting human impacts that may harm ecosystems and species. These areas contribute to the preservation of marine biodiversity and the restoration of ecosystems.
2. Sustainable Fishing Practices
An integral part of protecting oceans is the adoption of sustainable fishing practices. Overfishing can severely impact marine ecosystems and lead to the extinction of some fish species. Sustainable fishing balances fishing rates, preserving ecosystems while meeting human nutritional needs.
3. Combatting Marine Pollution
Another critical aspect of ocean conservation efforts is the effective fight against marine pollution. Measures such as preventing the release of plastic waste into the seas, controlling oil spills, and regulating chemical waste are vital to protect marine ecosystems. Practices like conscious consumption and recycling contribute to reducing marine pollution.
4. Combating Climate Change
Ocean conservation efforts play a role in addressing climate change. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, controlling ocean acidification, and implementing adaptation measures against rising sea levels are crucial to maintaining the long-term health of oceans.
5. Awareness and Education
Successful ocean conservation efforts require raising awareness and educating communities. Understanding the importance of marine ecosystems, the benefits of sustainable use, and knowledge about small environmental actions individuals can take are crucial first steps for the future of the oceans.
Conservation efforts for oceans involve global sustainable marine management and environmental awareness initiatives. Steps such as establishing marine protected areas, adopting sustainable fishing practices, combating marine pollution, addressing climate change, and educating communities are vital to ensure the sustainable well-being of oceans. These efforts will secure a healthy marine environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The plastic crisis stands as a global issue posing a severe threat to marine life. Nevertheless, various efforts against this crisis can yield promising results, and the steps taken to protect oceans aim to leave a clean and healthy marine legacy for future generations.
Firstly, interventions at the source, such as changing consumer habits and promoting sustainable packaging materials, play a crucial role in reducing the influx of plastic waste into oceans. Alongside conscientious consumption habits, the transition of companies and industries to sustainable production and packaging policies is a significant step toward resolving the plastic crisis.
Campaigns for marine cleanup and the regular cleaning of coastal areas are also urgent necessities. These efforts can limit the damage to ecosystems and marine life by preventing plastic waste from terrestrial regions from reaching the seas. Additionally, raising awareness and educating communities can be instrumental in reducing plastic usage and increasing recycling habits.
International cooperation and agreements are pivotal in this struggle. Collaborative efforts between countries can prevent the leakage of plastic waste into oceans, establish marine protection areas, and enhance the chances of reaching common goals. By working together, we can find effective solutions on a global scale to address the plastic crisis.
Technological advancements offer a promising avenue in this regard. Devices for marine cleanup, systems filtering microplastics, and technologies accelerating biological decomposition processes can play a crucial role in reducing and cleaning up plastic waste.
In conclusion, the progress made in the fight against the plastic crisis is promising. However, for these efforts to be sustainable and effective, individuals, companies, governments, and the international community must collaborate steadfastly. With a reduction in plastic usage, an increase in recycling habits, and the adoption of sustainable solutions, we can come closer to the goal of protecting oceans and passing on a clean and healthy marine environment to future generations.