Exploring Cryptocurrency Collaboration: A Multifaceted Landscape
Cryptocurrency networks are complex systems that facilitate the transfer of digital assets (cryptocurrencies) between participants in a secure and decentralized manner. Collaborating within these networks involves individuals or entities working together to achieve common goals, such as maintaining the network, developing new features, or conducting transactions. Here's a comprehensive breakdown of network and collaboration in cryptocurrency, covering various factors:
- Blockchain Technology:
- Cryptocurrency networks typically operate on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
- Each transaction is verified by network participants (nodes) through cryptographic algorithms, ensuring transparency and security.
- Decentralization:
- Cryptocurrency networks are decentralized, meaning there is no central authority controlling the network.
- Decentralization enhances security by eliminating single points of failure and censorship.
- Consensus Mechanisms:
- Consensus mechanisms are protocols used by cryptocurrency networks to achieve agreement on the validity of transactions.
- Examples include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Proof of Authority (PoA).
- Mining and Staking:
- In PoW-based networks like Bitcoin, mining involves using computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles and validate transactions in exchange for rewards.
- PoS-based networks rely on staking, where participants lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral to validate transactions and earn rewards.
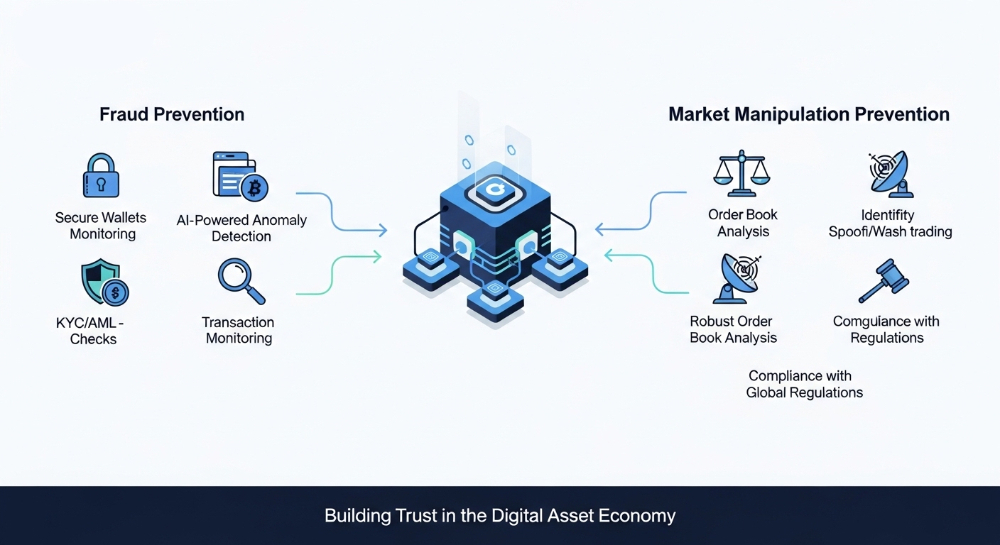
- Network Security:
- Cryptocurrency networks prioritize security to protect against attacks and ensure the integrity of transactions.
- Security measures include cryptographic encryption, network monitoring, and continuous protocol updates.
- Community Engagement:
- Collaboration within cryptocurrency networks often involves active participation from a diverse community of developers, miners, traders, and enthusiasts.
- Community engagement fosters innovation, fosters trust, and drives adoption of cryptocurrencies.
- Development and Improvement:
- Collaboration extends to the development and improvement of cryptocurrency protocols and software.
- Developers contribute code, propose upgrades, and address vulnerabilities through open-source platforms and community-driven initiatives.
- Governance:
- Some cryptocurrency networks implement governance models that allow stakeholders to participate in decision-making processes.
- Governance mechanisms may include voting on protocol upgrades, funding development projects, or resolving disputes within the community.
- Interoperability:
- Collaborative efforts aim to improve interoperability between different blockchain networks and cryptocurrencies.
- Interoperability enables seamless transfer of assets and data across multiple platforms, enhancing the utility and scalability of cryptocurrencies.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Collaboration with regulators and policymakers is essential to ensure compliance with legal frameworks and regulations.
- Regulatory clarity promotes mainstream adoption and legitimacy within the cryptocurrency industry.
In summary, network and collaboration in cryptocurrency encompass a wide range of factors including blockchain technology, decentralization, consensus mechanisms, security, community engagement, development, governance, interoperability, and regulatory compliance. These factors are interconnected and play crucial roles in shaping the present and future of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- Blockchain Technology:
- Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that organizes data into blocks, linked together in a chronological chain.
- It ensures transparency and immutability, as transactions are recorded sequentially and cryptographically secured.
- Cryptocurrency transactions are broadcasted to the network, verified by nodes, and added to the blockchain through consensus mechanisms.
- Decentralization:
- Decentralization mitigates the risk of centralized control, censorship, and manipulation.
- Participants in cryptocurrency networks retain control over their funds and transactions without relying on intermediaries like banks.
- Nodes in decentralized networks contribute to transaction validation, ensuring the integrity of the system.
- Consensus Mechanisms:
- Proof of Work (PoW) requires miners to solve computationally intensive puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain.
- Proof of Stake (PoS) selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral.
- Other consensus mechanisms, such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA), offer variations in governance and validation processes.
- Mining and Staking:
- Mining requires specialized hardware and consumes significant energy resources, leading to debates over environmental sustainability.
- Staking provides an alternative to mining, promoting energy efficiency and broader participation in network validation.
- Validators in PoS-based networks earn rewards based on their staked cryptocurrency and the accuracy of their validations.
- Network Security:
- Cryptocurrency networks employ cryptographic techniques like hash functions and digital signatures to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access.
- Security vulnerabilities, such as 51% attacks and double-spending, pose risks to network integrity and require proactive measures to mitigate.
- Ongoing research and development focus on enhancing security protocols and addressing emerging threats.
- Community Engagement:
- Communities surrounding cryptocurrency networks contribute to their development, adoption, and resilience.
- Online forums, social media platforms, and developer communities provide spaces for collaboration, discussion, and knowledge sharing.
- Community-driven initiatives, such as hackathons, bug bounties, and educational programs, foster innovation and inclusivity.
- Development and Improvement:
- Open-source development allows for transparency, peer review, and collaborative innovation in cryptocurrency protocols and applications.
- Forks, or software updates, may result in divergent blockchain histories and community consensus on protocol changes.
- Continuous improvement through protocol upgrades, scalability solutions, and interoperability standards addresses evolving user needs and technological challenges.
- Governance:
- Governance mechanisms vary across cryptocurrency networks and may involve on-chain voting, off-chain decision-making, or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
- Transparent governance fosters community trust and alignment of incentives among stakeholders, ensuring the sustainability of network operations.
- Balancing decentralization with governance efficiency remains a challenge, with ongoing experimentation and refinement of governance models.
- Interoperability:
- Interoperability protocols enable seamless communication and asset transfer between disparate blockchain networks.
- Standards like cross-chain bridges, atomic swaps, and interoperability layers facilitate interoperability while preserving security and decentralization.
- Interoperable solutions enhance user experience, liquidity, and utility by connecting fragmented ecosystems and unlocking new use cases.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Regulatory frameworks vary globally, posing challenges and opportunities for cryptocurrency adoption and innovation.
- Compliance measures, such as know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements, promote accountability and legitimacy within the cryptocurrency industry.
- Collaborative engagement with regulators, industry stakeholders, and policymakers seeks to establish clear guidelines and foster responsible growth of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- Scalability:
- Scalability refers to a network's capacity to handle increasing transaction volumes without sacrificing performance or security.
- Cryptocurrency networks face scalability challenges due to limitations in block size, transaction throughput, and consensus mechanisms.
- Solutions such as layer-2 protocols (e.g., Lightning Network), sharding, and off-chain scaling aim to improve scalability while maintaining decentralization and security.
- Privacy and Confidentiality:
- Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies aim to enhance user anonymity and transaction confidentiality.
- Techniques like ring signatures, zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge), and stealth addresses enable private transactions without compromising network integrity.
- Balancing privacy with regulatory compliance remains a complex challenge, with ongoing efforts to develop privacy-preserving technologies that align with legal requirements.
- Smart Contracts and DApps:
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined terms and conditions encoded on the blockchain.
- Decentralized applications (DApps) leverage smart contracts to automate processes, facilitate interactions, and deploy innovative services across various industries.
- Collaboration in developing smart contract standards, auditing practices, and DApp ecosystems drives adoption and interoperability within the cryptocurrency space.
- Tokenization and Asset Management:
- Tokenization involves representing real-world assets, such as real estate, securities, or art, as digital tokens on a blockchain.
- Asset-backed tokens enable fractional ownership, liquidity, and efficient transfer of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Collaborative efforts in token standards, asset tokenization platforms, and regulatory frameworks unlock new opportunities for asset management, investment diversification, and financial inclusion.
- Cross-Border Payments and Remittances:
- Cryptocurrencies offer a decentralized alternative for cross-border payments and remittances, bypassing traditional banking intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
- Stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies provide stability and predictability for cross-border transactions, mitigating volatility risks.
- Collaboration among payment processors, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies addresses compliance, liquidity, and interoperability challenges in cross-border payments.
- Education and Awareness:
- Education initiatives play a crucial role in promoting understanding, adoption, and responsible use of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology.
- Collaborative efforts in educational outreach, workshops, and online resources empower users to navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency investing, security best practices, and regulatory compliance.
- Building public trust and confidence through transparent communication, consumer protection measures, and risk mitigation strategies fosters mainstream adoption and long-term sustainability.
- Philanthropy and Social Impact:
- Cryptocurrency networks enable transparent and traceable charitable donations, empowering individuals and organizations to support social causes and humanitarian efforts.
- Collaborative philanthropic initiatives leverage blockchain technology to track donations, ensure accountability, and maximize impact in areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental conservation.
- Partnerships between cryptocurrency projects, non-profit organizations, and philanthropic foundations drive innovation in social impact initiatives, promoting positive change and global development.
In summary, network and collaboration in cryptocurrency extend beyond technical considerations to encompass scalability, privacy, smart contracts, tokenization, cross-border payments, education, philanthropy, and social impact. These factors reflect the diverse applications, challenges, and opportunities within the cryptocurrency ecosystem, highlighting the importance of collaborative efforts in driving innovation, adoption, and positive societal change.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Cryptocurrency mining, particularly in Proof of Work (PoW) networks, consumes significant energy resources and has raised concerns about its environmental impact.
- Collaborative efforts focus on developing more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing eco-friendly mining practices.
- Initiatives such as carbon offset programs, green mining initiatives, and research into alternative consensus algorithms aim to mitigate cryptocurrency's environmental footprint.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability:
- Cross-chain interoperability enables seamless communication and asset transfer between different blockchain networks, enhancing liquidity and accessibility.
- Collaborative projects and protocols, such as interoperability bridges, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and interoperable blockchain standards, facilitate interoperability across heterogeneous blockchain ecosystems.
- Interoperability fosters collaboration between disparate blockchain communities, promotes innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi), and expands the utility of cryptocurrencies.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
- DeFi encompasses a broad range of financial services and applications built on blockchain technology, including lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming.
- Collaboration in the DeFi space involves protocol development, liquidity provision, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- Interoperable DeFi platforms, composability of smart contracts, and decentralized governance mechanisms drive innovation and composability in decentralized finance.
- Token Economics and Governance:
- Tokenomics refers to the economic design and incentives within cryptocurrency networks, including token distribution, supply dynamics, and governance mechanisms.
- Collaborative efforts focus on designing robust tokenomic models that align incentives, encourage participation, and ensure the long-term sustainability of cryptocurrency networks.
- Token governance mechanisms, such as on-chain voting, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and governance tokens, empower community stakeholders to shape network policies and protocols.
- Cybersecurity and Threat Mitigation:
- Cryptocurrency networks face cybersecurity threats, including hacking attempts, phishing attacks, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
- Collaboration among cybersecurity experts, blockchain developers, and auditors is essential for identifying vulnerabilities, implementing security best practices, and responding to emerging threats.
- Threat intelligence sharing, security audits, and community-driven bug bounty programs enhance the resilience and trustworthiness of cryptocurrency networks.
- Regulatory Sandboxes and Innovation Hubs:
- Regulatory sandboxes provide controlled environments for testing new blockchain and cryptocurrency applications within existing regulatory frameworks.
- Collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulators, and policymakers in establishing regulatory sandboxes fosters innovation, promotes compliance, and facilitates dialogue on regulatory challenges.
- Innovation hubs, such as blockchain incubators and accelerators, support startups and entrepreneurs in developing and scaling innovative cryptocurrency projects while navigating legal and regulatory complexities.
- Cross-Industry Collaboration:
- Collaboration between the cryptocurrency industry and traditional sectors, such as finance, technology, healthcare, and supply chain management, drives cross-industry innovation and adoption.
- Partnerships, pilot projects, and cross-industry consortia explore blockchain use cases, interoperability standards, and regulatory implications across diverse sectors.
- Cross-industry collaboration accelerates the integration of blockchain technology into mainstream applications, unlocking new efficiencies, transparency, and value creation.
These additional factors deepen our understanding of the multifaceted nature of network and collaboration in cryptocurrency, highlighting the interconnectedness of technical, economic, regulatory, and social dimensions within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- Cryptography and Privacy Enhancements:
- Cryptography plays a central role in ensuring the security and privacy of cryptocurrency transactions.
- Collaborative research and development efforts focus on advancing cryptographic techniques, such as post-quantum cryptography, homomorphic encryption, and multi-party computation, to enhance privacy and security.
- Innovations in privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), including zero-knowledge proofs, ring signatures, and confidential transactions, aim to protect user data and transactional privacy without compromising network integrity.
- Education and Skill Development:
- Education and skill development initiatives are essential for fostering talent and expertise in blockchain technology and cryptocurrency ecosystems.
- Collaborative programs, such as coding bootcamps, online courses, and academic partnerships, provide training and certification opportunities for developers, entrepreneurs, and industry professionals.
- Skill-building efforts contribute to workforce development, knowledge dissemination, and the growth of a skilled talent pool capable of driving innovation and adoption in the cryptocurrency space.
- Identity Management and Digital Identity:
- Identity management solutions aim to address challenges related to user authentication, identity verification, and data privacy in decentralized ecosystems.
- Collaborative projects explore self-sovereign identity (SSI), decentralized identity protocols, and verifiable credentials to empower individuals with control over their digital identities.
- Interoperable identity frameworks and cross-industry partnerships facilitate the development of secure, privacy-preserving identity solutions that enable seamless access to services and applications across diverse platforms.
- Regulatory Sandboxes and Testnets:
- Regulatory sandboxes and testnets provide controlled environments for experimenting with new blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies while complying with regulatory requirements.
- Collaboration between industry participants, regulators, and legal experts in establishing regulatory sandboxes and testnet environments fosters innovation, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation.
- Sandboxes allow for the testing of new products, services, and business models within a supervised framework, facilitating dialogue, feedback, and iteration before broader market deployment.
- Cross-Protocol Collaboration:
- Cross-protocol collaboration involves interoperability and compatibility efforts between different blockchain protocols and networks.
- Standards bodies, interoperability projects, and cross-protocol initiatives aim to establish common frameworks, communication protocols, and interoperability standards that facilitate seamless interaction and asset transfer between disparate blockchain platforms.
- Cross-protocol collaboration enhances liquidity, accessibility, and utility by breaking down silos and enabling interoperability between ecosystems, protocols, and applications.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs):
- DAOs are autonomous entities governed by smart contracts and operated by their community members without centralized control.
- Collaborative efforts in DAO governance, tokenomics, and smart contract development empower stakeholders to collectively manage resources, make decisions, and govern decentralized networks.
- DAOs enable decentralized decision-making, transparent governance, and community-driven initiatives that align incentives and foster collective action within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
These additional dimensions highlight the diverse range of collaborative efforts and initiatives shaping the evolution of network and collaboration in cryptocurrency. From cryptography and privacy enhancements to regulatory sandboxes and cross-