Exploring the Dynamic Interplay of Geography and Human Society
Introduction:
Geography is far more than just the study of landforms and natural features; it encompasses a complex interplay of physical, environmental, cultural, and human factors that shape the world we inhabit. From the impact of climate and topography on human settlement patterns to the ways in which human activities influence the natural environment, geography provides a lens through which we can better understand the intricate relationships between the Earth and its inhabitants.
The Power of Place: Understanding Physical Geography
- Explore the fundamental principles of physical geography, including landforms, climate, ecosystems, and natural resources.
- Discuss how physical geography shapes human societies and cultures, influencing everything from agricultural practices to urban development and transportation networks.
Mapping Human Landscapes: Cultural and Social Geography
- Examine the cultural and social aspects of geography, including language, religion, ethnicity, and migration patterns.
- Explore how human societies have transformed the landscape through settlement, agriculture, industry, and infrastructure development.
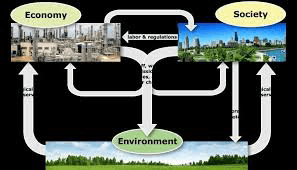
Environmental Dynamics: Human Impact and Sustainability
- Investigate the ways in which human activities have altered the natural environment, leading to issues such as deforestation, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction.
- Discuss the concept of sustainability and explore strategies for mitigating environmental degradation and promoting ecological balance.
Geopolitical Forces: Boundaries, Conflict, and Cooperation
- Analyze the geopolitical dimensions of geography, including the role of borders, territorial disputes, and international relations.
- Examine how geography influences political and economic systems, shaping alliances, trade routes, and global power dynamics.
Geography in the Digital Age: Technology and Spatial Analysis
- Explore the use of geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and other digital technologies to analyze spatial data and solve real-world problems.
- Discuss how technology is revolutionizing the field of geography, enabling more accurate mapping, monitoring, and prediction of environmental phenomena.
some additional information expanding on the various aspects of geography mentioned in the topic above:
Physical Geography:
- Landforms: Physical geography encompasses the study of landforms such as mountains, plains, plateaus, and valleys, which are shaped by geological processes like erosion, tectonic activity, and weathering.
- Climate: It examines climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and weather phenomena, and their impact on ecosystems, agriculture, and human activities.
- Ecosystems: Physical geography studies various ecosystems, from forests and grasslands to deserts and marine environments, and the interactions between living organisms and their physical environment.
Cultural and Social Geography:
- Language and Religion: Cultural geography explores the distribution and diversity of languages, religions, customs, and traditions across different regions, and how they influence social identities and interactions.
- Migration Patterns: It analyzes patterns of human migration, including voluntary migration for economic opportunities or resettlement, as well as forced migration due to conflict, persecution, or environmental factors.
Environmental Dynamics:
- Human Impact: Environmental geography examines the ways in which human activities, such as agriculture, industry, urbanization, and resource extraction, impact the natural environment, leading to issues like deforestation, pollution, and habitat loss.
- Sustainability: Environmental geography focuses on promoting sustainable practices and policies to minimize environmental degradation and conserve natural resources for future generations.
Geopolitical Forces:
- Borders and Boundaries: Geopolitical geography studies the significance of borders and boundaries in defining political territories, sovereignty, and territorial disputes between nations.
- International Relations: It analyzes the geopolitical relationships between countries, including alliances, conflicts, trade agreements, and diplomatic negotiations, and how geography influences these dynamics.
Geography in the Digital Age:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology allows geographers to capture, store, analyze, and visualize spatial data, facilitating decision-making in various fields such as urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
- Remote Sensing: Remote sensing techniques, including satellite imagery and aerial photography, provide valuable information about Earth's surface features, vegetation cover, land use, and environmental changes over time.
Conclusion:
By examining the dynamic interplay of geography and human society, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of our world. Geography not only helps us understand the past and present but also provides valuable insights for addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in an increasingly interconnected and rapidly changing global landscape.