Tokenization: Transforming Ownership, Investment, and Fundraising

Introduction
In the world of Web 3, tokenization has emerged as a transformative concept that is revolutionizing the way we think about ownership, investment, and fundraising. By leveraging blockchain technology, tokenization enables the representation of real-world assets or rights as digital tokens. These tokens can be bought, sold, and traded on decentralized platforms, opening up new opportunities for individuals and businesses alike. One of the key benefits of tokenization is its ability to fractionalize assets.
Traditionally, ownership of assets like real estate, art, or even company shares required significant capital. However, with tokenization, these assets can be divided into smaller units, allowing for broader ownership and investment opportunities. For example, a high-value property can be tokenized into multiple digital tokens, enabling investors to buy fractions of the property and benefit from potential returns. Tokenization also enhances liquidity in traditionally illiquid markets.
Digital Representation of an Asset
By creating a digital representation of an asset, tokens can be easily bought and sold on blockchain-based platforms, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs. This increased liquidity opens up access to new investment opportunities and allows for greater flexibility in managing portfolios. Furthermore, tokenization has the potential to democratize fundraising.
Through Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) or Security Token Offerings (STOs), companies can raise capital by issuing tokens that represent ownership or rights in their projects. This enables startups and entrepreneurs to access a global pool of investors, breaking down geographical barriers and providing a more inclusive and efficient fundraising mechanism. Investors, on the other hand, benefit from increased transparency and security through tokenization. 
Conclusion
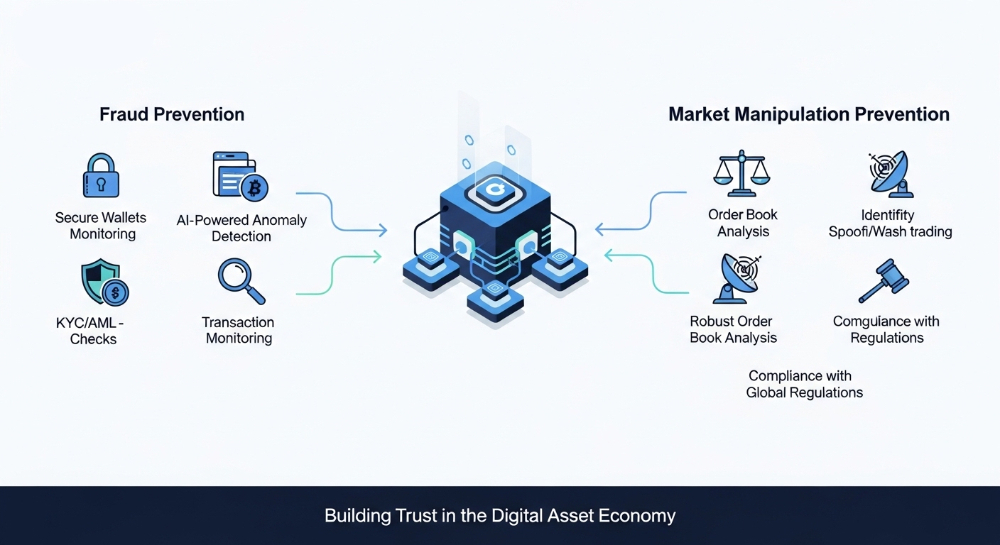
In conclusion, tokenization is transforming the way we approach ownership, investment, and fundraising. It opens up new opportunities for individuals and businesses to access and participate in previously inaccessible markets. By leveraging blockchain technology, tokenization enhances liquidity, increases transparency, and democratizes fundraising. However, it is important to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape and be mindful of market volatility.
As we continue to explore the potential of tokenization, it is crucial to embrace best practices, stay informed, and adapt to the changing landscape of this exciting technology.
Reference
"Tokenization demystified". IDEMIA. 2017-09-19. Archived from the original on 2018-01-26. Retrieved 2018-01-26.
^ "Payment Tokenization Explained". Square. Archived from the original on 2018-01-02. Retrieved 2018-01-26. ^ CardVault: "Tokenization 101"
^ Ogigau-Neamtiu, F. (2016). "Tokenization as a data security technique". Regional Department of Defense Resources Management Studies. Zeszyty Naukowe AON. 2 (103).
Brasov, Romania: Akademia Sztuki Wojennej: 124–135. ISSN 0867-2245. ^ Ogîgău-Neamţiu, F. (2017). "Automating the data security process". Journal of Defense Resources Management (JoDRM). 8 (2).
^ "OWASP Top Ten Project". Archived from the original on 2019-12-01. Retrieved 2014-04-01.
^ Stapleton, J.; Poore, R. S. (2011). "Tokenization and other methods of security for cardholder data". Information Security Journal: A Global Perspective. 20 (2): 91–99. doi:10.1080/19393555.2011.560923. S2CID 46272415.
^ Y., Habash, Nizar (2010). Introduction to Arabic natural language processing. Morgan & Claypool. ISBN 978-1-59829-796-6. OCLC 1154286658.