Jordan, Nebateans and The Mystery Of The Ancient City Of Petra
Jordan: A Land of History, Diversity, and Natural Beauty
Nestled in the heart of the Middle East, Jordan is a captivating country with a rich tapestry of history, diverse culture, and breathtaking natural landscapes. From ancient archaeological wonders to vibrant modern cities, Jordan offers a wealth of experiences for travelers seeking adventure, exploration, and cultural immersion.
Historical Heritage
Jordan's history dates back millennia, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Paleolithic period. Throughout the ages, the land that is now Jordan has been home to a succession of civilizations, including the Nabateans, Romans, Byzantines, and Umayyads, each leaving their mark on the landscape in the form of magnificent ruins, temples, and monuments.
Perhaps the most iconic symbol of Jordan's ancient heritage is the ancient city of Petra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the New Seven Wonders of the World. Carved into rose-colored sandstone cliffs over 2,000 years ago by the Nabateans, Petra's elaborate facades and rock-cut tombs are a testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship of its builders.
Other notable historical sites in Jordan include the Roman ruins of Jerash, with its well-preserved theaters, temples, and colonnaded streets; the crusader castle of Kerak, perched atop a hill overlooking the Dead Sea; and the desert citadel of Qasr Amra, adorned with exquisite frescoes dating back to the Umayyad period.
Cultural Diversity
Jordan is a melting pot of cultures, religions, and traditions, with influences from the Arab, Bedouin, Circassian, and Chechen communities that call the country home. Visitors to Jordan can immerse themselves in the vibrant atmosphere of bustling souks, where the sights, sounds, and aromas of spices, textiles, and handicrafts create a sensory feast for the senses.
One of the most striking aspects of Jordanian culture is its tradition of hospitality, known as "diwan," where guests are welcomed with warmth and generosity. Whether sipping sweet mint tea with Bedouin nomads in the desert or sharing a traditional Jordanian feast with a local family, visitors to Jordan are sure to experience the genuine warmth and hospitality of its people.
Natural Beauty
In addition to its rich history and cultural heritage, Jordan boasts some of the most spectacular natural landscapes in the Middle East. From the dramatic canyons of Wadi Rum to the crystalline waters of the Red Sea, Jordan's diverse terrain offers a paradise for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
The Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, is a natural wonder renowned for its buoyant waters and therapeutic muds, making it a popular destination for wellness retreats and spa treatments. The Dana Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve, is a haven for biodiversity, with its rugged mountains, verdant valleys, and diverse wildlife.
For adventure seekers, Jordan offers a plethora of outdoor activities, from hiking and camping in the desert to snorkeling and diving in the Red Sea. The Jordan Trail, a 650-kilometer hiking route that traverses the length of the country, offers a unique opportunity to experience Jordan's diverse landscapes and meet local communities along the way.
Conclusion
In summary, Jordan is a land of contrasts, where ancient history and modernity coexist, and where desert landscapes give way to lush oases and pristine beaches. Whether exploring ancient ruins, sampling traditional cuisine, or trekking through stunning natural scenery, visitors to Jordan are sure to be captivated by the country's beauty, diversity, and hospitality. With its rich cultural heritage, warm and welcoming people, and breathtaking landscapes, Jordan truly offers a journey of discovery unlike any other.
The Nabataeans: Masters of Trade and Architecture in Ancient Arabia
The Nabataeans were an ancient Arab civilization whose kingdom flourished in the region of present-day Jordan, Israel, and Saudi Arabia from the 4th century BCE to the 1st century CE. Renowned for their mastery of trade, architecture, and water management, the Nabataeans played a crucial role in the cultural and economic landscape of the ancient Near East, leaving behind a legacy that continues to fascinate historians, archaeologists, and travelers alike.
Origins and Early History
The origins of the Nabataeans are shrouded in mystery, with little known about their early history prior to the 4th century BCE. It is believed that they were originally a nomadic tribe of Arab descent, migrating from the Arabian Peninsula to the region of southern Jordan and northern Saudi Arabia. Over time, the Nabataeans established themselves as a sedentary society, settling in fortified cities and towns along key trade routes.
Trade and Commerce
One of the key factors behind the success of the Nabataean kingdom was its strategic location along major trade routes linking Arabia, Egypt, and the Mediterranean world. The Nabataeans capitalized on this geographical advantage by establishing a vast network of trade routes and caravan stations, facilitating the exchange of goods such as spices, incense, silk, and precious metals.
The Nabataeans' control of trade routes allowed them to amass wealth and influence, enabling the development of a sophisticated urban civilization characterized by elaborate architecture, urban planning, and cultural patronage. The city of Petra, the capital of the Nabataean kingdom, served as a hub of commerce and culture, boasting magnificent temples, palaces, and tombs carved into the rose-colored sandstone cliffs.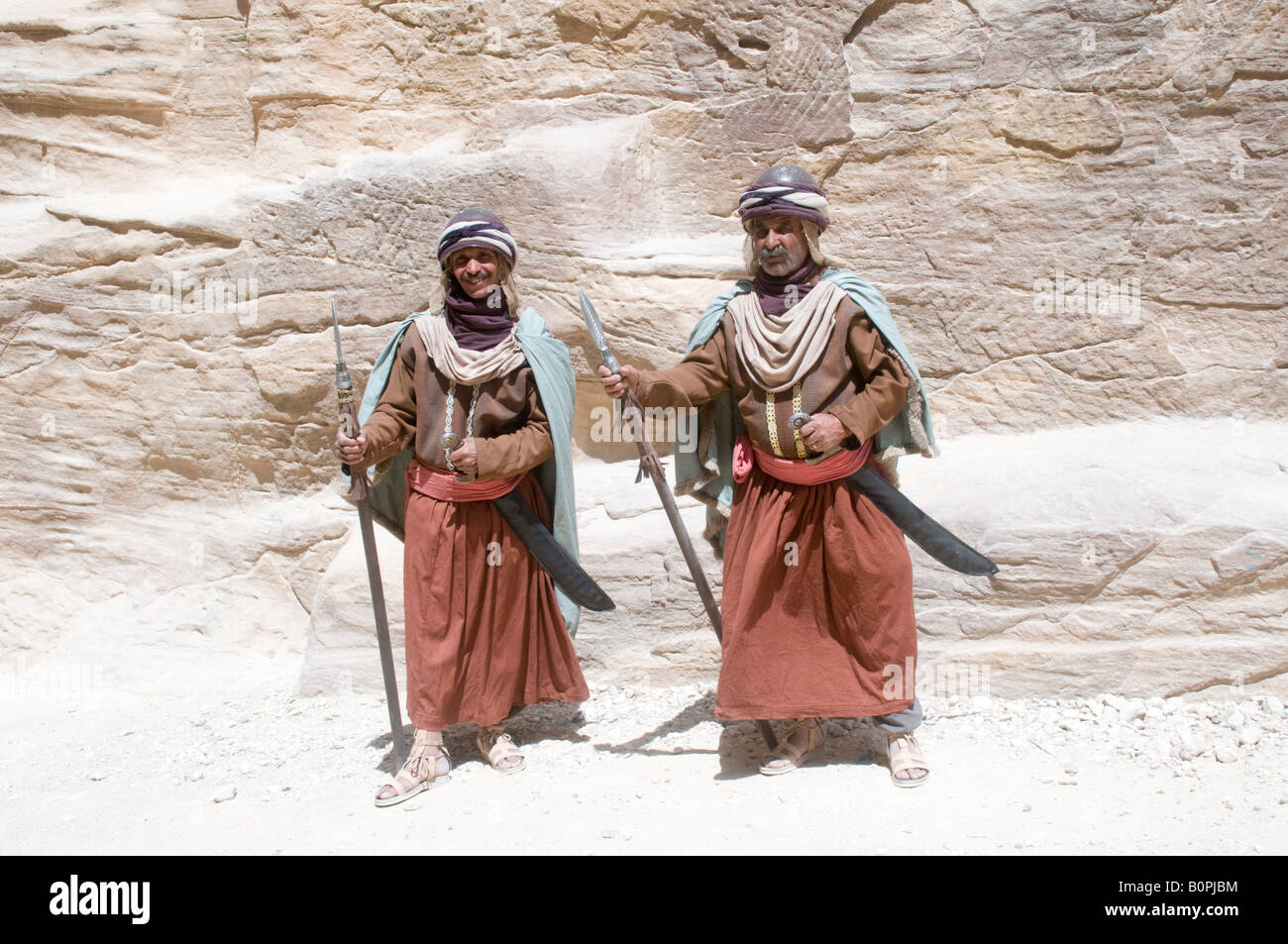
Architecture and Engineering
One of the most enduring legacies of the Nabataeans is their remarkable architectural achievements, particularly their mastery of rock-cut architecture. The most iconic example of Nabataean architecture is the ancient city of Petra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the New Seven Wonders of the World. Carved into the sandstone cliffs of southern Jordan, Petra is home to breathtaking structures such as the Treasury, the Monastery, and the Royal Tombs, each a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of its builders.
In addition to their architectural prowess, the Nabataeans were also renowned for their innovative water management systems, which allowed them to thrive in the arid desert environment. Petra's sophisticated system of dams, cisterns, and aqueducts enabled the Nabataeans to capture and store rainwater, providing a reliable source of water for drinking, irrigation, and agriculture.
Decline and Legacy
The prosperity of the Nabataean kingdom reached its zenith during the 1st century CE, but it began to decline following the annexation of Petra by the Roman Empire in 106 CE. Over the centuries, Petra was gradually abandoned and fell into obscurity, its magnificent structures hidden beneath layers of sand and debris.
Despite its decline, the legacy of the Nabataeans lives on through their architectural marvels, cultural achievements, and contributions to the history of the ancient Near East. Today, Petra stands as a symbol of the Nabataeans' ingenuity, resilience, and enduring legacy, attracting visitors from around the world to marvel at its beauty and explore its secrets. Through ongoing archaeological research and preservation efforts, scholars continue to uncover new insights into the history, culture, and achievements of this remarkable ancient civilization.
Petra: An Ancient City Carved in Stone
Located in present-day Jordan, Petra stands as one of the most awe-inspiring archaeological sites in the world. Carved into the rose-colored sandstone cliffs of the Jordanian desert, Petra is a testament to the ingenuity, craftsmanship, and cultural heritage of the ancient Nabatean civilization. With its stunning architecture, rich history, and dramatic natural setting, Petra continues to captivate visitors from around the globe, earning its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the New Seven Wonders of the World.
History of Petra
The history of Petra dates back over two millennia, with evidence of human habitation in the area dating as far back as the Neolithic period. However, Petra rose to prominence during the heyday of the Nabatean kingdom, which flourished from the 4th century BCE to the 1st century CE. As a vital hub along the ancient trade routes that connected Arabia, Egypt, and the Mediterranean, Petra grew into a thriving city of commerce, culture, and religion.
The Nabateans, a nomadic Arab tribe, were masterful engineers and architects, harnessing the natural resources of the region to create a city of unparalleled beauty and grandeur. The most iconic feature of Petra is the Treasury, or Al-Khazneh, a magnificent temple facade carved into the sandstone cliffs and adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures. Other notable structures include the Monastery, the Royal Tombs, and the Great Temple, each a testament to the architectural achievements of the Nabateans.
Rediscovery of Petra
Despite its historical significance, Petra was largely forgotten by the outside world for centuries, known only to local Bedouin tribes who inhabited the area. It was not until the early 19th century that Petra was rediscovered by Swiss explorer Johann Ludwig Burckhardt, who disguised himself as a Bedouin and infiltrated the city, bringing it to the attention of the Western world.
Since its rediscovery, Petra has captured the imaginations of travelers, scholars, and artists alike, inspiring countless works of literature, art, and film. It has been featured in films such as "Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade" and "Transformers: Revenge of the Fallen," further cementing its status as an iconic symbol of ancient mystery and adventure.
Preservation and Tourism
Today, Petra is one of Jordan's most popular tourist destinations, attracting hundreds of thousands of visitors each year. Efforts to preserve and protect the site have been ongoing, with UNESCO and the Jordanian government working to safeguard Petra's fragile archaeological remains from the impacts of erosion, weathering, and tourism.
Visitors to Petra can explore the city's ancient streets, temples, and tombs on foot, following winding paths through narrow canyons and towering cliffs. Guided tours offer insight into the history, culture, and significance of Petra, while camel rides and horse-drawn carriage tours provide alternative ways to experience the site.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Petra stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of the Nabatean civilization and the timeless allure of ancient history. Its stunning architecture, rich history, and dramatic natural setting make it a must-see destination for travelers seeking adventure, exploration, and cultural immersion. As one of the world's most iconic archaeological sites, Petra continues to inspire wonder and fascination, inviting visitors to step back in time and experience the grandeur of a lost civilization carved in stone.