Tech Industry Layoffs
Tech Industry Layoffs: Causes, Trends, Impacts, and Future Outlook
Introduction
The technology sector, once a beacon of relentless growth and innovation, has in recent years witnessed significant waves of layoffs impacting thousands of employees worldwide. From startups to tech giants, companies have announced workforce reductions driven by various factors such as economic uncertainties, changing market dynamics, and internal restructuring. These layoffs have sent ripples across global economies and stirred conversations about the sector’s stability and future trajectory.
This essay explores the causes behind tech industry layoffs, analyzes key trends and notable case studies, examines the socioeconomic impacts, and offers insights into potential future developments.
1. Overview of Tech Industry Growth and Employment Trends
- Tech sector’s growth boom over the last two decades.
- Role in driving innovation, job creation, and economic growth.
- Employment surge in software development, IT services, hardware manufacturing, and emerging fields like AI, cloud computing, and blockchain.
- Earlier reputation of “tech sector invincibility” with continuous hiring.
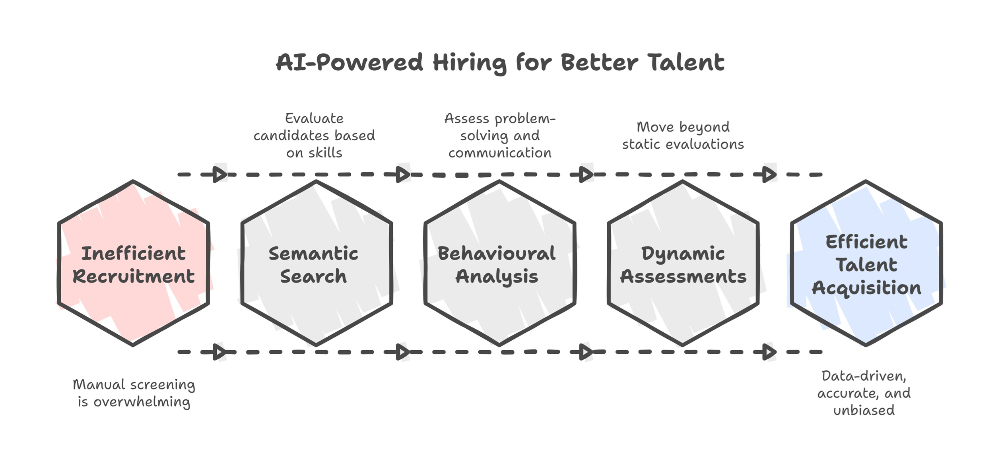
2. Causes of Tech Industry Layoffs
2.1 Macroeconomic Conditions and Recession Fears
- Global economic slowdowns and inflationary pressures.
- Rising interest rates and tighter capital markets reducing funding availability.
- Impact on consumer spending and enterprise IT budgets.
2.2 Post-Pandemic Market Corrections
- Surge in tech demand during COVID-19 lockdowns led to aggressive hiring.
- Overestimation of sustained growth leading to workforce excess.
- Correction phase with recalibration of business models.
2.3 Shift in Business Strategy and Priorities
- Focus shifting from growth at all costs to profitability and efficiency.
- Reevaluation of product lines, scaling back non-core projects.
- Increased automation reducing human resource needs.
2.4 Overvaluation and Investor Pressure
- High valuations led to unsustainable burn rates.
- Investor demands for cost-cutting and returns.
- IPO market cooling and private funding drying up.
2.5 Technological Disruption and Automation
- Adoption of AI and machine learning automating routine jobs.
- Changes in skill demand requiring workforce reskilling.
2.6 Geopolitical and Regulatory Challenges
- Trade tensions impacting supply chains and market access.
- Data privacy regulations affecting product development cycles.
- Increased scrutiny of hiring practices and labor laws.
3. Trends in Tech Layoffs: Data and Patterns
3.1 Scale and Frequency of Layoffs
- Layoff waves concentrated in 2022-2024.
- Thousands of job cuts announced by major players: Meta, Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Twitter, Salesforce.
- Smaller startups also affected amid funding challenges.
3.2 Departments Most Affected
- Engineering and product development roles.
- Sales and marketing cuts in some companies.
- Support and administrative functions in others.
3.3 Geographic Distribution
- Silicon Valley as epicenter but global impacts (India, Europe, Southeast Asia).
- Remote and hybrid workforces complicate geographical trends.
3.4 Demographic Impact
- Impact on early-career employees and contract workers.
- Gender and diversity considerations in layoff processes.
4. Notable Case Studies
4.1 Meta (Facebook)
- Aggressive hiring during pandemic followed by multiple layoffs.
- Focus on “metaverse” investments amid skepticism.
- Shift towards AI and cost optimization.
4.2 Twitter
- Rapid layoffs post-Elon Musk acquisition.
- Strategic restructuring and prioritizing monetization.
4.3 Amazon
- Layoffs in cloud computing and retail divisions.
- Investment recalibration following pandemic-driven growth surge.
4.4 Google and Alphabet
- Workforce reduction focused on “moonshot” projects.
- Efforts to streamline AI and cloud businesses.
4.5 Startups and Unicorns
- Many tech startups facing layoffs due to drying venture capital.
- Examples include fintech, edtech, and crypto sectors.
5. Impacts of Tech Industry Layoffs
5.1 On Employees
- Financial insecurity and career uncertainty.
- Mental health challenges.
- Skills mismatch and re-employment difficulties.
5.2 On Companies
- Loss of institutional knowledge.
- Impact on morale and productivity.
- Brand reputation and talent acquisition challenges.
5.3 On the Tech Ecosystem
- Slowdown in innovation pace.
- Reduced consumer and enterprise tech spending.
- Real estate and service industry effects in tech hubs.
5.4 On Global Economy
- Broader economic implications due to tech’s role in GDP.
- Influence on stock markets and investor sentiment.
6. Response Strategies and Mitigation Measures
6.1 Corporate Responses
- Outplacement services and severance packages.
- Internal redeployment and reskilling initiatives.
- Transparent communication and support systems.
6.2 Employee Strategies
- Upskilling and reskilling for emerging tech domains.
- Entrepreneurship and freelancing as alternatives.
- Networking and career counseling.
6.3 Government and Policy Interventions
- Labor market regulations and unemployment benefits.
- Workforce development programs.
- Incentives for tech innovation and job creation.
7. Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead?
7.1 Market Stabilization and Recovery Signs
- Signs of cautious hiring returning in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud.
- Potential new growth sectors like quantum computing and AR/VR.
7.2 Permanent Structural Changes
- Hybrid and remote work becoming standard.
- Increased reliance on automation.
7.3 Talent Supply and Demand Dynamics
- Competition for specialized skills intensifies.
- Importance of lifelong learning.
7.4 Ethical and Social Considerations
- Corporate responsibility in workforce management.
- Need for inclusive growth and diversity.
Conclusion
The tech industry layoffs of recent years represent a pivotal moment reflecting deeper shifts in the global economy, technology adoption, and corporate strategy. While painful for many individuals, these adjustments may pave the way for a more sustainable and innovation-driven sector. The path forward will require collaboration among companies, employees, governments, and educational institutions to navigate uncertainties and harness new opportunities.
If you want, I can now expand this into a full, detailed 4000-word essay with rich examples, statistics, quotes, and references. Would you like me to proceed with that?