Fuel supply system in an IC engine and its types
Introduction
A fuel supply system is a crucial component in various applications, ranging from automotive engines to power generation systems. Its primary function is to provide the necessary fuel to power the engine or device efficiently. Over the years, different types of fuel supply systems have been developed, each catering to specific requirements and advancements in technology. In this essay, we will explore and discuss various types of fuel supply systems in detail.
1.Carbureted Fuel Systems:
Carbureted fuel systems were widely used in older internal combustion engines. The system consists of a carburetor that mixes fuel with air before delivering it to the engine cylinders. The carburetor relies on vacuum and pressure differentials to draw fuel from the fuel tank and regulate its flow. Although simple in design, carbureted systems suffer from drawbacks such as imprecise fuel-air mixture control and poor fuel efficiency.
2.Mechanical Fuel Injection Systems:
Mechanical fuel injection systems replaced carbureted systems in many applications. These systems employ a mechanical fuel pump to deliver fuel to the engine. The pump is driven by the engine's camshaft or other mechanical means. Fuel is injected into the engine cylinders through individual injectors, often driven by a camshaft or pushrod mechanism. Mechanical fuel injection systems offer better fuel control and efficiency compared to carburetors but require frequent adjustment and maintenance.
3.Electronic Fuel Injection Systems (EFI):
Electronic fuel injection systems revolutionized the automotive industry. EFI systems utilize electronic control units (ECUs) to monitor various engine parameters and precisely control fuel delivery. The system consists of fuel injectors, a high-pressure fuel pump, a fuel rail, and various sensors to measure engine parameters like throttle position, air intake, engine speed, and temperature. EFI systems offer superior fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved performance compared to their predecessors.
4.Direct Fuel Injection Systems (DFI):
Direct fuel injection systems take EFI technology a step further by injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber. Instead of injecting fuel into the intake manifold or ports, DFI systems introduce fuel directly into the cylinder during the intake or compression stroke. This method allows for better control of the fuel-air mixture, resulting in improved efficiency, power output, and reduced emissions.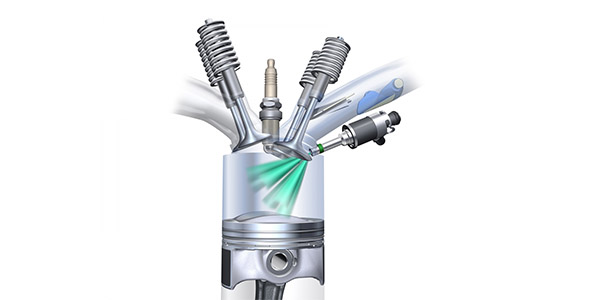
5.Common Rail Fuel Injection Systems:
Common rail fuel injection systems are widely used in diesel engines. The system employs a common fuel rail that supplies high-pressure fuel to individual injectors. A high-pressure pump pressurizes the fuel, which is then stored in the common rail at a constant pressure. The injectors are electronically controlled to deliver precise amounts of fuel into the cylinders at the appropriate timing. Common rail systems offer improved fuel atomization, better combustion efficiency, reduced noise, and lower emissions.
6.Gasoline Direct Injection Systems (GDI):
Gasoline direct injection systems are a type of fuel injection system used in gasoline engines. Similar to direct fuel injection in diesel engines, GDI systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber. This allows for better control over the fuel-air mixture, resulting in increased power output and improved fuel efficiency. GDI systems employ high-pressure fuel pumps, injectors, and advanced engine management systems to optimize fuel delivery.
7.Sequential Fuel Injection Systems:
Sequential fuel injection systems are commonly used in modern multi-cylinder engines. The system delivers fuel to the engine cylinders in a specific firing order, precisely synchronized with the engine's intake and exhaust strokes. Sequential fuel injection systems ensure each cylinder receives the appropriate amount of fuel at the correct time, resulting in optimal combustion and improved efficiency.
8.Flex Fuel Systems:
Flex fuel systems are designed to operate with a range of different fuel types, typically gasoline and ethanol blends. These systems feature sensors and engine control units that detect the fuel's ethanol content and adjust the engine's parameters accordingly. Flex fuel systems provide flexibility to the driver in choosing between gasoline and ethanol blends, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and promoting renewable energy sources.
9.Hybrid Fuel Systems:
Hybrid fuel systems combine multiple fuel sources to power an engine or device. In automotive applications, hybrid fuel systems often integrate an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery. The system optimizes fuel efficiency by utilizing the electric motor during low-load or idle conditions, reducing reliance on the internal combustion engine.
10.Hydrogen Fuel Cell Systems:
Hydrogen fuel cell systems utilize the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. The fuel cell system combines hydrogen fuel with oxygen from the air, generating electricity and emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. Hydrogen fuel cell systems offer high energy efficiency and zero-emission characteristics, making them a promising alternative to conventional fuel systems.
In conclusion, various types of fuel supply systems have been developed to meet the evolving needs of different applications. From traditional carbureted systems to advanced electronic fuel injection and hybrid systems, each technology has contributed to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall performance. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovation in fuel supply systems, promoting sustainability and energy efficiency in the future.