Niels Bohr: Pioneer of Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Theory
Introduction::max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/physicist-niels-bohr-514891628-5a6e41193418c60036a1ee35.jpg)
Niels Bohr stands as one of the most influential physicists of the 20th century, renowned for his groundbreaking contributions to the field of quantum mechanics and atomic theory. Born in Denmark in 1885, Bohr's insights revolutionized our understanding of the atom and laid the foundation for much of modern physics. Through his pioneering work, Bohr not only shaped scientific thought but also played a significant role in shaping the trajectory of 20th-century science and technology. This essay aims to explore the life, work, and legacy of Niels Bohr, delving into his key contributions to physics and his lasting impact on the scientific community.
Early Life and Education::max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-Niels_Bohr_Albert_Einstein3_by_Ehrenfest-58e5bf3a3df78c51625eb2aa.jpg)
Niels Henrik David Bohr was born on October 7, 1885, in Copenhagen, Denmark, into a highly educated and intellectual family. His father, Christian Bohr, was a prominent physiologist, while his mother, Ellen Adler Bohr, hailed from a wealthy Jewish family. Growing up in an environment steeped in academic pursuits, Bohr developed a keen interest in science from an early age.
Bohr received his primary and secondary education in Copenhagen before enrolling at the University of Copenhagen in 1903. Initially, he pursued a degree in physics, but his interests soon expanded to encompass mathematics and philosophy as well. Under the guidance of influential professors such as J.J. Thomson and Ernest Rutherford, Bohr developed a deep understanding of the emerging field of atomic physics.
Key Contributions to Physics:
Bohr's most significant contribution to physics came in 1913 when he proposed his model of the atom, which combined principles from classical physics with emerging quantum theory. At the heart of Bohr's model was the idea that electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom in discrete, quantized energy levels. This concept, known as quantization, represented a departure from classical physics, where electrons were thought to move in continuous orbits.
Bohr's model successfully explained many phenomena that had puzzled scientists at the time, including the discrete spectral lines observed in the emission and absorption of light by atoms. His model also laid the groundwork for understanding the behavior of atoms in the emerging field of quantum mechanics.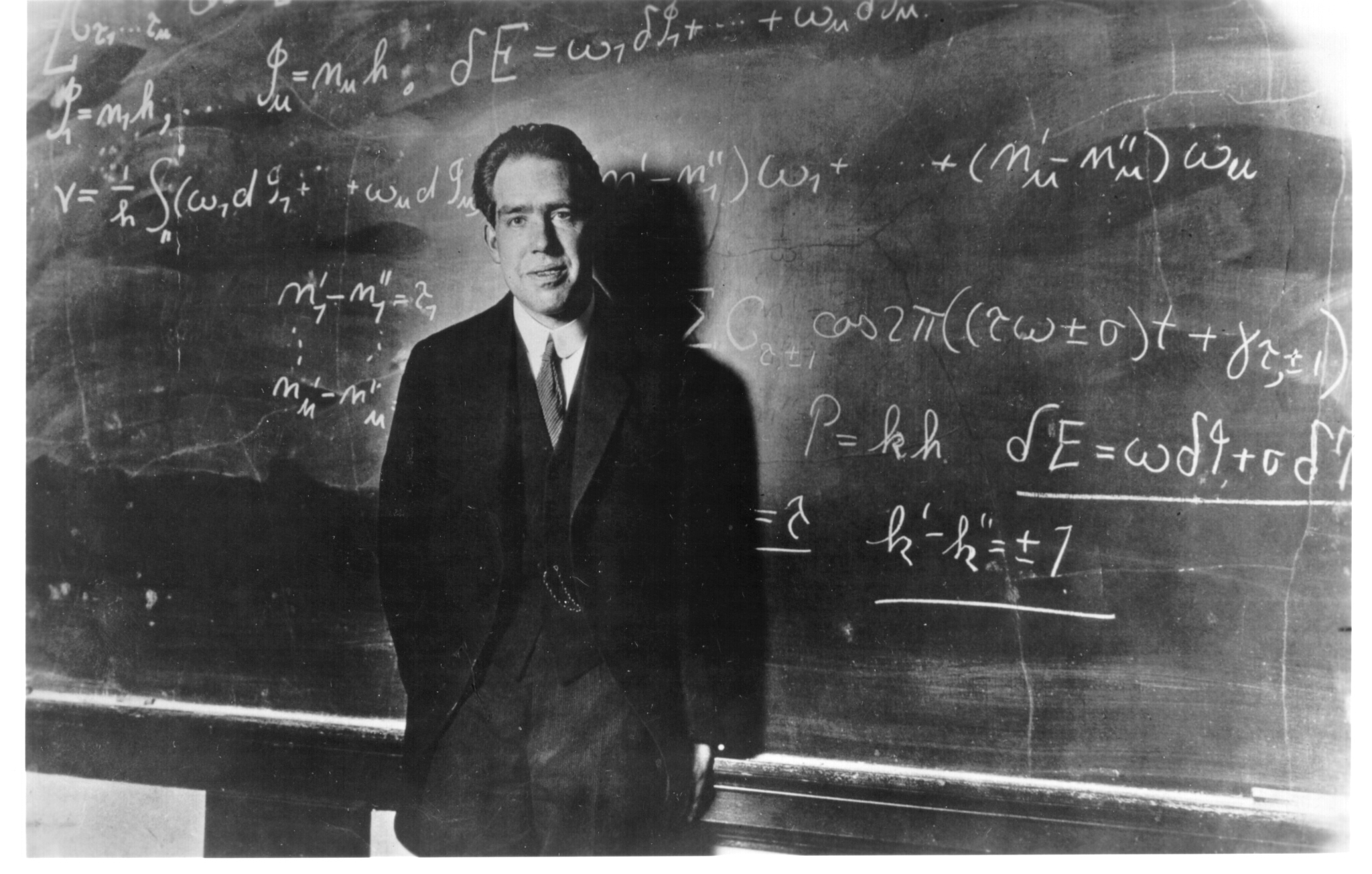 In 1922, Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the structure of atoms and the radiation they emit. The Nobel Committee praised Bohr for his "investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them."
In 1922, Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the structure of atoms and the radiation they emit. The Nobel Committee praised Bohr for his "investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them."
Bohr's influence extended beyond his own research, as he played a central role in the development of quantum mechanics as a formalized theory. He collaborated with other leading physicists of his time, including Werner Heisenberg, Wolfgang Pauli, and Max Born, to refine and expand upon the principles of quantum theory.
Copenhagen Interpretation:
One of Bohr's most enduring legacies is his formulation of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. Developed in the 1920s and 1930s, this interpretation posits that the behavior of particles at the quantum level is inherently probabilistic and that the act of measurement plays a crucial role in determining the outcome of a quantum experiment.
According to the Copenhagen interpretation, particles such as electrons exist in a state of superposition, meaning they can exist in multiple states simultaneously until they are observed or measured. This idea, famously encapsulated in Schrödinger's thought experiment involving a cat in a box, challenged conventional notions of reality and raised profound philosophical questions about the nature of observation and knowledge.
While the Copenhagen interpretation has been the subject of much debate and criticism over the years, it remains one of the most widely accepted frameworks for understanding quantum mechanics. Its influence extends beyond physics, shaping discussions in fields such as philosophy, psychology, and the philosophy of science.
Later Years and Legacy:
In the decades following his groundbreaking work on atomic theory, Bohr continued to make significant contributions to physics while also becoming increasingly involved in scientific diplomacy and advocacy. He played a key role in promoting international collaboration among scientists and was a vocal proponent of using atomic energy for peaceful purposes.
Bohr's later years were marked by upheaval and tragedy, as Europe descended into World War II and the specter of nuclear conflict loomed large. Fearing for his safety, Bohr fled Denmark in 1943 and eventually settled in the United States, where he worked on the Manhattan Project, the Allied effort to develop the atomic bomb.
After the war, Bohr returned to Denmark, where he continued to advocate for nuclear disarmament and international cooperation in the pursuit of scientific progress. He passed away on November 18, 1962, leaving behind a rich legacy of scientific achievement and humanitarianism.
Niels Bohr's impact on physics and the broader scientific community cannot be overstated. His work laid the foundation for much of modern physics, influencing generations of scientists and shaping our understanding of the fundamental nature of the universe. Beyond his scientific contributions, Bohr's advocacy for international collaboration and his efforts to promote the peaceful use of atomic energy serve as a reminder of the importance of science in addressing the pressing challenges facing humanity. In honoring his memory, we recognize not only the brilliance of his mind but also the depth of his humanity and his unwavering commitment to the pursuit of knowledge for the betterment of humankind.
Legacy in Physics and Quantum Mechanics:
Niels Bohr's contributions to physics and quantum mechanics reverberate through the scientific community to this day. His model of the atom, with its concept of quantized energy levels, laid the groundwork for the development of quantum theory and provided a framework for understanding the behavior of atoms and subatomic particles. The Bohr model, despite its limitations in describing more complex atoms, remains a fundamental concept in introductory physics courses and serves as a starting point for students learning about atomic structure.
Moreover, Bohr's work on the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics continues to shape discussions and debates about the nature of reality at the quantum level. While alternative interpretations have emerged over the years, the Copenhagen interpretation remains a cornerstone of quantum theory and continues to inspire new avenues of research and inquiry.
In addition to his theoretical contributions, Bohr's collaborative spirit and willingness to engage with other scientists helped foster a vibrant intellectual community during a period of rapid scientific advancement. His mentorship and guidance influenced a generation of physicists, many of whom went on to make their own groundbreaking discoveries in quantum mechanics and related fields.
Advocacy for Peaceful Use of Atomic Energy:
Beyond his scientific achievements, Niels Bohr's advocacy for the peaceful use of atomic energy and his efforts to promote international cooperation in science stand as a testament to his moral and humanitarian convictions. Throughout his life, Bohr was deeply concerned about the ethical implications of nuclear weapons and the potential for nuclear conflict to devastate humanity.
During World War II, Bohr's involvement in the Manhattan Project gave him firsthand insight into the destructive power of nuclear weapons and reinforced his commitment to preventing their use in warfare. Following the war, he became a vocal advocate for nuclear disarmament and argued passionately for the establishment of international institutions to control and regulate nuclear technology. Bohr's efforts helped lay the groundwork for the creation of organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR), which work to promote nuclear safety, security, and non-proliferation.
Bohr's efforts helped lay the groundwork for the creation of organizations such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR), which work to promote nuclear safety, security, and non-proliferation.
In recognition of his tireless advocacy for peace and his contributions to science, Niels Bohr received numerous awards and honors throughout his lifetime, including the Atoms for Peace Award in 1957 and the Order of the Elephant, Denmark's highest civilian honor, in 1947.
Conclusion:
Niels Bohr's life and work exemplify the profound impact that a single individual can have on the course of scientific progress and human history. From his revolutionary insights into atomic structure and quantum mechanics to his unwavering commitment to promoting international cooperation and peace, Bohr's legacy continues to inspire scientists, scholars, and activists around the world.
As we reflect on the achievements of Niels Bohr, we are reminded of the enduring power of curiosity, collaboration, and compassion in advancing human knowledge and understanding. His life serves as a testament to the transformative potential of science and the responsibility that scientists bear in harnessing that potential for the betterment of society.
In honoring Niels Bohr's memory, we not only celebrate his extraordinary intellect and achievements but also reaffirm our commitment to building a world guided by reason, empathy, and a shared vision of a brighter future for all.














































