The Power of Empathy: Fostering Connection and Understanding in a Diverse World
Introduction:
Empathy, often described as the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, stands as one of the most fundamental and transformative human qualities. It serves as a bridge that connects individuals across cultural, social, and emotional divides, fostering compassion, cooperation, and mutual understanding. In today's increasingly interconnected and diverse world, empathy has never been more essential for building resilient communities, fostering inclusive societies, and addressing the complex challenges we face. In this essay, we will explore the power of empathy, its role in promoting empathy, and the ways in which we can cultivate and nurture empathy in ourselves and others.
The Nature of Empathy: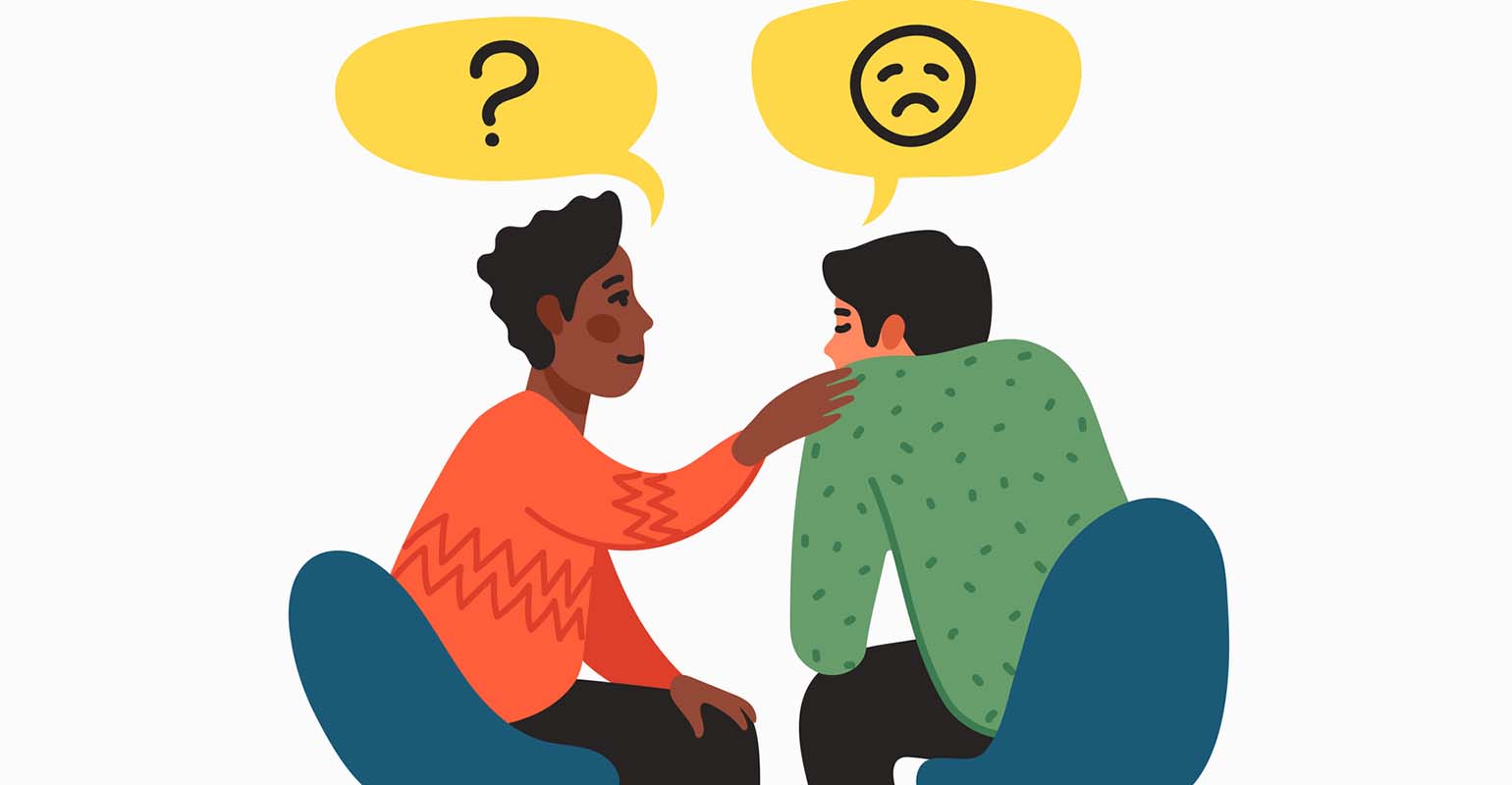
Empathy encompasses a range of cognitive, affective, and behavioral processes that enable individuals to perceive, understand, and respond to the emotions and experiences of others. It involves not only the ability to recognize and interpret the emotions of others but also the capacity to vicariously experience and resonate with those emotions. Empathy is rooted in neural mechanisms such as mirror neurons, which enable individuals to simulate and mirror the emotional states of others, as well as higher-order cognitive processes that facilitate perspective-taking and empathic concern.
Empathy can take various forms, including cognitive empathy, which involves understanding the thoughts and perspectives of others; emotional empathy, which involves sharing and resonating with the emotions of others; and compassionate empathy, which involves feeling concern for the well-being of others and being motivated to help alleviate their suffering. Each form of empathy plays a critical role in interpersonal relationships, social interactions, and moral decision-making, contributing to prosocial behavior, conflict resolution, and cooperation.
The Importance of Empathy:
Empathy serves as a cornerstone of healthy relationships, enabling individuals to connect with others on a deep emotional level, build trust and rapport, and foster a sense of belonging and community. In families, friendships, and romantic partnerships, empathy facilitates communication, understanding, and mutual support, strengthening bonds and promoting emotional intimacy. In workplaces and organizations, empathy fosters collaboration, teamwork, and effective leadership, enhancing productivity, morale, and employee satisfaction.
Beyond interpersonal relationships, empathy plays a crucial role in fostering social cohesion and promoting social justice and equity. Empathy enables individuals to recognize and challenge prejudice, discrimination, and injustice, by understanding and empathizing with the experiences of marginalized and oppressed groups. Empathy motivates individuals to advocate for social change, to speak out against systemic inequities, and to work towards creating a more just and inclusive society for all.
Moreover, empathy has far-reaching implications for health and well-being, both at the individual and societal levels. Research has shown that empathic interactions can reduce stress, enhance resilience, and improve mental health outcomes, contributing to overall happiness and life satisfaction. In healthcare settings, empathy is associated with better patient outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, and improved adherence to treatment regimens, highlighting its importance for quality patient care and provider-patient relationships.
Cultivating Empathy:
While empathy is a natural human capacity, it is also a skill that can be cultivated and nurtured through intentional practice and effort. Cultivating empathy requires openness, curiosity, and a willingness to step outside of one's own perspective to truly understand and connect with others. Here are some strategies for cultivating empathy:
- Active Listening: Practice attentive and nonjudgmental listening, paying close attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues and seeking to understand the underlying emotions and concerns of others.
- Perspective-Taking: Put yourself in someone else's shoes and try to see the world from their perspective, considering their thoughts, feelings, and experiences without imposing your own biases or assumptions.
- Empathic Imagination: Use your imagination to mentally simulate and empathize with the experiences of others, envisioning how they might feel and what they might need in a given situation.
- Cultivate Curiosity: Approach interactions with genuine curiosity and interest in others, asking open-ended questions and seeking to learn more about their experiences, perspectives, and values.
- Practice Self-Reflection: Reflect on your own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, and consider how they may impact others. Cultivate self-awareness and mindfulness to better regulate your own emotions and empathize with the emotions of others.
- Expose Yourself to Diversity: Seek out opportunities to engage with individuals from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and perspectives, expanding your empathy and understanding of the human experience.
Challenges to Empathy:
While empathy holds immense potential for positive change, it also faces challenges in today's fast-paced and often polarized world. One significant challenge is empathy fatigue or burnout, particularly among caregivers, activists, and individuals who regularly engage with others' suffering. Constant exposure to others' pain and distress can take a toll on one's emotional well-being, leading to emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and decreased empathy.
Moreover, empathy can be inhibited by factors such as stress, prejudice, and cognitive biases, which can distort perceptions, hinder perspective-taking, and undermine empathic responses. In situations of conflict or disagreement, empathy may be particularly difficult to maintain, as individuals may become defensive, closed-off, or dismissive of others' perspectives.
Furthermore, the digital age presents unique challenges to empathy, as online interactions often lack the nonverbal cues and face-to-face communication that facilitate empathy. Social media algorithms, echo chambers, and online anonymity can exacerbate polarization, tribalism, and dehumanization, making it harder to empathize with others and fostering online hostility and incivility.
Overcoming these challenges requires intentional efforts to promote empathy in our personal interactions, institutions, and broader society. By fostering empathy as a core value and skill, we can build more compassionate and resilient communities and address the complex challenges facing our world.
Empathy in Action:
Despite the challenges, there are countless examples of empathy in action, demonstrating its transformative power to bring about positive change in individuals, communities, and societies. Acts of kindness, compassion, and solidarity abound, from individuals reaching out to support neighbors in times of need to grassroots movements advocating for social justice and human rights.
One inspiring example of empathy in action is the global response to humanitarian crises, natural disasters, and public health emergencies. In times of crisis, individuals and organizations around the world rally together to provide aid, support, and solidarity to those affected, demonstrating the capacity for empathy to transcend boundaries of geography, nationality, and culture.
Moreover, empathy plays a crucial role in advancing social justice movements and promoting equity and inclusion for marginalized and oppressed groups. Empathy enables individuals to recognize and confront systemic injustices, to amplify the voices of those whose experiences are often unheard, and to advocate for policy changes that address structural inequalities.
In the realm of education, empathy-centered curricula and programs are gaining recognition for their role in promoting social and emotional learning, empathy, and compassion among students. By teaching empathy skills such as perspective-taking, active listening, and conflict resolution, educators can empower young people to become more empathic and socially responsible citizens.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, empathy stands as a fundamental human quality with the power to transform individuals, communities, and societies. By fostering empathy in ourselves and promoting empathy in our interactions and institutions, we can build more compassionate, inclusive, and resilient communities, where all individuals are valued, heard, and supported.
In a world marked by division, inequality, and uncertainty, empathy offers a guiding light that illuminates the path towards greater understanding, connection, and collective action. As we navigate the complexities of the human experience, let us embrace empathy as a guiding principle that unites us in our shared humanity and empowers us to create a more empathic and compassionate world for generations to come.























































